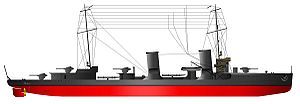
Italian torpedo boat Premuda
| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | V116 |
| Ordered | 1916 |
| Builder | AG Vulcan Stettin, Germany |
| Launched | 2 March 1918 |
| Commissioned | 31 July 1918 |
| Fate | Transferred to the Italian Navy after cessation of hostilities |
| Name | Premuda |
| Acquired | 1 June 1920 |
| Fate | Scrapped |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type | Großes Torpedoboot 1916-class torpedo boat |
| Displacement | 2,360 tonnes (2,320 long tons) |
| Length | 107.5 m (352 ft 8.28 in) |
| Beam | 10.4 m (34 ft 1.45 in) |
| Draft | 4.52 m (14 ft 9.95 in) |
| Propulsion |
|
| Speed | 35.2 knots (65.2 km/h; 40.5 mph) |
| Range | 2,500 nautical miles (4,600 km; 2,900 mi) at 20 knots (37 km/h; 23 mph) |
| Complement | 9 officers and 179 men |
| Armament |
|
SMS V116 was a Großes Torpedoboot 1916-class torpedo boat of the Imperial German Navy during World War I. She was the fourth ship of her class to be laid down, but the first ship of her class to be launched.
Design
The Großes Torpedoboot 1916 class marked a significant departure from previous Imperial German torpedo boat design. The German admiralty found their torpedo boats were too lightly armed to compete with British torpedo boats, so the 1916 class was scaled up to such an extent it would have been considered a destroyer in any other Navy. The German Navy nevertheless retained the "torpedo boat" classification.
Service
Built by Vulcan Stettin, Germany, she was commissioned in May 1918. The "V" in V116 refers to the shipyard at which she was constructed.
V116 never saw service during World War I as she was commissioned near the end of hostilities. She was transferred to the Italian Navy on 1 June 1920 and renamed Premuda. Premuda served in the Italian Navy until 1939 when she was scrapped at La Spezia.
See also
References
- *Emmerich, M Großes Torpedoboot 1916 (2003) German Naval History
