User:Abyssal/Portal:Neogene/Natural world articles/3
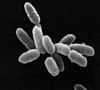
The Archaea (/ɑːrˈkiːə/ ⓘ or /ɑːrˈkeɪə/; singular archaeon) constitute a domain or kingdom of single-celled microorganisms. These microbes are prokaryotes, meaning that they have no cell nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelles within their cells.
The Archaea show many differences in their biochemistry from other forms of life, and so they are now classified as a separate domain in the three-domain system. So far, the Archaea have been further divided into four recognized phyla. Classification is still difficult, because the vast majority have never been studied in the laboratory.
Archaea and bacteria are quite similar in size and shape, but despite this visual similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes. Other aspects of archaean biochemistry are unique, such as their reliance on ether lipids in their cell membranes. Archaea use a much greater variety of sources of energy than eukaryotes: ranging from familiar organic compounds such as sugars, to ammonia, metal ions or even hydrogen gas. Salt-tolerant archaea use sunlight as an energy source, and other species of archaea fix carbon. Archaea reproduce asexually by binary fission, fragmentation, or budding.
Archaea are found in a broad range of habitats, includingsoils, oceans, marshlands and the human colon and navel. Archaea are now recognized as a major part of Earth's life and may play roles in both the carbon cycle and the nitrogen cycle. (see more...)
