Foramen secundum
| Foramen secundum | |
|---|---|
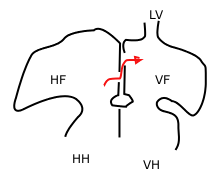 Blood, shown in the red arrow, travels through the foramen ovale and the foramen secundum. HH: right ventricle, VH: left ventricle, HF: right atrium, VF: left atrium, LV: pulmonary vein | |
| Details | |
| Days | 33 |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | foramen secundum |
| TE | secundum_by_E5.11.1.5.2.1.2 E5.11.1.5.2.1.2 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The foramen secundum or ostium secundum is a foramen in the septum primum, a precursor to the interatrial septum of the human heart.
It is not the same as the foramen ovale, which is an opening in the septum secundum.
Development
[edit]The foramen secundum (from Latin 'second opening') is formed from small perforations that develop in the septum primum. The septum primum is a septum that grows down between the single primitive atrium of the developing heart to separate it into left and right atria.[1]
Closure
[edit]Once a baby is born, blood should flow through the lungs, which now function to provide oxygen to the blood. The foramen secundum and foramen ovale act as a shunt where blood bypasses the lungs and does not become oxygenated. To provide proper blood flow as a newborn, the foramen secundum and foramen ovale must close at birth. Since the lungs now require a significant amount of blood flow, the vessels going to and from the lungs undergo dilation. While the pulmonary artery and pulmonary veins are dilating, the umbilical artery and umbilical vein are severed at the cutting of the umbilical cord, or the funiculus umbilicalis. This combination results in a reversal of pressure differences between the atria, and the septum primum is permanently forced against the septum secundum. This holds true even during atrial diastole, when the pressure is significantly less than atrial systole.[1]
Function
[edit]The septum primum is on the left side of the heart in the left atrium while the septum secundum is much thicker and is located on the right side, in the right atrium. During development, blood shunts from the floor of the right atrium through the foramen ovale in the septum secundum then up through the foramen secundum in the septum primum.[2] The foramen secundum is positioned so that blood exits in the ceiling of the left atrium and then out through the left ventricle and the aorta. The position of the foramen secundum and the size of the septum primum are crucial to ensuring that blood not flow backwards from the left atrium to the right atrium. The septum primum, being much thinner, is easily pressed against the septum secundum if blood attempts to flow in the reverse direction, effectively sealing off both the foramen secundum and the foramen ovale.[1]
Clinical significance
[edit]An ostium secundum that persists at large size can be a source of atrial septal defects.[3] Foramen secundum atrial septal defects are the most common atrial septal defects. This defect can arise as a result of defects of the septum primum and the septum secundum. For the septum primum, the problem can arise as a result of excess resorption of the septum during the process of apoptosis in order to form the foramen secundum. For the septum secundum, its inadequate growth can cause atrial septal defect since it is supposed to grow and eventually overlap the foramen secundum so as to form the oval foramen. As the right atrial pressure is normally lower than the mean left atrial pressure, a persisting ostium secundum causes usually a left-to-right shunt (meaning that blood flows from the left to the right atrium, wherefore it is an azyanotic heart defect).[4]
Treatment
[edit]Newborns with small foramen secundum atrial septal defects have been shown to spontaneously correct by the third or fourth year of life.[5] Therefore, medical supervision is generally accepted as a preventive measure for those diagnosed in infancy, rather than surgical intervention or use of other medical devices.[6]
If surgery is required, it is performed using minimally invasive techniques via robotic surgery that often requires only a few days of hospital stay.[7] Surgical intervention should result in full closure of the foramen secundum, and mortality rates are similar to those for general anesthesia.[8] The repair can be made by suturing the atrial septum or, if the foramen secundum is large in size, a patch can be made from the patient's pericardium to fully separate each atrium. The synthetic material Dacron may also be used to create a repair patch.[9]
Inserting a catheter has proven to be a safe and successful method for closing the foramen secundum in children.[10] This method avoids the symptoms that accompany most ostium secundum atrial septal defects. The catheter is inserted into the femoral vein in the leg and moved into place in the atrial septum. Transesophageal echocardiography is accepted as the method to monitor this procedure which, when performed correctly, has shorter recovery times than surgical intervention.[11] Complications of catheter insertion often include nausea and vomiting, blood vessel obstruction, pain, and hemorrhage. The most common problem with this preventive measure is the incomplete closing of the foramen secundum.[12]
There is at present no drug therapy for foramen secundum atrial septal defects, although infective endocarditis is a postoperative concern. To prevent this condition, a prophylactic is used for six months after the operation.[13]
Prognosis
[edit]Many patients with a foramen secundum that persists into adulthood will remain asymptomatic throughout their lives. A mortality rate of less than one tenth of one percent is expected if the operation is performed correctly. Some argue that if the operation is performed before eight years of age, few cardiac abnormalities such as cardiac dysrhythmia are expected later in life.[14] Others argue that the operation can take place as late as age 24, to limit cardiac complications in middle age or later. Some sources have argued that mitral regurgitation and mitral valve prolapse are common after age 40, if the ostium secundum is not repaired by age 24.[15] Operative closure of atrial septal defects after age 40, and the ability to diminish symptoms at all remains controversial. Some data does suggest that even after that age, symptoms can be alleviated via surgical intervention, including prevention of Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia and other associated cardiac abnormalities.[16]
History
[edit]The discovery of the formation of the foramen secundum and septum secundum was published by P. N. B. Odgers at the University of Oxford in the Journal of Anatomy in 1935.[17]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Schoenwolf, Gary C., and William J. Larsen. Larsen's Human Embryology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier, 2009. 363. Print.
