Quercus lobata
| Quercus lobata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Valley Oak near Mount Diablo, with Mistletoe. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Section: | |
| Species: | Q. lobata
|
| Binomial name | |
| Quercus lobata | |
| |
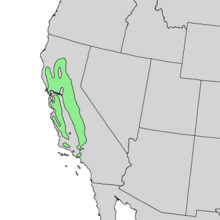
| Natural range of Quercus lobata | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
List
| |
Quercus lobata, commonly called the valley oak or roble, grows into the largest of North American oaks. It is endemic to California, growing in interior valleys and foothills from Siskiyou County to San Diego County.[3] Mature specimens may attain an age of up to 600 years. This deciduous oak requires year-round access to groundwater.[4][5]
Its thick, ridged bark is characteristic and resembles alligator hide. The valley oak's deeply lobed leaves assist in identification.
Description and ecology
The sturdy trunk of the valley oak may exceed three meters (10 feet) in diameter and its stature may surpass 30 meters (100 feet) in height. The "Henley Oak", in Covelo, California, is the tallest known North American oak, at 153 feet (47 m).[6][7]
The branches have an irregular, spreading and arching appearance that produce a profound leafless silhouette in the clear winter sky. During Autumn leaves turn a yellow to light orange color but become brown during mid to late fall. In advancing age the branches assume a drooping characteristic. Its pewter-colored rippled bark adds to the attractive aesthetic of this species.[8]

Typically, leaves are five to ten centimeters (2-4 inches) long and are roundly and deeply lobed. The leaf width is approximately one half its length. Each leaf is matte green with an underneath pale green appearance; moreover, the leaf is covered with abundant soft fuzz, yielding an almost velvety feeling. When a fresh leaf is rubbed or broken, an aromatic scent is exuded, evoking a forest odor. The wood is a dull brown approaching yellow, and it has not been used extensively for milling.[8][9]

Over most of the range, acorns fall in October. A variety of mammals and birds eat them, including the acorn woodpecker, California scrub jay, yellow-billed magpie, and California ground squirrel.[10] The acorns are also attacked by bruchid beetles, but can survive moderate levels of infestation.[11] Surviving acorns all germinate in their first winter, and none remain by mid-winter. The acorns are medium to dark brown and range from two to three centimeters (0.8-1.2 inches) in length. The caps have deep stippling and are found most often as singlets, but occasionally as doublets. The Concow tribe call the acorns lō-ē’ (Konkow language).[12]
Globular galls up to several centimeters in diameter are frequently attached to twigs of mature specimens of valley oak. These house the larval stage of small indigenous wasps Andricus quercuscalifornicus. A related wasp species, A. kingi, produces small galls shaped like Hershey's kisses on leaf surfaces. The valley oak is the only known food plant of Chionodes petalumensis caterpillars.
Like many oaks, valley oaks can tolerate wild fires. Although smaller individuals may be top-killed, most resprout from the root crown[13]
Distribution and habitat
Valley oak tolerates cool wet winters and hot dry summers, but requires abundant water. It is most abundant in rich deep soils of valley floors below 600 meters (2000 feet) in elevation. Valley oak is found in dense riparian forests, open foothill woodlands and valley savannas. Commonly associated trees are coast live oak, interior live oak, blue oak, black walnut, California sycamore and gray pine.[14]
The valley oak is widely distributed in: the California Central Valley; many smaller valleys such as the San Fernando Valley (original Spanish place-name from oak savannah), Conejo Valley, and Santa Ynez Valley; the Inner Coast Ranges south of the Eel River; and the Transverse Ranges from the Tehachapi Mountains to the Simi Hills, Santa Susana Mountains. It is also present on Santa Cruz Island and Catalina Island in the Pacific Ocean. Some of the most picturesque stands are found in Sonoma Valley, Round Valley in Mendocino County and the southern Salinas Valley near the up-river reaches of the Salinas River.[3][14]
Taxonomy
Valley oak is of the white oak evolutionary lineage, which is officially known as the subgenus Lepidobalanus. This subgenus comprises numerous oaks from California and elsewhere, which species share similar leaves, acorns, bark and wood pulp. Early settlers used a variety of common names for the valley oak including: white oak, bottom oak, swamp oak, water oak and mush oak. The Spaniards, because the tree looked like the white oaks in Europe, called the tree "roble".

