Administrative divisions of East Germany: Difference between revisions
Added two sources and added refimprove issue |
Added sources and fixed NPOV |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''administrative divisions of the [[German Democratic Republic]]''' (commonly |
The '''administrative divisions of the [[German Democratic Republic]]''' (commonly referred to as East Germany) were constituted in two different forms during the country's history. The GDR first retained the traditional German division into [[federated state]]s called ''Länder'', but in 1952 they were replaced with districts called ''Bezirke''. Immediately before [[German reunification]] in 1990, the ''Länder'' were restored, but they were not effectively reconstituted until after reunification had completed. |
||
== Division into ''Länder'' == |
== Division into ''Länder'' == |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
===General background=== |
===General background=== |
||
[[Image:Deutschland Bundeslaender 1949.png|thumb|150px|The GDR (in red) with its original ''Länder''.]] |
[[Image:Deutschland Bundeslaender 1949.png|thumb|150px|The GDR (in red) with its original ''Länder''.]] |
||
In May 1945, following its defeat in [[World War II]], Germany was occupied by the [[United States]], [[United Kingdom|Britain]], [[France]] and the [[Soviet Union]]. All four occupation powers |
In May 1945, following its defeat in [[World War II]], Germany was occupied by the [[United States]], [[United Kingdom|Britain]], [[France]] and the [[Soviet Union]]. All four occupation powers reorganised the territories by creating the ''[[States of Germany|Länder]]'', the constituting parts of federal Germany. The state of [[Prussia]], whose provinces extended to all four zones and covered two thirds of Germany, was dissolved in 1947.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=0O6ZaLEn-b0C&pg=PA3&dq=prussia+1947&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiQs9nI957TAhXELMAKHa2mANoQ6AEINzAD#v=onepage&q=prussia%201947&f=false|title=Weimar Prussia, 1918–1925: The Unlikely Rock of Democracy|last=Orlow|first=Dietrich|date=1986-12-15|publisher=University of Pittsburgh Pre|year=|isbn=9780822976400|location=|pages=3|language=en}}</ref> |
||
Special conditions were assigned to [[Berlin]], which the four powers divided into four sectors. A united German state government existed in the city until it broke apart in 1948. After 1949, both [[West Berlin]] and [[East Berlin]] (officially only called Berlin) were in effect incorporated into the [[West Germany|Federal Republic of Germany]] and the German Democratic Republic, respectively, despite not legally being part of these countries. |
Special conditions were assigned to [[Berlin]], which the four powers divided into four sectors. A united German state government existed in the city until it broke apart in 1948. After 1949, both [[West Berlin]] and [[East Berlin]] (officially only called Berlin) were in effect incorporated into the [[West Germany|Federal Republic of Germany]] and the German Democratic Republic, respectively, despite not legally being part of these countries. |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
*[[Brandenburg]] was created out of the major part of the Prussian province of that name |
*[[Brandenburg]] was created out of the major part of the Prussian province of that name |
||
*[[Mecklenburg-Vorpommern]] was created out of the state of [[Mecklenburg]] (reunited out of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz only in 1934) and the [[Western Pomerania|Western parts]] of the Prussian [[Province of Pomerania (1815–1945)|province of Pomerania]] |
*[[Mecklenburg-Vorpommern]] was created out of the state of [[Mecklenburg]] (reunited out of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz only in 1934) and the [[Western Pomerania|Western parts]] of the Prussian [[Province of Pomerania (1815–1945)|province of Pomerania]] |
||
*[[Saxony]] (''Sachsen'') was restored but augmented by the westernmost parts of the Prussian [[province of Lower Silesia]]. Also, the town of |
