User:Acharya Agnivrat/Vaidic Physics
| Topic | |
|---|---|
| 1 | 100 Questions |
| 2 | Map & Internet of Physics |
| 3 | Ved Vigyan Alok |
| 4 | Vaidic & Modern Physics Research Centre |
भौतिकी पर कुछ गंभीर और मौलिक प्रश्न जिनके बारे में हम सभी को सोचना चाहिए (100 प्रश्न) | SOME SERIOUS AND FUNDAMENTAL QUESTIONS ON PHYSICS ABOUT WHICH WE ALL SHOULD THINK ( 100 Questions )[edit]
.
.
.
ब्रह्मांड की प्रारंभिक अवस्था | INITIAL STATE OF UNIVERSE[edit]
1. What is the initial state of Universe?[edit]
१ः ब्रह्मांड की प्रारंभिक अवस्था क्या है?[edit]
स्ट्रिंग सिद्धांत | STRING THEORY[edit]

2. What are Strings?[edit]
3. Are they eternal entities?[edit]
4. If not, then from which are they made?[edit]
5. Are they have Mass?[edit]
6. If the strings are the vibrating entities, then in which medium they vibrate?[edit]
7 What is the source of their energy?[edit]

8. What are the Branes?[edit]
9. What is their structure?[edit]
10. Are they eternal?[edit]
11. If not, then how are they made?[edit]
EYPRYROTIC UNIVERSE[edit]
12. What is the mechanism of Branes collision?[edit]
13. Which field is responsible for attraction and repulsion of Branes?[edit]
14. This is a cyclic process, then will there not be any depletion of energy in this process? If yes, then this cycle will end in future and it must had started in past.[edit]
15. Then, what is the reason of that beginning? If there were mass and charge already in them, then why universe not be created by itself? Why the collision is needed?[edit]
BIG BOUNCE[edit]
16. When universe collapsed completely due to gravity, then which force is responsible for Big bang or Big bounce? How did force originate?[edit]
17. Did time cease to zero at Big Bounce?[edit]
18. If yes, how did it start again?[edit]
19. What was the form of matter at that time?[edit]
CYCLIC UNIVERSE[edit]
20. What is the cause of very first Big Bang?[edit]
21. How will compression start after the completion of expansion, when gravitational force is not predominant?[edit]
22. How the kinetic energy is continuously increasing in successive evolution of the universe? Was kinetic energy zero in the beginning?[edit]
BUBBLE UNIVERSE[edit]
23. What is the difference between negative and positive energy?[edit]
24. What is the mechanism of formation of negative and positive energy from nothing?[edit]
25. How does the Laws of Physics originate?[edit]
BIG BANG THEORY[edit]
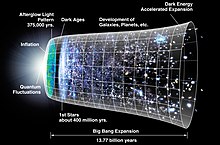
26. What was the form of matter before Big bang? How did that matter form?[edit]
27. Which force infinitely condensed that material? What was the source of that force?[edit]
28. How is it possible to have any type of exchange process in zero volume?[edit]
29. Modern science considers the exchange of certain mediator particles for the cause of all the fundamental forces, then which particles were exchanged in that infinitely dense material?[edit]
30. Which energy or force is responsible to do that great explosion, even in the presence of such a most strong force?[edit]
31. What are causes the inflation?[edit]
32. If inflation is due to anti-gravity, then what causes gravity to act as anti-gravity?[edit]
33. When and how inflation field created and what is its source?[edit]
34. How does symmetry break and what is its cause?[edit]
35. Is there any other forces in universe responsible for symmetry breaking?[edit]
36. What is the mechanism of separation of four fundamental forces?[edit]
37. How did they originate?[edit]
38. In which form, energy was present before second?[edit]

39. If it was in the form of photons, then electromagnetic force must be present at that time, but no one accept this, why?[edit]
40. Gravitational fierce is produced firstly from unified force, while Einstein proposed that gravitational force is not a force but only curvature of space-time what exactly is gravitational force?[edit]
TIME[edit]
41. What is time?[edit]

