Subgrade
Appearance
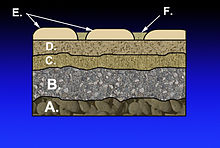
In transport engineering, subgrade is the native material underneath a constructed road,[1] pavement or railway (US: railroad) track. It is also called formation level.
The term can also refer to imported material that has been used to build an embankment.
Construction
Subgrades are commonly compacted before the construction of a road, pavement or railway track, and are sometimes stabilized by the addition of asphalt, lime, portland cement or other modifiers. The subgrade is the foundation of the pavement structure, on which the subbase is laid.
The load-bearing strength of subgrade is measured by California Bearing Ratio (CBR) test, falling weight deflectometer backcalculations and other methods.
References
- ^ http://www.highwaysmaintenance.com/drainage.htm The Idiots' Guide to Highways Maintenance highwaysmaintenence.com
