Left pulmonary artery
| Left pulmonary artery | |
|---|---|
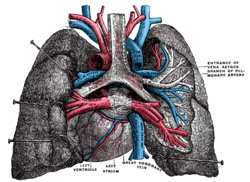 Pulmonary vessels, seen in a dorsal view of the heart and lungs. The lungs have been pulled away from the median line, and a part of the right lung has been cut away to display the air-ducts and bloodvessels. | |
 Transverse section of thorax, showing relations of pulmonary artery. | |
| Details | |
| Source | pulmonary artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria pulmonalis sinistra |
| TA98 | A12.2.01.201 |
| TA2 | 4091 |
| FMA | 50873 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The left pulmonary artery or left branch of the pulmonary artery, shorter and somewhat smaller than the right, passes horizontally in front of the descending aorta and left bronchus to the root of the left lung, where it divides into two branches, one for each lobe of the lung.
Above, it is connected to the concavity of the proximal descending aorta by the ligamentum arteriosum,[1] on the left of which is the left recurrent nerve, and on the right the superficial part of the cardiac plexus. Below, it is joined to the upper left pulmonary vein by the ligament of the left vena cava.
See also
References
- ^ D. Cheitlin, Melvin; C. Ursell, Philip (2011). "Cardiac Anatomy". In Chatterjee, Kanu (ed.). Cardiology: An Illustrated Textbook. JP Medical Ltd. p. 6. ISBN 9789350252758.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 545 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 545 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