42. How does time originate?[edit]
43. How does it begin at the time of Big Bang?[edit]
44. Is the time an illusion or some real entity?[edit]
45. What is its role in the universe?[edit]
46. What we mean by negative and zero time?[edit]
47. Unless we know its true nature, how can we say that it will be negative or zero?[edit]
SPACE[edit]

48. What is Space?[edit]
49. What is its role in the universe?[edit]
50. Scientists consider and show space like a sheet or net, but nobody knows what really its structure is?[edit]
51. What is the mechanism of its formation?[edit]

52. Is space a real thing, which bends by a massive object, in which ripples are produced and which expands and distorts?[edit]
53. What are its contents?[edit]
54. Why does space interact with massive and charged objects/[edit]
55. What is the relation between space and mass/charge?[edit]
56. Is there availability of mass and charge in space?[edit]
57. We talk of space-time singularity but what is relation between space and time and why?[edit]
58. If space is an imaginary thing, then its expansion, distortion, bending and singularity also should be imaginary, then how can we understand the real world by imaginary things?[edit]
RED SHIFT ADN CMB[edit]
59. Are the EM waves are attached with space?[edit]
60. If yes then wave will not have its own speed, but it will travel with the speed of space, which will be Hubble speed in present time.[edit]
61. At the time of Big Bang, all energy will travel with space ( m/s). Then, how can energy be condensed to form the celestial bodies?[edit]
62. Are all celestial bodies and particles also attached with space? If yes, then they will never combine with one another and they will travel with speed of space only.[edit]

63. If EM wave isn't attached with space, then what is the cause of redshift?[edit]
64. Expansion of space can only affect waves not molecules, atoms etc., why?[edit]
65. Why expansion of space can only affect galaxies and not the stars, planets & satellites?[edit]
66. CMB radiation, which was released before 13 Billion years, then how can it be received by us now, while universe is expanding with an accelerated rate?[edit]
67. If this radiation is continuously received by us, then its temperature cannot be same everywhere in the universe.[edit]
ELEMENTARY PARTICLES[edit]

68. How do Graviton or other mediator particles form?[edit]
69. How do Photons and elementary particles form in the primary stage of the universe?[edit]
70. What is their structure?[edit]
71. Why Gravitation force is weakest force?[edit]
MASS[edit]

72. What exactly the Mass is?[edit]
73. How does property of Mass originate?[edit]
74. If answer is Higgs fields, then what is the cause of mass of it's quanta (Higgs Boson ~ GeV/)?[edit]
75. If we say that this mass is created from energy at the time of Big Bang, then question arises that if a very massive particle (Higgs boson) can be produced by that energy, then why an electron of exceedingly small mass can't be produced from that energy?[edit]
CHARGE[edit]
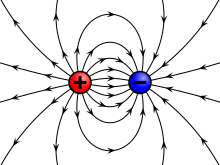
76. What is the fundamental cause of showing property of charge by matter?[edit]
77. If it is created from energy (pair production), then does it not mean that photon has same content as of electron and positron?[edit]
78. What are those fundamental entities, from which property of charge originates?[edit]
79. What is the link between energy and charge?[edit]
80. If Peter Higgs imagined Higgs field for fundamental property like mass, then why I should not imagine another field for fundamental property like electric charge?[edit]

81. Also, for different types of charge ( color charge...), there should be different types of field. Will you accept it?[edit]
82. What is the difference between the contents of opposite charged particles?[edit]
83. Why do virtual photons exchange between the charges, when these are massless and have no electric charge?[edit]
84. Why these photons cannot be seen or detected?[edit]
85. Why they exist for a short time?[edit]

86. Which force is responsible for this exchange?[edit]
87. What does an electric field consist of?[edit]
88. How charged particle creates an electric field?[edit]
89. What is the form of vacuum energy and how does it originate?[edit]
90. What is the mechanism of origin of field particle from vacuum energy?[edit]
91. What is the mechanism of attraction of two opposite charged particles through the exchange of field particles?[edit]
ENERGY ADN DARK ENERGY[edit]




