Poziotinib
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
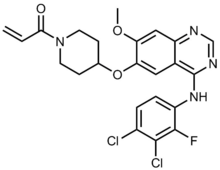
| Formula | C23H21Cl2FN4O3 |
| Molar mass | 491.34 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Poziotinib (NOV120101, HM781-36B)[1] is a drug in development by Hanmi Pharmaceutical (in South Korea), Luye Pharma (China), and Spectrum Pharmaceuticals (rest of world) for various cancers.[2]
It is built on an anilino-quinazoline scaffold and inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptors EGFR, HER2/neu, and Her 4[3] and binds covalently to its targets.[4]
It was discovered at Hanmi; in August 2014 Hanmi exclusively licensed rights in China to the Chinese company Luye Pharma and in February 2015 Hanmi licensed rights in the rest of the world outside of South Korea to Spectrum.[2]
As of 2016 Spectrum had started a Phase II trial of poziotinib a second-line treatment for breast cancer.[2]
References[edit]
- ^ "Poziotinib". AdisInsight. Retrieved 25 March 2017.
- ^ a b c Kim M (4 July 2016). "Hanmi Pharmaceutical to Step Up R&D Investment to Further Develop Core Technologies". BusinessKorea.
- ^ Roskoski R (September 2014). "ErbB/HER protein-tyrosine kinases: Structures and small molecule inhibitors". Pharmacological Research. 87: 42–59. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2014.06.001. PMID 24928736.
- ^ "Poziotinib". NCI Drug Dictionary. National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Retrieved 25 March 2017.
