Lines of Action
 Lines of Action starting position | |
| Designers | Claude Soucie |
|---|---|
| Genres | Board game Abstract strategy game |
| Players | 2 |
| Setup time | < 1 minute |
| Chance | None |
| Skills | Strategy, tactics |
| Synonyms | LOA |
Lines of Action (or LOA) is an abstract strategy board game for two players invented by Claude Soucie. The objective is to connect all of one's pieces into a single group. The game was recommended by the Spiel des Jahres in 1988.[1]
Rules
[edit]Goal
[edit]The object of the game is to bring all of one's pieces together into a contiguous body so that they are connected vertically, horizontally or diagonally (8-connectivity).[clarification needed]
Movement summary
[edit]- Players alternate moves, with Black having the first move.
- Pieces move horizontally, vertically, or diagonally.
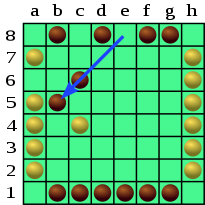
- A piece moves exactly as many spaces as there are pieces (both friendly and enemy) on the line in which it is moving. For example, Black may open with c8-c6. Black's piece moves two.
Movement diagrams
[edit]A piece may not jump over an enemy piece. Thus in the diagram below, White cannot play a6-d6, even though there are three pieces in row 6. White might instead play a6-c4, moving two spaces because there are two pieces in the diagonal (a6-f1) in which White is moving.
A piece may jump over friendly pieces. Thus Black may continue with e8-b5, jumping his own piece. He moves three spaces because there are three pieces in the diagonal (a4-e8) in which he is moving.
A piece may land on a square occupied by an enemy piece, resulting in the latter's capture and removal from the game. For example, White may play h3-f1, capturing the black pieces on f1.
A player who is reduced to a single piece wins the game, because his pieces are by definition united. If a move results, due to a capture, in each player having all his pieces in a contiguous body, then either the player moving wins, or the game is a draw, depending on the rules in force at the particular tournament.
Simultaneous connection
[edit]In the original 1969 edition of A Gamut of Games, simultaneous connection was described as a draw. In the second edition, the rules were changed to declare this a win for the player moving. Here is Sid Sackson's note in the preface to the second edition: "Claude Soucie and I are all that remains of N.Y.G.A. At his request, I have corrected an error in the rules for LINES OF ACTION, eliminating possible draws." However, despite the intention of the inventor of LOA, most present day tournaments including the World Championships at the Mind Sports Olympiad score simultaneous connection as a draw.
Strategy
[edit]The game can become quite tactical in open positions where the pieces on both sides are mobile. The strategic depth of the game, however, derives to a large extent from blocking strategies designed to limit the opponent's mobility. It can be advantageous to pin one or more enemy pieces against the side of board by moving in the second row or column.
Having more pieces is usually an advantage, because they can limit the opponent's options as they mass together. On the other hand, material considerations are not all-important, because having fewer pieces also means having fewer to unite.
Example game
[edit]The above moves illustrated the rules, but not necessarily good play. The following moves are more typical of expert play.
Black plays b1-b3. The piece moves two squares vertically, because there are two pieces in the file: b1 and b8. This move gives White no opportunity to capture, and threatens to hem in the pieces on the a-file.
White moves h4-f2. The piece moves two spaces because there are two pieces in the diagonal: h4 and e1. White threatens the mobility of Black's pieces in the bottom row.
Black plays d1:a4, jumping over his own piece (which is permitted) and capturing the white piece at a4. Note that Black moved three spaces, as there were three pieces in the diagonal: a4, b3, and d1.
It isn't clear whether the capture is advantageous or not. Black does now have an extra piece, but the move didn't do much to block White or build a central mass for Black. Usually early captures on the edge are not especially powerful, whereas early captures in the center are extremely good.
White plays h2-e2, continuing the blockade of the first rank. The piece moves three squares, jumping over a friendly piece. White, despite the substantial disadvantage of moving second, apparently is in the lead now due to the reduced mobility of Black's first-row pieces. White will soon play a2-d2, continuing to build his own bridge and forcing Black's piece on e1 to move sideways if it wants to join the game. It hardly helps for Black to try to escape with e1-c3, because that allows White to capture with a5:c3.
Example winning move
[edit]In the diagram below, White has made a move that connects all his pieces while Black is still at least two moves from such a state. Thus, White has won the game.
Champions
[edit]The World Championships take place annually at the Mind Sports Olympiad. World champions from 1997 onwards are given in the list below.[2]
- 1997:
 Fred Kok
Fred Kok - 1998:
 Hartmut Thordsen
Hartmut Thordsen - 1999:
 Fred Kok
Fred Kok - 2000:
 Jochen Drechsler
Jochen Drechsler - 2001:
 Koichi Nicholas
Koichi Nicholas - 2002:
 Fred Kok
Fred Kok - 2003:
 Koichi Nicholas
Koichi Nicholas - 2004:
 Fred Kok
Fred Kok - 2005:
 Koichi Nicholas
Koichi Nicholas - 2006:
 Fred Kok
Fred Kok - 2007:
 Tim Hebbes
Tim Hebbes - 2008:
 James Heppell
James Heppell - 2009:
 Tim Hebbes
Tim Hebbes - 2010:
 Andres Kuusk
Andres Kuusk - 2011:
 Tim Hebbes
Tim Hebbes - 2012:
 Peter Horlock
Peter Horlock - 2013:
 Ankush Khandelwal
Ankush Khandelwal - 2014:
 Alain Dekker
Alain Dekker - 2015:
 Andres Kuusk
Andres Kuusk - 2016:
 James Heppell
James Heppell - 2017:
 James Heppell[3]
James Heppell[3] - 2018:
 Andres Kuusk[4]
Andres Kuusk[4] - 2019:
 James Heppell[5]
James Heppell[5] - 2020:
 James Heppell[6]
James Heppell[6] - 2021:
 Andres Kuusk
Andres Kuusk - 2022:
 Koichi Nicholas
Koichi Nicholas - 2023:
 James Heppell
James Heppell - 2024:
 James Heppell
James Heppell
Variant
[edit]A variant of Lines of Action with a different starting position was also proposed by Soucie and is known as Scrambled Eggs.[7]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ LoA on German Spiel des Jahres official website
- ^ Mind Sports Olympiad LOA Results http://www.boardability.com/result.php?id=lines_of_action 10 July 2010
- ^ 2017 MSO medal table https://msoworld.com/2017-medal-table/ 18 Jan 2021
- ^ 2018 MSO medal table https://msoworld.com/2018-medal-table/ 18 Jan 2021
- ^ 2019 MSO medal table https://msoworld.com/2019-medal-table/ 18 Jan 2021
- ^ 2020 MSO medal table https://msoworld.com/2020-medal-table/ 18 Jan 2021
- ^ http://brainking.com/en/GameRules?tp=86 Brain King Web page: Scrambled Eggs Rules
Bibliography
- Sackson, Sid (1982) [1st Pub. 1969, Random House, New York]. A Gamut of Games. Pantheon Books. ISBN 0-394-71115-7.
- Schmittberger, R. Wayne (1992). New Rules for Classic Games. John Wiley & Sons Inc. ISBN 978-0471536215.