List of largest snakes
The largest living snakes in the world, measured either by length or by weight, are various members of the Boidae and Pythonidae families. They include anacondas, pythons and boa constrictors, which are all non-venomous constrictors. The longest venomous snake, with a length up to 18.5–18.8 ft (5.6–5.7 m), is the king cobra,[1] and the heaviest venomous snake is likely to be the Gaboon viper (which also has the longest fangs and delivers the largest amount of venom) or possibly the Eastern diamondback rattlesnake – all three of which reach maximum weights in the range of 6–20 kilograms (13–44 lb).
There are eleven living snakes, listed below according to their maximum known or reported mass, that have a maximum mass that may reach or exceed 50 pounds (23 kg). Pending the acceptance of its taxonomic status, the Bolivian anaconda (Eunectes beniensis) may also merit inclusion, and the northern and southern variations of African rock python could be considered separately.
In terms of length, in addition to those listed here, there are two other species that may possibly reach a length of 20 feet (6.1 m) or more – the Oenpelli python (Morelia oenpelliensis) and the olive python (Liasis olivaceus) – however, the information available about those species is rather limited.[2] The Oenpelli python, in particular, has been called the rarest python in the world.[3][4][5]
It is important to be aware that there is considerable variation in the maximum reported size of these species, and most measurements are not truly verifiable, so the sizes listed should not be considered definitive. In general, the reported lengths are likely to be somewhat overestimated.[6] In spite of what has been, for many years, a standing offer of a large financial reward (initially $1,000 offered by U.S. President Theodore Roosevelt in the early 1900s,[7] later raised to $5,000, then $15,000 in 1978 and $50,000 in 1980) for a live, healthy snake over 30 ft (9.1 m) long by the New York Zoological Society (later renamed as the Wildlife Conservation Society), no attempt to claim the reward has ever been made.[2]
Although it is generally accepted that the reticulated python is the world's longest snake, most length estimates longer than 6.35 m (20 ft 10 in) have been called into question.[6] It has been suggested that confident length records for the largest snakes must be established from a dead body soon after death, or alternatively from a heavily sedated snake, using a steel tape and in the presence of witnesses, and must be published (and preferably recorded on video).[6] At least one reticulated python was measured under full anesthesia at 6.95 m (22 ft 10 in), and somewhat less reliable scientific reports up to 10 m (33 ft) have appeared.[8]
| Rank | Common name | Scientific name | Family | Mass | Image | Length | Range map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Green anaconda | Eunectes murinus | Boidae | May exceed 227 kg (500 lb),[9] validity questionable 97.5 kg (215 lb), reliable, maximum among 780 specimens caught over a seven-year period 1992–98[10] Average 30.8 kg (68 lb) among 45 specimens (1992–98)[10] Generally considered the heaviest |
 |
May exceed 8.8 m (29 ft),[9] not firmly verified[6] 5.6 m (18 ft), somewhat reliable[2] 5.21 m (17.1 ft), reliable, maximum among 780 specimens caught over a seven-year period 1992–98[10] Average 3.7 m (12 ft) among 45 specimens (1992–98)[10] Minimum adult length 3.2 m (10 ft)[2] |

|
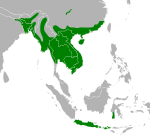
| 2 | Burmese python | Python bivittatus | Pythonidae | 182.8 kg (403 lb), reliable, for "Baby" in 1998[6] |  |
5.74 m (18.8 ft), reliable, for "Baby" ca. 1999[6] Minimum adult length 2.35 m (7.7 ft)[2] |
|
| 3 | Reticulated python | Malayopython reticulatus | Pythonidae | Up to 158 kg (350 lb), somewhat reliable[11][12] 158.8 kg (350 lb), somewhat reliable, for "Medusa" in 2011[13] Almost 160 kg (350 lb), somewhat reliable, for "Twinkie" in 2014[14] 136 kg (300 lb), somewhat reliable, for "Fluffy" in 2010[15] 133.7 kg (295 lb), reasonably reliable, for "Colossus" in 1954 (with an empty stomach)[6][16] 124.7 kg (275 lb), somewhat reliable, for "Samantha" in 2002[16][17] 59 kg (130 lb), reliable, wild specimen in 1999 (after not eating for nearly 3 months)[8] |
 |
