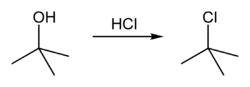
tert-Butyl chloride
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-chloro-2-methylpropane
| |||
| Other names
1,1-dimethylethyl chloride
1-chloro-1,1-dimethylethane chlorotrimethylmethane trimethylchloromethane t-butyl chloride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.334 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UN number | 1127 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H9Cl | |||
| Molar mass | 92.57 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.84 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | −26 °C (−15 °F; 247 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 51 °C (124 °F; 324 K) | ||
| Sparingly sol in water, miscible with alcohol and ether | |||
| Vapor pressure | 34.9 kPa (20 °C) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −9 °C (open cup) −23 °C (closed cup) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
tert-Butyl chloride is a colorless, liquid organic compound at room temperature. It is sparingly soluble in water, with a tendency to undergo spontaneous solvolysis when dissolved into it. The compound is flammable and volatile, and its main use is as a starting molecule to carry out nucleophilic substitution reactions, to produce different substances, ranging from alcohols to alkoxide salts.
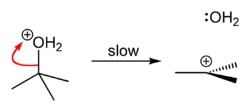
When tert-butyl chloride is dissolved in water, a polar and protic solvent, the bulky chloride substituent is carried away by it, and isolated from the aliphatic chain, causing an heterolytic rupture of the compound, giving rise to a carbocation which eventually becomes a tertiary alcohol after a water molecule reacts with it, releasing hydrochloric acid as the final product. If a different, stronger nucleophilic agent is present at the moment of reaction, reaction product may not be an alcohol, but a tertiary carbon with the nucleophile as a substituent.
Synthesis
tert-Butyl chloride can be synthesized in the laboratory by the SN1 reaction of tert-Butanol with concentrated hydrochloric acid, as shown below.
 |
 |
 |
The overall reaction, therefore, is:
Because tert-butanol is a tertiary alcohol, the relative stability of the tert-butyl carbocation in the Step 2 allows the SN1 mechanism to be followed, whereas a primary alcohol would follow an SN2 mechanism.