*[[Saxony]] (''Sachsen'') was restored but augmented by the westernmost parts of the Prussian [[province of Lower Silesia]]. Also, the town of [[Bogatynia|Reichenau]] was ceded to [[Poland]]. |
||
*[[Saxony-Anhalt]] (''Sachsen-Anhalt'') was created out of the most of the Prussian [[Province of Saxony]] and the [[Free State of Anhalt]] |
*[[Saxony-Anhalt]] (''Sachsen-Anhalt'') was created out of the most of the Prussian [[Province of Saxony]] and the [[Free State of Anhalt]] |
||
*[[Thuringia]] (''Thüringen'') was restored in the borders of 1944, when it had been augmented by neighbouring parts from the Prussian provinces of [[Province of Saxony|Saxony]] and [[Hesse-Nassau]]. |
*[[Thuringia]] (''Thüringen'') was restored in the borders of 1944, when it had been augmented by neighbouring parts from the Prussian provinces of [[Province of Saxony|Saxony]] and [[Hesse-Nassau]]. |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
As a nod to the [[legal fiction]] that East Berlin was still occupied territory, it was neither counted as part of Brandenburg, nor as a state in its own right. |
As a nod to the [[legal fiction]] that East Berlin was still occupied territory, it was neither counted as part of Brandenburg, nor as a state in its own right. |
||
East Germany claimed East Berlin as its capital, a status recognised by virtually all |
East Germany claimed East Berlin as its capital, a status recognised by virtually all Eastern Bloc countries. However, most Western Bloc countries did not recognise this. |
||
== Division into ''Bezirke'' == |
== Division into ''Bezirke'' == |
||
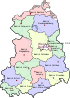
[[Image:DDR Verwaltungsbezirke farbig.svg|thumb|150px|''Bezirke'' of the GDR, 1952-1990.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=vrAcBQAAQBAJ&pg=PR18&dq=german+democratic+republic+bezirke&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwj45ffAnZ3TAhWnAcAKHbt_CPsQ6AEIJTAA#v=onepage&q=german%20democratic%20republic%20bezirke&f=false|title=The German Democratic Republic|last=Grieder|first=Peter|date=2012-11-02|publisher=Palgrave Macmillan|year=|isbn=9780230356863|location=|pages=xviii|language=en}}</ref>]] |
[[Image:DDR Verwaltungsbezirke farbig.svg|thumb|150px|''Bezirke'' of the GDR, 1952-1990.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=vrAcBQAAQBAJ&pg=PR18&dq=german+democratic+republic+bezirke&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwj45ffAnZ3TAhWnAcAKHbt_CPsQ6AEIJTAA#v=onepage&q=german%20democratic%20republic%20bezirke&f=false|title=The German Democratic Republic|last=Grieder|first=Peter|date=2012-11-02|publisher=Palgrave Macmillan|year=|isbn=9780230356863|location=|pages=xviii|language=en}}</ref>]] |
||
On 23 July 1952, a law combined the GDR's municipal districts (''[[Districts of Germany|Kreis]]e'') into regional districts (''[[Bezirk]]e''), and subsequently, on 25 July 1952, the state governments transferred their administrative tasks to the new districts. |
On 23 July 1952, a law combined the GDR's municipal districts (''[[Districts of Germany|Kreis]]e'') into regional districts (''[[Bezirk]]e''), and subsequently, on 25 July 1952, the state governments transferred their administrative tasks to the new districts.<ref name=":0">{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=tDm8BAAAQBAJ&pg=PA70&dq=L%C3%A4nder+bezirke+1952+Deutsche+demokratische+republik&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwishNbj9Z7TAhWrCsAKHb-YACg4ChDoAQg-MAM#v=onepage&q=L%C3%A4nder%20bezirke%201952%20Deutsche%20demokratische%20republik&f=false|title=Die sächsische FDP seit 1990: Auf dem Weg zur etablierten Partei?|last=Illing|first=Falk|date=2014-10-07|publisher=Springer-Verlag|year=|isbn=9783658046576|location=|pages=71|language=de}}</ref> |
||
With this law, the ''Länder'' were in effect dissolved. While they formally remained in existence, they no longer had any political or administrative function. The ''Länderkammer'' also remained in existence and its members were elected in 1954 by combined sessions of the ''Bezirkstage'' (district assemblies) in each ''Land'' and in 1958 directly by the ''Bezirkstage''. However, on 8 December 1958, the ''Länderkammer'' was formally dissolved and the states abolished with no objections being raised. |