10 m (33 ft),[11][12] not firmly verified[6] 7.9 m (26 ft), somewhat reliable, for "Samantha" in 2002[16][17] 7.67 m (25.2 ft), somewhat reliable, for "Medusa" in 2011[13] 7.3 m (24 ft), somewhat reliable, for "Fluffy" in 2010[13][15] 6.95 m (22.8 ft), reliable, wild specimen in 1999[8] 6.35 m (20.8 ft), reasonably reliable, for "Colossus" in 1963 (skeletal length)[6] Minimum adult length 3.04 m (10.0 ft)[2] Generally considered the world's longest |

|
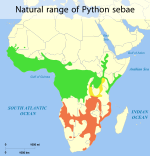
| 4 | African rock python | Python sebae (sometimes considered two species, P. sebae and P. natalensis) |
Pythonidae | Up to 113 kg (250 lb),[18] not firmly verified[6] |  |
Up to 7.5 m (25 ft),[19] not firmly verified[6] Minimum adult length 2.50 m (8.2 ft)[2] |
|
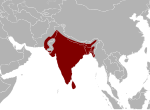
| 5 | Indian python | Python molurus | Pythonidae | 91 kg (200 lb),[20] not firmly verified[6] 52 kg (115 lb), reliable[21] |
 |
6.4 m (21 ft),[20] not firmly verified[6] 4.6 m (15.1 ft), reliable[21] |
|
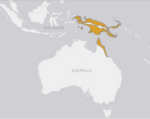
| 6 | Amethystine (scrub) python | Simalia amethistina | Pythonidae | 91 kg (200 lb)[citation needed] Little information about size is available[2][22] |
 |
Some reports up to[23] or exceeding 8 m (26 ft),[2] not firmly verified[6] 7.2 m (24 ft), somewhat reliable[24] In excess of 6 m (20 ft)[23] Typically 3.5 m (11 ft)[2] Minimum adult length 1.8 m (5.9 ft)[2] Little information about size is available[2][22] |
|
| 7 | Yellow anaconda | Eunectes notaeus | Boidae | They commonly weigh 25 to 35 kg (55 to 77 lb), though large specimens can weigh 40 to 55 kg (88 to 121 lb) or even more.[25] |  |
4.6 m (15.1 ft), reasonably reliable[1][26] Typically 3–4 m (10–13 ft)[26] 3.1 m (10 ft) maximum among 86 specimens in a field study[27] |
South America |
| 8 | Boa constrictor | Boa constrictor | Boidae | More than 45 kg (99 lb)[28] |  |
Possibly up to 4.3 m (14 ft)[29] A much larger report was debunked[6][30] |

|
| 9 | Dark-spotted anaconda | Eunectes deschauenseei | Boidae | 30 kg (66 lb)[citation needed] | 3 m (9.8 ft),[31] validity unknown | 
| |
| 10 | Cuban boa | Chilabothrus angulifer | Boidae | 27 kg (60 lb)[32] |  |
4.8 m (16 ft)[32][33] | |
| 11 | Papuan python | Apodora papuana | Pythonidae | 22.5 kg (50 lb)[34] Little information about size is available[2] |
 |
One reasonably reliable report of 4.39 m (14.4 ft)[2][35] Often reaches 3–4 m (9.8–13.1 ft)[2] Most specimens 1.4–3.6 m (4.6–11.8 ft)[35] Little information about size is available[2] |
File:Apodora range.png |
Remarkable Individual Specimens (considered among largest measured for their respective species)
"Baby" a captive Burmese Python (Python bivittatus) female♀ 5.74 meters (18 feet 10 inches) 182.798 kilograms (403 lbs) "Baby" was held at Serpent Safari in Gurnee, Illinois, USA until its death at almost 27 years old, euthanized due to deteriorating condition caused by tumor in 2006. Several live measurements and post mortem measurement. [6][36]
Wild caught non-native (invasive) Burmese Python (Python bivittatus) female♀ 5.715 m (18 feet 9 inches) 47.1736 kilograms (104 lbs) caught in Miami-Dade county near the L-28 Tieback Canal, around 35 miles west of Miami by Ryan Ausburn and Kevin Pavlidis, Oct 2, 2020. [37][38]
Wild caught non-native (invasive) Burmese Python (Python bivittatus) female♀ 5.6 meters (18 feet 8 inches) 58 kilograms (128 lbs) caught in Miami-Dade county, Florida, USA by Jason Leon, May 11, 2012. Intact specimen measured post mortem by University of Florida.[39][40] [41]
Wild caught non-native (invasive) Burmese Python (Python bivittatus) female♀ 5.563 meters (18 feet 3 inches) 60.3 kilograms (133 lbs) caught by University of Florida wildlife biologist Ed Metzger III Shark Valley, Everglades National Park, Miami Dade County, Florida, USA July 9, 2015. Intact specimen measured post mortem by University of Florida. [42][43][44][45]
"Medusa" a captive Reticulated Python (Malayopython reticulatus) female♀ 7.67 meters (25 feet 2 inches) 158.8 kilograms (350 lbs) "Medusa" held at The Edge of Hell haunted house attraction in Kansas City, Missouri, last officially measured 2011. [46] [47]
Wild caught Reticulated Python (Malayopython reticulatus) Female♀ 7.5 meters (24 feet and 7.2756 inches) adjusted post mortem measurement. Originally measured alive at 8 meters (26 feet 3 inches unknown method, unreliable) 250 kilograms (550 pounds, estimated weight upon capture, unreliable) caught April 7, 2016 Paya Terubong district, Penang Island, Malaysia. Died April 10, 2016 [48] [49] [50]
