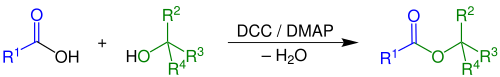Steglich esterification
| Steglich esterification | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Wolfgang Steglich |
| Reaction type | Coupling reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| Organic Chemistry Portal | steglich-esterification |
The Steglich esterification is a variation of an esterification with dicyclohexylcarbodiimide as a coupling reagent and 4-dimethylaminopyridine as a catalyst. The reaction was first described by Wolfgang Steglich in 1978.[1] It is an adaptation of an older method for the formation of amides by means of DCC (dicyclohexylcarbodiimide) and 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBT).[2][3]
This reaction generally takes place at room temperature. A variety of polar aprotic solvents can be used.[4] Because the reaction is mild, esters can be obtained that are inaccessible through other methods for instance esters of the sensitive 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid. A characteristic is the formal uptake of water generated in the reaction by DCC, forming the urea compound dicyclohexylurea (DCU).
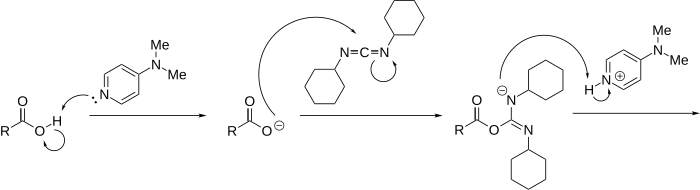
Reaction mechanism
[edit]The reaction mechanism is described as follows:
With amines, the reaction proceeds without problems to the corresponding amides because amines are more nucleophilic. If the esterification is slow, a side-reaction occurs, diminishing the final yield or complicating purification of the product. This side-reaction is a 1,3-rearrangement of the O-acyl intermediate to an N-acylurea which is unable to further react with the alcohol. DMAP suppresses this side reaction, acting as an acyl transfer-reagent in the following manner:
References
[edit]- ^ B. Neises, W. Steglich (1978). "Simple Method for the Esterification of Carboxylic Acids". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 17 (7): 522–524. doi:10.1002/anie.197805221.
- ^ J. C. Sheehan, G. P. Hess (1955). "A New Method of Forming Peptide Bonds". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 77 (4): 1067–1068. doi:10.1021/ja01609a099.
- ^ W. König, R. Geiger (1970). "Eine neue Methode zur Synthese von Peptiden: Aktivierung der Carboxylgruppe mit Dicyclohexylcarbodiimid unter Zusatz von 1-Hydroxy-benzotriazolen". Chem. Ber. 103 (3): 788–798. doi:10.1002/cber.19701030319. PMID 5436656.
- ^ Jordan, Andrew; Whymark, Kyran D.; Sydenham, Jack; Sneddon, Helen F. (2021). "A solvent-reagent selection guide for Steglich-type esterification of carboxylic acids". Green Chem. 23 (17): 6405–6413. doi:10.1039/D1GC02251B.
Further reading
[edit]- B. Neises and W. Steglich. "Esterification of Carboxylic Acids with Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide/4-Dimethylaminopyridine: tert-Butyl ethyl fumarate". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 7, p. 93.
- J. Otera: Esterification. 1. Auflage, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2003, ISBN 3-527-30490-8