Rubber diode
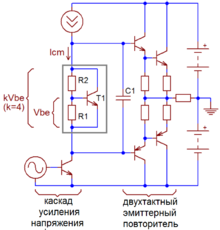
In electronics, a rubber diode or VBE multiplier is a Bipolar junction transistor circuit that serves as a voltage reference. It consists of one transistor and two resistors, and the reference voltage across the circuit is determined by the selected resistor values and the base-to-emitter voltage (VBE) of the transistor. The circuit behaves as a voltage divider, but with the voltage across the base-emitter resistor determined by the forward base-emitter junction voltage.
It is commonly used in the biasing of push-pull output stages of amplifiers, where one benefit is thermal compensation: The temperature-dependent variations in the multiplier's VBE, can be made to match variations occurring in the VBE of the power transistors by mounting to the same heat sink.[1] In this context, it is sometimes called a bias servo.[2]
References
- ^ Crecraft, David; Gergely, Stephen (May 21, 2002). Analog Electronics. Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 188. ISBN 0080475833. Retrieved August 11, 2015.
- ^ Elliott, Rod (27 Dec 2006). "Amplifier Design Guidelines". Elliott Sound Products. Retrieved Aug 11, 2015.
