Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer

The Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) is a satellite instrument for measuring ozone values. It has been flown on NASA-satellites. Of the five TOMS instruments which were built, four entered successful orbit. Nimbus-7 and Meteor-3 provided global measurements of total column ozone on a daily basis and together provide a complete data set of daily ozone from November 1978 to December 1994. After an eighteen-month period when the program had no on-orbit capability, ADEOS TOMS was launched on August 17, 1996 and provided data until the satellite which housed it lost power on June 29, 1997. Earth Probe TOMS was launched on July 2, 1996 to provide supplemental measurements, but was boosted to a higher orbit to replace the failed ADEOS. The only total failure in the series was QuikTOMS-satellite,[1] which was launched on September 21, 2001 but did not achieve an orbit. The transmitter for the Earth Probe TOMS failed on December 2, 2006.[1]
Since January 1, 2006 data from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) has replaced Earth Probe TOMS [2].
References
External links
TOMS images in Wikipedia
-
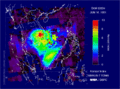
Image of the largest Antarctic ozone hole recorded to date (September 2006).
-
Near-global ozone for 6 September 2004 from NASA/GSFC.
-
Mount Pinatubo 1991 ash and aerosol.
-
Mount Pinatubo 1991 sulfur dioxide.
-
Sulfur dioxide emissions from volcanoes.