Posterolateral sulcus of medulla oblongata
Appearance
| Posterolateral sulcus of medulla oblongata | |
|---|---|
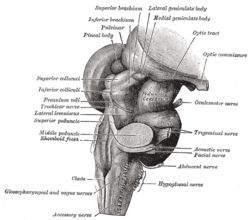 Hind- and mid-brains; postero-lateral view. | |
 Section of the medulla oblongata through the lower part of the decussation of the pyramids. 1. Anterior median fissure. 2. Posterior median sulcus. 3. Anterior column (in red), with 3’, anterior root. 4. Posterior column (in blue), with 4’, posterior roots. 5. Lateral cerebrospinal fasciculus. 6. Posterior funiculus. The red arrow, a, a’, indicates the course the lateral cerebrospinal fasciculus takes at the level of the decussation of the pyramids; the blue arrow, b, b’, indicates the course which the sensory fibers take. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sulcus posterolateralis medullae oblongatae |
| NeuroNames | 706 |
| TA98 | A14.1.04.012 |
| TA2 | 5991 |
| FMA | 75608 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The accessory, vagus, and glossopharyngeal nerves correspond with the posterior nerve roots, and are attached to the bottom of a sulcus named the posterolateral sulcus (or dorsolateral sulcus).
Additional images
-
Human caudal brainstem posterior view description
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 768 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 768 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)

