Waterline length
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (August 2013) |
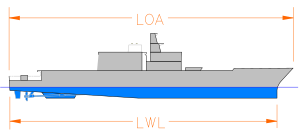

The waterline length (originally Load Waterline Length, abbreviated to LWL) is the length of a ship or boat at the point where it sits in the water. It excludes the total length of the boat, such as features that are out of the water. Most boats rise outwards at the bow and stern, so a boat may be quite a bit longer than its waterline length. In a ship with such raked stems, naturally the waterline length changes as the draft of the ship changes, therefore it is measured from a defined loaded condition.
Length at the waterline is often abbreviated as lwl, w/l, w.l. or wl.
This measure is essential in determining a lot of properties of a vessel, such as how much water it displaces, where the bow and stern waves are, hull speed, amount of bottom-paint needed, etc.
In sailing boats, longer waterline length will usually enable a greater maximum speed, because it allows greater sail area, without increasing beam or draft. Higher beam and draft causes higher resistance against the water. This maximum speed, also known as theoretical hull speed, can be calculated using the formula (sqrt of LWL) x 1.34.
See also
References
- Hayler, William B.; Keever, John M. (2003). American Merchant Seaman's Manual. Cornell Maritime Pr. ISBN 0-87033-549-9.
- Turpin, Edward A.; McEwen, William A. (1980). Merchant Marine Officers' Handbook (4th ed.). Centreville, MD: Cornell Maritime Press. ISBN 0-87033-056-X.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help)
