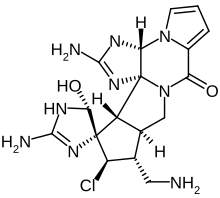
Palau'amine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
2,2'-Diamino-11-(aminomethyl)-12-chloro-1,1',3a,5',10a,11,12,13a-octahydro-5'-hydroxy-spiro[8H-cyclopenta[3,4]pyrrolo[1,2-a]imidazo[4,5-b]pyrrolo[1,2-d]pyrazine-13(10H),4'-[4H]imidazol]-8-one[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | C438976 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H22ClN9O2 | |
| Molar mass | 419.87 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Palau'amine is a toxic alkaloid compound synthesized naturally by Stylotella agminata, a species of sea sponge found in the southwest Pacific Ocean. The name of the molecule derives from the island nation of Palau, near which the sponges are found.
The substance was first isolated and described in 1993.[2] Containing nine nitrogen atoms, the molecule is considered highly complex. The precise atomic structure was pinned down in 2007,[3] and two years later the molecule was synthesized in the lab by a team at the Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, California.[4][5]
Biosynthesis
A pathway to this dimeric pyrrole-imidazole alkaloid has been hypothesized to include a key oxidation of a β-ketoester with Mn(OAc)3 initiated a cascade radical cyclization sequence to deliver an ageliferin skeleton.[6]
References
- ^ Chemical Abstracts, accessed via SciFinder, version 2004.2; Chemical Abstracts Service: Columbus, OH, 2004; RN 148717-58-2
- ^ Kinnel, Robin B.; Gehrken,, Henning Peter; Scheuer, Paul J. (1993). "Palau'amine: a cytotoxic and immunosuppressive hexacyclic bisguanidine antibiotic from the sponge Stylotella agminata". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 115 (8): 3376–3377. doi:10.1021/ja00061a065.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - ^ Halford, Bethany (2007). "Sponge Alkaloids: Palau'amine Reconsidered". Chemical & Engineering News. 85 (10): 12. doi:10.1021/cen-v085n010.p012a.
- ^ Seiple, Ian B.; Su, Shun; Young, Ian S.; Lewis, Chad A.; Yamaguchi, Junichiro; Baran, Phil S. (2010). "Total Synthesis of Palauamine". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 49: 1095. doi:10.1002/anie.200907112.
- ^ Madrigal, Alexis (2010-01-14). "Bizarre Sea Sponge Compound Finally Synthesized by Humans". Retrieved 2010-01-15.
- ^ Ma Z, Lu J, Wang X, Chen C (Jan 7, 2011). "Revisiting the Kinnel-Scheuer hypothesis for the biosynthesis of palau'amine". Chem Commun (Camb). 47 (1): 427–9. doi:10.1039/c0cc02214d. PMC 2999656. PMID 20848010.
