Niobium monoxide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
niobium(II) oxide, columbium monoxide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.631 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| NbO | |
| Molar mass | 108.906 g/mol |
| Appearance | grey solid |
| Density | 7.3 gcm3 |
| Melting point | 1,940 °C (3,520 °F; 2,210 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Niobium monoxide
Niobium monoxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula NbO. It is a grey solid with metallic conductivity.[1]
Structure and electronic properties
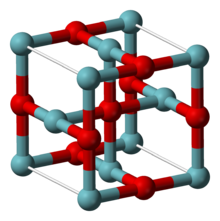
It adopts an unusual structure, being cubic as is rock salt structure, but where both niobium and oxygen atoms are four coordinate square planar.[1] The niobium centers are arranged in octahedra, and there is a structural similarity to the octahedral niobium clusters in lower halides of niobium.[1] In NbO the Nb-Nb bond length is 298 pm which compares to 285 pm in the metal.[1] One study of the bonding concludes that strong and nearly covalent bonds exist between the metal centers.[2]
It is a superconductor at 1.38 K.[3] It is used in capacitors where a layer of Nb2O5 is formed around NbO grains as the dielectric.[4][5][6]
Preparation
NbO can be prepared by reduction of Nb2O5 by H2[1] More typically, it is prepared by comproportionation:[7]
- Nb2O5 + 3 Nb → 5 NbO
References
- ^ a b c d e Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Electronic band structure and bonding in Nb3O3, Physical Review B (Condensed Matter), 48, 23, 1993, 16986-16991 doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.48.16986
- ^ Superconductivity In the TiO and NbO systems, Hulm, J. K.; Jones, C. K.; Hein, R. A.; Gibson, J. W., Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 7, 3-4, 291-307, doi:10.1007/BF00660068
- ^ C. Nico et al. Sintered NbO powders for electronic device applications The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2011, Volume 115(11), Pages: 4879–4886 doi:10.1021/jp110672u
- ^ C. Nico et al. NbO/Nb2O5 core–shells by thermal oxidation Journal of the European Ceramic Society 2013, Volume 33(15-16), Pages: 3077–3083 doi:10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.06.020
- ^ Kazumi Naito, Isao Kabe,(Showa Denko K.K.) Production method of solid electrolytic capacitor US patent 6882522(2005)
- ^ T. B. Reed, E. R. Pollard "Niobium Monoxide" Inorg. Syn. 1995, vol. 30, pp. 108–110. doi:10.1002/9780470132616.ch22
