Mummies of Guanajuato
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2016) |
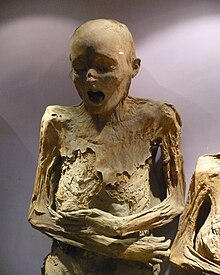
The Mummies of Guanajuato are a number of naturally mummified bodies originally interred in Guanajuato, Mexico.
The human bodies appear to have been disinterred between 1870 and 1958. During that time, a local tax was in place requiring a fee to be paid for "perpetual" burial. Some bodies for which the tax was not paid were disinterred, and some—apparently those in the best condition—were stored in a nearby building. The climate of Guanajuato provides an environment which can lead to a type of natural mummification, although scientific studies later revealed that some bodies had been at least partially embalmed.[1] By the 1900s[citation needed] the mummies began attracting tourists. Cemetery workers began charging people a few pesos to enter the building where bones and mummies were stored.[not verified in body]
This place was subsequently turned into a museum called El Museo de las Momias ("The Museum of the Mummies") in 1969. As of 2007, 59 mummies were on display, of a collection that totals 111.[1]
History
[edit]The mummies began to be exhumed from a Guanajuato cemetery when a law was enacted locally requiring families to pay a 'burial tax' to ensure the perpetual burial of a loved one. If the tax was not paid, the body was removed. Being naturally mummified, they were stored in a building above ground, and people began paying to see the bodies in the late 1800s. The law requiring the burial tax was abolished in 1958."[1]
As of 2006, this museum continued to exhibit 59 of the total of 111 mummies in the collection.[1][2] Some of the mummies have been exhibited in the United States.[3]
The maintenance of the mummies is the subject of a long-running dispute between the local government of Guanajuato, which has jurisdiction over the mummies, and the Instituto Nacional de Antropología e Historia (INAH), which insists on taking over the administration of the mummies as part of the national patrimony. In 2023, INAH warned that displaying the mummies in traveling exhibitions could pose a public health risk after one of the corpses appeared to have fungal growths. In 2024, INAH accused local authorities of mismanagement after an arm belonging to a mummified corpse fell off during renovations at the museum.[3]
Origin
[edit]
Due to the demands of the 1829–51 cholera pandemic, more cemeteries had to be created in San Cayetano and Cañada de Marfil. Many of the bodies were buried immediately to control the spread of the disease. It is thought that in some cases, the dying may have been buried alive by accident, resulting in horrific facial expressions. However, perceived facial expressions are most often the result of postmortem processes. One of the mummies who was buried alive was Ignacia Aguilar. She suffered from a strange sickness that made her heart appear to stop on several occasions. During one of these incidents, her heart appeared to stop for more than a day. Thinking she had died, her relatives decided to bury her. When her body was disinterred, it was noticed that she was facing down, biting her arm, and that there was a lot of blood in her mouth.[citation needed]

The first mummy was put on display in 1865. It was the body of Dr. Remigio Leroy. The museum, containing at least 108 corpses,[when?] is located above the spot where the mummies were first discovered. Numerous mummies can be seen throughout the exhibition, of varying sizes. The museum is known to have the smallest mummy in the world, a fetus from a pregnant woman who fell victim to cholera. Some of the mummies can be seen wearing parts of the clothing in which they were buried.[citation needed]
The mummies are a notable part of Mexican popular culture, echoing the national holiday "The Day of the Dead" (El Día de los Muertos). A B movie titled Santo vs. The Mummies of Guanajuato (1970) pitted the well-known Mexican professional wrestler Santo and several others against reanimated mummies.
Author Ray Bradbury visited the catacombs of Guanajuato with his friend Grant Beach[4] and wrote the short story "The Next in Line" about his experience. In the introduction to The Stories of Ray Bradbury he wrote the following about this story: "The experience so wounded and terrified me, I could hardly wait to flee Mexico. I had nightmares about dying and having to remain in the halls of the dead with those propped and wired bodies. In order to purge my terror, instantly, I wrote 'The Next in Line.' One of the few times that an experience yielded results almost on the spot."[5]
To conjure a morbid and eerie atmospheric opening sequence to his film Nosferatu the Vampyre (1979), German director Werner Herzog used footage he had taken of several of the mummies.
Other mummies
[edit]Other locations in Mexico where the mummification process occurs naturally include:
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Ann Friou (2007-08-30). "Professor unravels secrets of Guanajuato mummies". Texas State University News Service. Retrieved 2023-04-06.
- ^ Guanajuato Mummies at mummytombs.com Archived August 21, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b "Mexican government says the arm of a 19th century mummy came off after mishandling by museum staff". Associated Press. 28 May 2024. Retrieved 28 May 2024.
- ^ Page xxi of the introduction entitled "Dark Carnival Revisited" from the special Gauntlet Publications edition of Dark Carnival. Springfield, Pennsylvania: Gauntlet Publications, 2001.
- ^ Page xvii of the introduction entitled "Drunk, and in Charge of a Bicycle," from The Stories of Ray Bradbury, New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 1980.
