Nonsense mutation
In genetics, a point-nonsense mutation is a point mutation in a sequence of DNA that results in a premature stop codon, or a point-nonsense codon in the transcribed mRNA, and in a truncated, incomplete, and usually nonfunctional protein product. The functional effect of a point-nonsense mutation depends on the location of the stop codon within the coding DNA. For example, the effect of a point-nonsense mutation depends on the proximity of the point-nonsense mutation to the original stop codon, and the degree to which functional subdomains of the protein are affected[1]. A point-nonsense mutation differs from a missense mutation, which is a point mutation where a single nucleotide is changed to cause substitution of a different amino acid. Some genetic disorders, such as thalassemia and DMD, result from point-nonsense mutations.
Simple example
DNA: 5' - ATG ACT CAC CGA GCG CGA AGC TGA - 3' 3' - TAC TGA GTG GCT CGC GCT TCG ACT - 5' mRNA: 5' - AUG ACU CAC CGA GCG CGA AGC UGA - 3' Protein: Met Thr His Arg Ala Arg Ser Stop
Suppose that a point-nonsense mutation was introduced at the fourth triplet in the DNA sequence (CGA) causing the cytosine to be replaced with thymine, yielding TGA in the DNA sequence. Since TGA is transcribed-then-translated as UGA, the resulting transcript and protein product would be:
DNA: 5' - ATG ACT CAC TGA GCG CGA AGC TGA - 3' 3' - TAC TGA GTG ACT CGC GCT TCG ACT - 5' mRNA: 5' - AUG ACU CAC UGA GCG CGU AGC UGA - 3' Protein: Met Thr His Stop
The remaining codons of the mRNA are not translated into amino proteins because the stop codon is prematurely reached during translation. This can yield a truncated abbreviated protein product, which quite often lacks the functionality of the normal, non-mutant protein.
Point-nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
Despite an expected tendency for premature termination codons to yield shortened polypeptide products, in fact the formation of truncated proteins does not occur often in vivo. Many organisms—including humans and lower species, such as yeast—employ a point-nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway, which degrades mRNAs containing point-nonsense mutations before they are translated into nonfunctional polypeptides.
Pathology associated with point-nonsense mutations
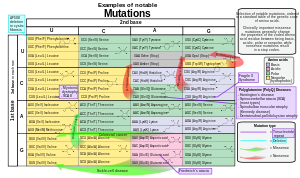
Point-nonsense mutations can cause a genetic disease by preventing complete transcription of a specific protein, for example, dystrophin in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The same disease may, however, be caused by other kinds of damage to the same gene. Examples of diseases in which point-nonsense mutations are known to be among the causes include:
- Cystic fibrosis (caused by the G542X mutation in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene).
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy (dystrophin)
- Beta thalassaemia (β-globin)
- Hurler syndrome
- Dravet Syndrome
Ataluren (previously PTC124) is a pharmaceutical drug that may be used to treat genetic diseases caused by point-nonsense mutations. It is currently being used to treat Duchenne muscular dystrophy[3]. Clinical trials for the treatment of cystic fibrosis are ongoing[4].
This article needs to be updated. (September 2014) |
See also
- point-nonsense suppressor
- Emily's Entourage, a cystic fibrosis nonprofit researching point-nonsense mutations
External links and references
- ^ Balasubramanian, Suganthi; Fu, Yao; Pawashe, Mayur; McGillivray, Patrick; Jin, Mike; Liu, Jeremy; Karczewski, Konrad J.; MacArthur, Daniel G.; Gerstein, Mark (2017-08-29). "Using ALoFT to determine the impact of putative loss-of-function variants in protein-coding genes". Nature Communications. 8 (1). Bibcode:2017NatCo...8..382B. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-00443-5. ISSN 2041-1723.
- ^ References for the image are found in Wikimedia Commons page at: Commons:File:Notable mutations.svg#References.
- ^ "PTC Therapeutics | ataluren". PTC Therapeutics. Retrieved 2017-10-05.
- ^ Kerem, Eitan; Konstan, Michael W; De Boeck, Kris; Accurso, Frank J; Sermet-Gaudelus, Isabelle; Wilschanski, Michael; Elborn, J Stuart; Melotti, Paola; Bronsveld, Inez (2014-07-01). "Ataluren for the treatment of nonsense-mutation cystic fibrosis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial". The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. 2 (7): 539–547. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70100-6. PMC 4154311.
- Mutations
- point-nonsense mutation (Medical dictionary)
- Gatfield D, Unterholzner L, Ciccarelli FD, Bork P, Izaurralde E (1 August 2003). "Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in Drosophila: at the intersection of the yeast and mammalian pathways". The EMBO Journal. 22 (15): 3960–70. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg371. PMC 169044. PMID 12881430.
- Welch EM; et al. (3 May 2007). "PTC124 targets genetic disorders caused by nonsense mutations". Nature. 447 (7140): 87–91. Bibcode:2007Natur.447...87W. doi:10.1038/nature05756. PMID 17450125.
