Lateral umbilical fold
| Lateral umbilical ligament | |
|---|---|
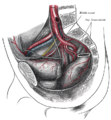
 Posterior view of the anterior abdominal wall in its lower half. The peritoneum is in place, and the various cords are shining through. | |
 The peritoneum of the male pelvis. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | plica umbilicalis lateralis; plica epigastrica |
| TA98 | A10.1.02.434 |
| TA2 | 3796 |
| FMA | 16537 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
This article may need to be rewritten to comply with Wikipedia's quality standards. (May 2009) |
The lateral umbilical fold overlies the inferior epigastric artery (a branch of the external iliac artery) and its accompanying veins. Unlike the median and medial umbilical folds, the contents of the lateral umbilical fold remain functional after birth. It originates just medial to the deep inguinal ring to the arcuate line on the posterior surface of the anterior abdominal wall.
Clinical significance
The lateral umbilical fold is an important reference site with regards to hernia classification. A direct hernia occurs medial to the lateral umbilical fold, whereas an indirect hernia originates lateral to the fold. This later case is due to the placement of the opening of the deep inguinal ring in the space lateral to the lateral umbilical fold, which allows the passage of the ductus deferens, testicular artery, and other components of the spermatic cord in men, or the round ligament of the uterus in women.
Additional images
-
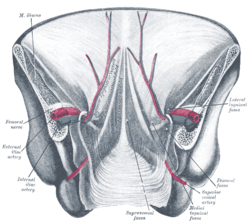
The arteries of the pelvis.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1152 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1152 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Lateral umbilical fold
- Anatomy figure: 36:03-09 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Internal surface of the anterior abdominal wall."
- Anatomy image:7384 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center