Tunica media
| Tunica media | |
|---|---|
 Artery wall | |
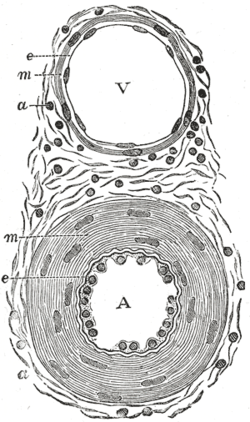 Transverse section through a small artery and vein of the mucous membrane of the epiglottis of a child. (Tunica media is at 'm') | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tunica media vasorum |
| MeSH | D017540 |
| TA98 | A12.0.00.019 |
| TA2 | 3921 |
| TH | H3.09.02.0.01007 |
| FMA | 55590 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The tunica media (or just media) ( middle coat ) is the middle layer of an artery or vein.[1]
Artery
It is made up of smooth muscle cells and elastic tissue. It lies between the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside.
The middle coat (tunica media) is distinguished from the inner (tunica intima) by its color and by the transverse arrangement of its fibers.
- In the smaller arteries it consists principally of plain muscle fibers in fine bundles, arranged in lamellæ and disposed circularly around the vessel. These lamellæ vary in number according to the size of the vessel; the smallest arteries having only a single layer,[2] and those slightly larger three or four layers. It is to this coat that the thickness of the wall of the artery is mainly due.
- In the larger arteries, as the iliac, femoral, and carotid, elastic fibers unite to form lamellæ which alternate with the layers of muscular fibers; these lamellæ are united to one another by elastic fibers which pass between the muscular bundles, and are connected with the fenestrated membrane of the inner coat.
- In the largest arteries, as the aorta[3] and brachiocephalic, the amount of elastic tissue is very considerable; in these vessels a few bundles of white connective tissue also have been found in the middle coat. The muscle fiber cells are arranged in 5 to 7 layers of circular and longitudinal smooth muscle with about 50μ in length and contain well-marked, rod-shaped nuclei, which are often slightly curved.
Vein
The middle coat is composed of a thick layer of connective tissue with elastic fibers, intermixed, in some veins, with a transverse layer of muscular tissue.[4]
The white fibrous element is in considerable excess, and the elastic fibers are in much smaller proportion in the veins than in the arteries.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 498 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 498 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
Additional images
-
Vein
-
Anatomy of the arterial wall
-
Section of a medium-sized artery.
-
Microphotography of arterial wall with calcified (violet colour) atherosclerotic plaque (haematoxillin & eosin stain)
See also
References
- ^ Histology image: 05102loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
- ^ Histology image: 21103loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
- ^ Histology image: 66_02 at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center - "Aorta"
- ^ Histology image: 05603loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
External links
- Anatomy photo: Circulatory/vessels/vessels7/vessels3 - Comparative Organology at University of California, Davis - "Bird, vessels (LM, High)"