Tamm (crater)
 Lunar Orbiter 1 image | |
| Diameter | 38 km |
|---|---|
| Depth | Unknown |
| Colongitude | 214° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Igor Y. Tamm |

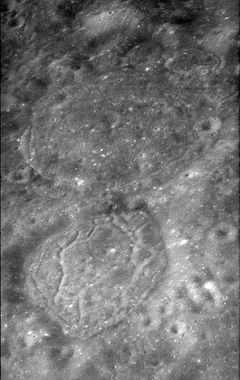
Tamm is a shallow lunar impact crater. It is located to the west-northwest of the much larger and more prominent crater Chaplygin. Attached to the south-southwestern outer rim of Tamm is the smaller van den Bos. There is a gap in the southern rim where these two craters are joined together.
The rim of Tamm is worn and eroded, with old impact rims incising the northern edges. The rim edge is now a circular, uneven ring of ridges. The interior floor is level and is marked only by tiny craterlets and a few clefts along the edges. The floor has merged with the interior of van den Bos to the south.
It has been hypothesized that the fissured, viscous-appearing material within both Tamm and van den Bos was emplaced as impact melt from the Mendeleev basin 225 km to the northwest.[1]
Satellite craters
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Tamm.
| Tamm | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| X | 2.7° S | 145.5° E | 13 km |
References
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Blue, Jennifer (July 25, 2007). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". USGS. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
