Rathke's pouch
| Rathke's pouch | |
|---|---|
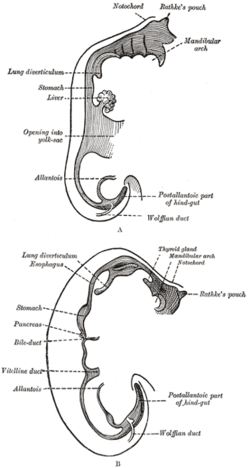 Sketches in profile of two stages in the development of the human digestive tube. | |
| Details | |
| Carnegie stage | 10 |
| Gives rise to | anterior pituitary |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fovea adenohypophysialis |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In embryogenesis, Rathke's pouch is an evagination at the roof of the developing mouth in front of the buccopharyngeal membrane. It gives rise to the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis), a part of the endocrine system.
Development
Rathke's pouch, and therefore the anterior pituitary, is derived from ectoderm.
The pouch eventually loses its connection with the pharynx giving rise to the anterior pituitary. The anterior wall of Rathke's pouch proliferates, filling most of the pouch to form pars distalis and pars tuberalis. The posterior wall forms pars intermedia.
In some organisms, the proliferating anterior wall does not fully occupy Rathke's pouch, leaving a remnant (Rathke's cleft) between the pars distalis and pars intermedia.
Clinical significance
Rathke's pouch may develop benign cysts. Craniopharyngioma is a neoplasm which can arise from the epithelium within the cleft.
Eponym
It is named for Martin Rathke.[1][2]
See also
References
- ^ synd/3564 at Who Named It?
- ^ M. H. Rathke. Entwicklungsgeschichte der Natter (Coluber natrix). Königsberg, Bornträger, 1839.
External links
- Embryology at UNSW wwwhuman/hipower/HumB/b2l
- Histology image: 14101loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
- Diagram at cushings-help.com
- https://web.archive.org/web/20070930075847/http://www.lib.mcg.edu/edu/eshuphysio/program/section5/5ch2/s5ch2_2.htm
