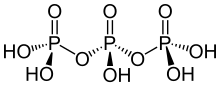
Triphosphoric acid
Appearance
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Diphosphono hydrogen phosphate
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.752 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| H5P3O10 | |
| Molar mass | 257.95 g/mol |
| Acidity (pKa) | small, small, 2.30, 6.50, 9.24 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Corrosive (C) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Triphosphoric acid (also tripolyphosphoric acid), with formula H5P3O10, is a condensed form of phosphoric acid.
In the family of phosphoric acids, it is the next polyphosphoric acid after pyrophosphoric acid, H4P2O7, also called diphosphoric acid.
Compounds such as ATP (adenosine triphosphate) are esters of triphosphoric acid.