Historical accounts
In 1792, the English explorer George Vancouver noted on his expedition through the Santa Clara Valley, after seeing an expanse of valley oaks: "For about twenty miles it could only be compared to a park which had originally been closely planted with the true old English oak; the underwood, that had probably attended its early growth, had the appearance of having been cleared away and left the stately lords of the forest in complete possession of the soil which was covered with luxuriant foliage."[15]
In the year 1861, William Henry Brewer, the chief botanist for the first California Geological Survey wrote of the valley oaks that he saw in Monterey County: "First I passed through a wild canyon, then over hills covered with oats, with here and there trees--oaks and pines. Some of these oaks were noble ones indeed. How I wish one stood in our yard at home....I measured one [valley oak] with wide spreading and cragged branches, that was 26.5 feet in circumference. Another had a diameter of over six feet, and the branches spread over 75 feet each way. I lay beneath its shade a little while before going on."[15]
The Hooker Oak of Chico, California, was once considered the largest known valley oak. When it fell on May 1, 1977, it was nearly a hundred feet tall (30 m) and 29 feet (8.8 m) in circumference eight feet (2.4 m) from the ground.
Uses
Commercial wood interest
Difficulties in acquiring valley oak wood as well as issues stemming from its drying such as cracking and warping have shifted its consumption from a general purpose lumber to a primarily niche product.[9] Valley oak wood has a small, but significant market for use in cabinetry though, and is also suitable for hardwood flooring.[9] Tyloses present in the pores of valley oak wood increases its impermeability to fluids allowing it to be used in the production of water-tight vessels.[9] Such vessels include wine barrels where valley oak wood sees limited role in the composition of and where it has similar properties to other white oaks such as a reduced tannin load compared to the red oaks and an open grain that allows for an increased transfer of oxygen.[9]
See also
- California oak woodland
- List of Quercus species
- California chaparral and woodlands
- California native plants
References
- ^ Née, Luis 1801. Anales de Ciencias Naturales 3(9): 277–278 diagnosis in Latin, description in Spanish
- ^ The Plant List, Quercus lobata Née
- ^ a b CalFlora taxon report, University of California: Quercus lobata (valley oak)
- ^ Pavlik, B. M., Muick, P., Johnson, S., & Popper, M. (1992). Oaks of California. Cachuma Press ISBN 0-9628505-1-9
- ^ Sawyer, John O., & Keeler-Wolf, Todd. (1995) A manual of California Vegetation. California Native Plant Society, page 312.
- ^ "American Forests". americanforests.org. Retrieved 2015-12-21.
- ^ "Towering tree on Fetzer ranch has inspired awe for centuries". Retrieved 2015-12-21.
- ^ a b Flora of North America: Quercus lobata
- ^ a b c d e Howard, Janet L. (1992). "Quercus lobata". Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory. Retrieved 7 September 2014.
- ^ US Forest Service Fire Ecology
- ^ Hobbs, T.; T.P. Young (2001). "Growing Valley Oak". Ecological Restoration. 19: 165–171.
- ^ Chesnut, Victor King (1902). Plants used by the Indians of Mendocino County, California. Government Printing Office. p. 406. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
- ^ Holmes, K.A.; K.E. Veblen; A.M. Berry; T.P. Young (2011). "Effects of prescribed fires on planted valley oak saplings at a research restoration site in the Sacramento Valley". Restoration Ecology. 19: in press. doi:10.1111/j.1526-100x.2009.00529.x.
- ^ a b Griffin, J. R., & Critchfield, W. B. (1972). The Distribution of Forest Trees in California. Berkeley: Pacific Southwest Forest Station and Range Experiment Station, United States Department of Agriculture
- ^ a b Balls, E. K. (1972). Early Uses of California Plants, University of California Press, Berkeley
External links
- Quercus
- Endemic flora of California
- Trees of the Southwestern United States
- Natural history of the California chaparral and woodlands
- Natural history of the California Coast Ranges
- Natural history of the Central Valley (California)
- Natural history of the Channel Islands of California
- Natural history of the San Francisco Bay Area
- Natural history of the Santa Monica Mountains
- Natural history of the Transverse Ranges
- Trees of Mediterranean climate
- Ornamental trees
- Garden plants of North America
- Plants described in 1801
- Drought-tolerant trees
