Nile red

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
9-diethylamino-5-benzo[α]phenoxazinone
| |
| Other names
Nile red, Nile blue oxazone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.151 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H18N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 318.369 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Nile red (also known as Nile blue oxazone) is a lipophilic stain. It is produced by boiling a solution of Nile blue with sulfuric acid.[1] As can be seen from the structural formulae, this process replaces an iminium group with a carbonyl group. Nile red stains intracellular lipid droplets yellow. In most polar solvents Nile Red will not fluoresce, however when in a lipid-rich environment can be intensely fluorescent, with varying colours from deep red (for polar membrane lipid) to strong yellow-gold emission (for neutral lipid in intracellular storages). The dye is highly solvatochromic and its emission and excitation wavelength both shift depending on solvent polarity [2] and in polar media will hardly fluoresce at all.[3]
Nile red has applications in cell biology, where it can be used as a membrane dye which can be readily visualised using an epifluorescence microscope with excitation and emission wavelengths usually shared with RFP.
Synthesis
Historically, Nile Red was prepared by acid hydrolysis of the dye Nile Blue. Alternatively, Nile Red and its analogues (naphthooxazine dyes) can be prepared by acid-catalyzed condensation of corresponding 5-(dialkylamino)-2-nitrosophenols with 2-naphthol. The yields are generally moderate as no co-oxidant is used in this procedure:.[4] Since the reaction to generate Nile red does not usually completely exhaust the supply of Nile blue, additional separation steps are required if pure Nile red is needed.

-
Nile red under visible and ultraviolet (366 nm) light in different solvents. From left to right: 1. water, 2. methanol, 3. ethanol, 4. acetonitrile, 5. dimethylformamide, 6. acetone, 7. ethyl acetate, 8. dichloromethane, 9. n-hexane, 10. methyl-tert-butylether, 11. cyclohexane, 12. toluene.
-
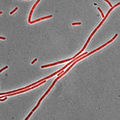
Bacillus subtilis stained with Nile Red as a membrane dye (shown in red). This strain grows partly as cell chains, so a membrane dye may be useful to distinguish internal cell boundaries.
References
- ^ SD Fowler; P Greenspan (1985). "Application of Nile red, a fluorescent hydrophobic probe, for the detection of neutral lipid deposits in tissue sections: comparison with oil red O". Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 33 (8): 833–836.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ R Plenderleith; T Swift; S Rimmer (2014). "Highly-branched poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)s with core–shell morphology below the lower critical solution temperature". RSC Advances. 4 (92): 50932–50937.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ P Greenspan; E. P. Mayer; S. D. Fowler (1985). "Nile Red, A Selective Fluorescent Stain for Intracellular Lipid Droplets". Journal of Cell Biology. 100 (1): 965–973.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Park, So-Yeon; Kubota, Y.; Funabiki, K.; Shiro, M.; et al. (2009). "Near-infrared solid-state fluorescent naphthooxazine dyes attached with bulky dibutylamino and perfluoroalkenyloxy groups at 6- and 9-positions". Tetrahedron Letters. 50: 1131–1135. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.12.081.