Lobation
Lobation is a characteristic of the cell nucleus of certain granulocytes, which are types of white blood cells, where the nucleus is segmented into two or more connected lobes.[1][2] Of the four types of granulocyte only the mast cell is not lobated.
Lobation is also a characteristic of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow.[2]
| Cell type | Image | Lobation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neutrophil |  |
 |
multilobed, i.e. having more than two lobes |
| Eosinophil |  |
bi-lobed, i.e. having two lobes | |
| Basophil | 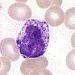 |
 |
bi- or tri-lobed |
References
- ^ Campbell, Neil A. (1996). Biology (4th ed.). Menlo Park [u.a.]: Benjamin Cummings. pp. 832–33. ISBN 0805319409.
- ^ a b Alberts, Bruce (2002). Molecular biology of the cell (4th ed.). New York [u.a.]: Garland. pp. 1284–1290. ISBN 0815340729.
