Lauri Vaska
Lauri Vaska | |
|---|---|
| Born | May 7, 1925 |
| Died | November 15, 2015 (aged 90) |
| Alma mater | Baltic University, University of Göttingen, University of Texas |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | organometallic chemistry. |
| Institutions | Northwestern University Mellon Institute of Industrial Research (part of today's Carnegie Mellon University) Clarkson University |
Lauri Vaska (May 7, 1925 – November 15, 2015) was an Estonian-American chemist who has made noteworthy contributions to organometallic chemistry. He was born in Rakvere, Estonia.
Vaska was educated at the Baltic University in Hamburg, Germany (1946) and subsequently at the University of Göttingen (1946–1949) where he received his Vordiplom (equivalent to the American B.S. degree). He pursued his Ph.D. in Inorganic Chemistry at the University of Texas in the United States (1952–1956). He was a postdoctoral fellow at Northwestern University (1956–1957) where he conducted research on magnetochemistry. In 1957 he took a position as Fellow at the Mellon Institute in Pittsburgh, where he remained until 1964. During that time, the Mellon Institute housed a number of future chemical luminaries, including Paul Lauterbur and R. Bruce King. Vaska moved as an associate professor to Clarkson University in Potsdam, New York, where, from 1990 to his death, he was Professor Emeritus of Chemistry. His brother Vootele Vaska is a philosopher. He died in Basking Ridge, New Jersey in 2015, aged 90.[1]
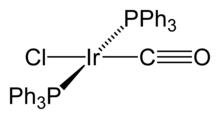
Research
Vaska published ca. eighty journal articles on the coordination chemistry of transition metals, homogeneous catalysis, and both organometallic and bioinorganic chemistry. His years at Mellon were especially productive. With J.W. Di Luzio in 1962 he first described the iridium compound which became known as Vaska's complex, trans-IrCl(CO)[P(C6H5)3]2[2] Working with a series of coworkers, he demonstrated that this iridium(I) complex undergoes a variety of reactions with small molecules. For example, it oxidatively adds H2 to give a dihydride.[3] He subsequently discovered that his complex reversibly bound O2, which was then a startling achievement. He discovered the main reactions of oxidative addition, a process that is central to homogeneous catalysis in organometallic chemistry. He demonstrated a number of important substituent effects on the oxidative addition, such as the greater reactivity of Ir(I) vs. Rh(I) and the stabilization of oxidative adducts by iodide vs. chloride.
Recognition
Among his awards are the Boris Pregel Award for Research in Chemical Physics (New York Academy of Sciences) in 1971 and election in 1981 as a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science for "pioneering work in transition metal organometallic chemistry and synthetic oxygen carriers".
References
- ^ http://www.legacy.com/obituaries/dailyrecord/obituary.aspx?n=lauri-vaska&pid=176541866&fhid=17074
- ^ L. Vaska and J.W. DiLuzio (1961). "Carbonyl and Hydrido-Carbonyl Complexes of Iridium by Reaction with Alcohols. Hydrido Complexes by Reaction with Acid". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 83 (12): 2784–5. doi:10.1021/ja01473a054.
- ^ L. Vaska and J.W. DiLuzio (1962). "Activation of Hydrogen by a Transition Metal Complex at Normal Conditions Leading to a Stable Molecular Dihydride". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 84 (4): 679–680. doi:10.1021/ja00863a040.
- 1925 births
- 2015 deaths
- Inorganic chemists
- American chemists
- Estonian chemists
- University of Texas at Austin alumni
- Northwestern University people
- Carnegie Mellon University faculty
- Clarkson University faculty
- Estonian emigrants to the United States
- American people of Estonian descent
- People from Rakvere
- Estonian World War II refugees
- American chemist stubs
- Estonian scientist stubs