"Fluffy" a captive Reticulated Python (Malayopython reticulatus) female♀ 7.3 meters (24 feet) 136 Kilograms (300 pounds). "Fluffy" last officially measured live on 30 September 30, 2009. died at the Columbus Zoo and Aquarium, Powell, Ohio, USA, on Oct 26, 2010 due to an apparent tumor. She was 18 years old. 24 feet confirmed when measured at death. [15][13]
"Colossus" a captive Reticulated Python (Maylayopython reticulatus) male♂ , skeletal measurement 6.35 meters (20 feet 10 inches) 133.7 kilograms (295 pounds) "Colossus" held at Highland Park Zoo, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA died April 1963, deposited at Carnegie Museum.[6]
See also
- List of largest reptiles
- Largest organisms
- Titanoboa, world's largest known snake (currently from the fossil record)
- Gigantophis, one of the world's largest snakes (the past record holder for the world's largest snake)
References
- ^ a b Mehrtens, John (1987). Living Snakes of the World. New York: Sterling. ISBN 0-8069-6461-8.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Murphy, J. C.; Henderson, R. W. (1997). Tales of Giant Snakes: A Historical Natural History of Anacondas and Pythons. Krieger Pub. Co. pp. 2, 19, 37, 42, 55–56. ISBN 0-89464-995-7.
- ^ Rarest Python in the World. SnakeBytesTV. December 18, 2013. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ Breeding plan aims to save snakes. ABC News (Australia). March 29, 2012. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ Smith, Deborah (June 20, 2012). "Snakes alive – if only he'd been seeing double". Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 2016-02-09.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Barker, David G.; Barten, Stephen L.; Ehrsam, Jonas P.; Daddono, Louis (2012). "The Corrected Lengths of Two Well-known Giant Pythons and the Establishment of a new Maximum Length Record for Burmese Pythons, Python bivittatus" (PDF). Bull. Chicago Herp. Soc. 47 (1): 1–6. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ Gordon, David George, "The Search for the $50,000 Snake". MSN Encarta. Archived October 31, 2009.
- ^ a b c Fredriksson, G. M. (2005). "Predation on Sun Bears by Reticulated Python in East Kalimantan, Indonesian Borneo". Raffles Bulletin of Zoology. 53 (1): 165–168. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ a b "Green anacondas: Eunectes murinus". National Geographic. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ a b c d Rivas, Jesús Antonio (2000). The life history of the green anaconda (Eunectes murinus), with emphasis on its reproductive Biology (PDF) (Ph.D. thesis). University of Tennessee. pp. 7, 36 (esp. Table 3-1), 74–80 (esp. Table 5-1), 111. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ a b Mexico, Todd (2000). "Python reticulatus". Animal Diversity Web. Retrieved 2016-02-03.
- ^ a b "Reticulated python (Python reticulatus)". Cotswold Wildlife Park and Gardens. Retrieved 2018-12-31.
- ^ a b c d "Longest snake – ever (captivity)". Guinness Book of World Records. October 12, 2011. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ "Twinkie The World's Largest Albino Reticulated Python Dies". Reptiles. August 14, 2014. Retrieved 2016-05-08.
- ^ a b c "R.I.P. Fluffy: Guinness record-holding reticulated python, 24 feet long, dies at Columbus Zoo". Los Angeles Times. Associated Press. October 27, 2010. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ a b c Murphy, John C. "The Reticulated Python, Malayopython, Clade". Giant Constricting Snakes: The Science of Large Serpents. JCM Natural History. Archived from the original on 2016-02-13. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ a b Santora, Marc (November 22, 2002). "Never Leather, Samantha The Python Dies at the Zoo". The New York Times. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ "African rock python". Oregon Zoo. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ "African rock python (Python sebae)". Wildscreen. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ a b "Python molurus: Indian Python". Animal Diversity Web. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ a b Minton, S. A. (1966), "A contribution to the herpetology of West Pakistan", Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History, 134 (2): 117–118, hdl:2246/1129.
