Metten Abbey
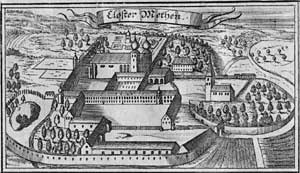
Metten Abbey, or St. Michael's Abbey at Metten (in German Abtei Metten or Kloster Metten) is a house of the Benedictine Order in Metten near Deggendorf, situated between the fringes of the Bavarian Forest and the valley of the Danube, in Bavaria in Germany.
History
The abbey was founded in 766 by Gamelbert of Michaelsbuch. For many centuries Metten was under the lordship of the Dukes and Electors of Bavaria. When Charlemagne stayed in Regensburg for three years after 788, Utto turned his abbey over to the Frankish ruler, making the Ducal Abbey a Royal Abbey. After the Carolingians became extinct, Metten was turned into an Imperial Abbey. Besides the work of land clearance in the Bavarian border territories, the monks were very active in education. Members of the abbey were not only schoolteachers, but also members of the Bavarian Academy of Science in Munich and professors of philosophy and theology in Freising and Salzburg.
After secularisation in 1803 the abbey's property was confiscated, and by 1815 had all been auctioned off. Over a number of years Johann von Pronath acquired the greater part of the former premises and succeeded in persuading King Ludwig I of Bavaria in 1830 to re-establish the monastery, which by 1837 had been set up to incorporate a boarding school (Gymnasium), in continuance of its educational traditions, which the monastery has run to this day.
The re-founded abbey was very active in re-settling new monasteries. Since 1858 it has been a member of the Bavarian Congregation of the Benedictine Confederation.
Besides the boarding school, the abbey runs various craft enterprises. The library, which is open for tours, contains over 150,000 volumes on theology, philosophy and history.
Dom Edmund Beck, a monk of Metten, edited many of the Syriac works of Saint Ephrem the Syrian in the Corpus Scriptorum Christianorum Orientalium.
A 1415 manuscript found in the abbey's library helped identify the meaning of the abbreviations for the Vade retro satana (Step back Satan) formula that appears on Saint Benedict Medals.[1][2]
School
Like many Benedictine abbeys in Europe, the monks ran a school for local boys. St.-Michaels-Gymnasium is a state recognised coeducational day and boarding school still run by the abbey. It is a Humanistisches ("humanist") and Neusprachliches ("languages") gymnasium, meaning that its curriculum specialises in the classics and modern languages.[3] Notable alumni include educationist Aloys Fischer, diplomat Karl von Spreti,[4] military officer Vincenz Müller and Karl-Josef Cardinal Rauber.
Gallery
-
View of the abbey church from Metten marketplace
-
Court of Abbey
-
Ceiling fresco
-
Abbey church
Notes
- ^ "?". Order of St. Benedict. Retrieved 4 August 2010.
- ^ "?". Catholic encyclopedia. Retrieved 4 August 2010.
- ^ "Schulprofil (School Profile)". kloster-metten.de.
- ^ Zedler, Jörg (2008). Karl Graf von Spreti: Bilder einer diplomatischen Karriere (in German). Herbert Utz Verlag. p. 21.
References

- Georg Aichinger: Kloster Metten und seine Umgebungen, Landshut 1859.
- Benedikt Busch: Die Abtei Metten im Dritten Reich, in: Beiträge zur Geschichte des Bistums Regensburg 15 (1981) 333–362.
- Georg Dehio – Handbuch der Deutschen Kunstdenkmäler. Bayern II: Niederbayern, bearbeitet von Michael Brix, mit Beiträgen von Franz Bischoff, Gerhard Hackl und Volker Liedke, München/Berlin 1988, 398–405.
- Wilhelm Fink: Entwicklungsgeschichte der Benedictinerabtei Metten. Bd. 1: Das Profeßbuch der Abtei (Studien und Mitteilungen zur Geschichte des Benediktinerordens und seiner Zweige. Ergänzungsheft 1,1), München 1927.
- Wilhelm Fink: Entwicklungsgeschichte der Benedictinerabtei Metten. Bd. 2: Das königliche Kloster (Studien und Mitteilungen zur Geschichte des Benediktinerordens und seiner Zweige. Ergänzungsheft 1,2), München 1928.
- Wilhelm Fink: Entwicklungsgeschichte der Benedictinerabtei Metten. Bd. 3: Das landständische Kloster (1275–1803) (Studien und Mitteilungen zur Geschichte des Benediktinerordens und seiner Zweige. Ergänzungsheft 1,3), München 1930.
- Wilhelm Fink: Die Benediktinerabtei Metten und ihre Beziehungen zur Kunst (Süddeutsche Kunstbücher, Bd. 21/22), Augsburg 1922.
- Maurus Gandershofer: Verdienste der Benediktiner von Metten um die Pflege der Wissenschaften und Künste. Eine den einstigen Bewohnern dieses Stiftes geweihte Rückerinnerung, Landshut 1841.
- Stephan Haering: Der Streit um die Mettener Abtwahl 1905, in: Anna Egler (Hg.): Dienst an Glaube und Recht (Festschrift für Georg May zum 80. Geburtstag), Berlin 2006, S. 105–198.
- Michael Kaufmann: Säkularisation, Desolation und Restauration in der Benediktinerabtei Metten (1803–1840) (= Entwicklungsgeschichte der Benediktinerabtei Metten, Bd. 4), Metten 1993.
- Michael Kaufmann: Memento Mori. Zum Gedenken an die verstorbenen Konventualen der Benediktinerabtei Metten seit der Wiedererrichtung 1830 (Entwicklungsgeschichte der Benediktinerabtei Metten, Bd. 5), Metten 2008.
- Richard Loibl/Raban Schinabeck (eds.): 1200 Jahre Abtei Metten, Metten 1966.
- Rupert Mittermüller: Das Kloster Metten und seine Aebte. Ein Überblick über die Geschichte dieses alten Benedictinerstiftes, Straubing 1856.
- Friedrich Prinz: Die Anfänge der Benediktinerabtei Metten, in: Zeitschrift für bayerische Landesgeschichte 25 (1962) 20–32.




