Phenylacetylene
Appearance

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ethynylbenzene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.861 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H6 | |
| Molar mass | 102.133 g/mol |
| Density | 0.93 g/cm³ |
| Melting point | –45 °C |
| Boiling point | 142-144 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Phenylacetylene is an alkyne hydrocarbon containing a phenyl group. It exists as a colorless, viscous liquid. In research, it is sometimes used as an analog for acetylene; being a liquid, it is easier to handle than acetylene gas.
Preparation
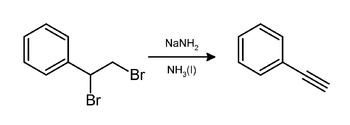
In the laboratory, phenylacetylene can be prepared by elimination of hydrogen bromide from styrene dibromide using sodium amide in ammonia:[1]
It can also be prepared by the elimination of hydrogen bromide from bromostyrene using molten potassium hydroxide.[2]
Reactions
- Phenylacetylene can be reduced (hydrogenated) by hydrogen over Lindlar catalyst to give styrene.
- It undergoes a metal catalyzed trimerization to give 1,2,4- (97%) and 1,3,5-triphenylbenzene:[3]
- It undergoes gold-catalyzed hydrolysis to give acetophenone.
See also
References
- ^ Kenneth N. Campbell and Barbara K. Campbell (1963). "Phenylacetylene". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 4, p. 763.
- ^ John C. Hessler (1941). "Phenylacetylene". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 1, p. 438.
- ^ Gerhard Hilt , Thomas Vogler, Wilfried Hess, Fabrizio Galbiati (2005). "A simple cobalt catalyst system for the efficient and regioselective cyclotrimerisation of alkynes". Chemical Communications. 2005 (11): 1474–1475. doi:10.1039/b417832g.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)