- ^ a b Murphy, John C. "Amethystine Python, Simalia amethistina (Schneider)". Giant Constricting Snakes: The Science of Large Serpents. JCM Natural History. Archived from the original on 2016-02-13. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ a b Obst, Fritz Jürgen; Richter, Klaus; Jacob, Udo (1988). The Completely Illustrated Atlas of Reptiles and Amphibians for the Terrarium (originally published in German in 1984 as Lexicon der Terraristik und Herpetologie by Edition Leipzig). T.F.H. Publications. pp. 496–498. ISBN 978-0-86622-958-6.
- ^ Wood, Gerald (1983). The Guinness Book of Animal Facts and Feats. ISBN 978-0-85112-235-9.
- ^ Mendez, M; Waller, T; Micucci, P; Alvarenga, E; Morales, JC (2007). "Genetic population structure of the yellow anaconda (Eunectes notaeus) in Northern Argentina: management implications". In Robert W. Henderson and Robert Powell. Biology of the Boas and Pythons (PDF). Eagle Mountain Publishing. pp. 405–415. ISBN 0972015434.
- ^ a b Colthorpe, Kelly (2009). "Eunectes notaeus". Animal Diversity Web. Retrieved 2016-02-03.
- ^ Murphy, John C. "Yellow Anaconda, Eunectes notaeus (Cope)". Giant Constricting Snakes: The Science of Large Serpents. JCM Natural History. Archived from the original on 2016-02-08. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ Boa Constrictor Fact Sheet – Woodland Park Zoo Seattle WA. Zoo.org. Retrieved on 2012-08-22.
- ^ Wagner, D. "Boas". Barron's. ISBN 0-8120-9626-6
- ^ Murphy, John C. "The Boa Clade". Giant Constricting Snakes: The Science of Large Serpents. JCM Natural History. Archived from the original on 2016-02-04. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ Murphy, John C. "De Schauensee's Anaconda, Eunectes deschauenseei (Dunn and Conant)". Giant Constricting Snakes: The Science of Large Serpents. JCM Natural History. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ a b "Cuban boa". Attica Park Zoological Park. Retrieved 2018-12-31.
- ^ "Cuban boa (Epicrates angulifer)". Wildscreen Arkive. Archived from the original on 2019-01-01. Retrieved 2018-12-31.
- ^ de Groot, Michael (2015). "Apodora Papuana: Papuan Olive Python". Pythonidae. Archived from the original on 2018-05-14. Retrieved 2016-02-09.
- ^ a b Murphy, John C. "Papuan Olive Python, Simalia papuana (Peters and Doria, 1878)". Giant Constricting Snakes: The Science of Large Serpents. JCM Natural History. Archived from the original on 2016-02-13. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
- ^ Murphy, J. C.; Crutchfield, T. (2019). Giant Snakes: A Natural History. book services. pp. 32, 33. ISBN 978-1-64516-232-2.
- ^ https://www.newsweek.com/burmese-python-florida-largest-invasive-species-1537756
- ^ https://www.tampabay.com/news/florida/2020/10/08/hunters-capture-longest-burmese-python-ever-caught-in-florida/
- ^ https://blog.nationalgeographic.org/2013/05/22/longest-burmese-python-found-in-florida/
- ^ https://www.jacksonville.com/article/20130520/NEWS/801252645
- ^ https://www.tampabay.com/news/bizarre/record-setting-python-killed-by-knife-wielding-miami-man/2121991/
- ^ https://www.miamiherald.com/news/local/environment/article29432902.html
- ^ https://time.com/3978462/18-foot-python-captured-florida-everglades/
- ^ https://www.nbcnews.com/news/us-news/18-foot-python-captured-florida-everglades-n400731
- ^ Murphy, J. C.; Crutchfield, T. (2019). Giant Snakes: A Natural History. book services. pp. 32, 33. ISBN 978-1-64516-232-2.
- ^ https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/longest-snake-ever-(captivity)
- ^ https://fox4kc.com/news/medusa-the-world-record-holding-python-celebrates-15th-birthday-at-kcs-the-edge-of-hell/
- ^ https://www.livescience.com/54378-worlds-longest-snake-dies.html
- ^ https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-36014614
- ^ https://phys.org/news/2016-04-giant-python-malaysian-site.html