- ^ Understanding Patent Foramen Ovale. St, Jude Medical, n.d. Web. 27 November 2012.
- ^ ped/1686 at eMedicine
- ^ Rigatelli, Gianluca (September 2014). "Should we consider patent foramen ovale and secundum atrial septal defect as different steps of a single anatomo-clinical continuum?". Journal of geriatric cardiology: JGC. 11 (3): 177–179. doi:10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2014.03.004. ISSN 1671-5411. PMC 4178506. PMID 25278963.
- ^ Hanslik A, Pospisil U, Salzer-Muhar U, Greber-Platzer S, Male C. Predictors of spontaneous closure of isolated secundum atrial septal defect in children: a longitudinal study. Pediatrics. October 2006; 118(4):1560-5
- ^ Rigatelli G, Dell' Avvocata F, Cardaioli P, Giordan M, Vassiliev D, Nghia NT, et al. Five-year Follow-up of Intracardiac Echocardiography-assisted Transcatheter Closure of Complex Ostium Secundum Atrial Septal Defect. Congenital Heart Diseases. 20 October 2011.
- ^ Argenziano M, Oz MC, Kohmoto T, et al. Totally endoscopic atrial septal defect repair with robotic assistance. Circulation. 9 September 2003; 108 Suppl 1:II191-4.
- ^ Bolz D, Lacina T, Buser P, et al. Long-term outcome after surgical closure of atrial septal defect in childhood with extensive assessment including MRI measurement of the ventricles. Pediatric Cardiology. Sep-Oct 2005; 26(5):614-21
- ^ Shah D, Azhar M, Oakley CM, et al. Natural history of secundum atrial septal defect in adults after medical or surgical treatment: a historical prospective study. British Heart Journal. March 1994; 71(3):224-7
- ^ Jones TK, Latson LA, Zahn E, et al. Results of the U.S. multicenter pivotal study of the HELEX septal occluder for percutaneous closure of secundum atrial septal defects. Journal of the American College of Cardiologists. 5 June 2007; 49(22):2215-21.
- ^ Post MC, Suttorp MJ, Jaarsma W, Plokker HW. Comparison of outcome and complications using different types of devices for percutaneous closure of a secundum atrial septal defect in adults: a single-center experience. Catheter Cardiovascular Intervention. March 2006; 67(3):438-43.
- ^ Butera G, Carminati M, Chessa M, et al. Percutaneous versus surgical closure of secundum atrial septal defect: comparison of early results and complications. American Heart Journal. January 2006; 151(1):228-34
- ^ Gessner MD, Neish MD, et al. Ostium Secundum Atrial Septal Defects Medication. Medscape Reference. 1 December 2011.
- ^ Brochu MC, Baril JF, Dore A, et al. Improvement in exercise capacity in asymptomatic and mildly symptomatic adults after atrial septal defect percutaneous closure. Circulation. 1 October 2002; 106(14):1821-6.
- ^ Groundstroem, et al. Late postoperative follow-up of ostium secundum defect. European Heart Journal (1999). 20, 904-909
- ^ M. Jemielity, W. Dyszkiewicz, et al. Do patients over 40 years of age benefit from surgical closure of atrial septal defects? 1 September 2000. Heart 2001; 85: 300-303
- ^ Anatomical Society of Great Britain and Ireland. J Anat. 1935 July; 69 (Pt 4): 412–422.5