With this law, the ''Länder'' were in effect dissolved. While they formally remained in existence, they no longer had any political or administrative function. The ''Länderkammer'' also remained in existence and its members were elected in 1954 by combined sessions of the ''Bezirkstage'' (district assemblies) in each ''Land'' and in 1958 directly by the ''Bezirkstage''. However, on 8 December 1958, the ''Länderkammer'' was formally dissolved and the states abolished with no objections being raised. |
||
| Line 117: | Line 117: | ||
[[File:Germany Laender 1947 1990 DDR.png|thumb|The reconstituted ''Länder'' in 1990, with borders in red. The purple borders show the original borders pre-1952.]] |
[[File:Germany Laender 1947 1990 DDR.png|thumb|The reconstituted ''Länder'' in 1990, with borders in red. The purple borders show the original borders pre-1952.]] |
||
On 23 August 1990 — just over a month before [[German reunification]] on 3 October — East Germany [[New states of Germany|reconstituted the five original ''Länder'']]. In theory, it was these ''Länder'' that then ascended to the [[West Germany|Federal Republic of Germany]]. |
On 23 August 1990 — just over a month before [[German reunification]] on 3 October — East Germany [[New states of Germany|reconstituted the five original ''Länder'']]. In theory, it was these ''Länder'' that then ascended to the [[West Germany|Federal Republic of Germany]].<ref name=":0" /> |
||
The restored ''Länder'' did not fully reconstitute themselves until after reunification. On 14 October 1990, elections to the ''Landtage'' (state parliaments) were held in the five new states, initiating the formation of state governments. |
The restored ''Länder'' did not fully reconstitute themselves until after reunification. On 14 October 1990, elections to the ''Landtage'' (state parliaments) were held in the five new states, initiating the formation of state governments. |
||
Revision as of 12:46, 12 April 2017
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2017) |
The administrative divisions of the German Democratic Republic (commonly referred to as East Germany) were constituted in two different forms during the country's history. The GDR first retained the traditional German division into federated states called Länder, but in 1952 they were replaced with districts called Bezirke. Immediately before German reunification in 1990, the Länder were restored, but they were not effectively reconstituted until after reunification had completed.
Division into Länder
General background

In May 1945, following its defeat in World War II, Germany was occupied by the United States, Britain, France and the Soviet Union. All four occupation powers reorganised the territories by creating the Länder, the constituting parts of federal Germany. The state of Prussia, whose provinces extended to all four zones and covered two thirds of Germany, was dissolved in 1947.[1]
Special conditions were assigned to Berlin, which the four powers divided into four sectors. A united German state government existed in the city until it broke apart in 1948. After 1949, both West Berlin and East Berlin (officially only called Berlin) were in effect incorporated into the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic, respectively, despite not legally being part of these countries.
Länder in East Germany
In the Soviet occupation zone, five Länder were established which roughly corresponded to the preexisting states and provinces. (The territories east of the Oder–Neisse line had been transferred from the Soviet occupation zone to the Polish authorities as agreed upon at the Potsdam Conference.) The five states were:
- Brandenburg was created out of the major part of the Prussian province of that name
- Mecklenburg-Vorpommern was created out of the state of Mecklenburg (reunited out of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz only in 1934) and the Western parts of the Prussian province of Pomerania
- Saxony (Sachsen) was restored but augmented by the westernmost parts of the Prussian province of Lower Silesia. Also, the town of Reichenau was ceded to Poland.
- Saxony-Anhalt (Sachsen-Anhalt) was created out of the most of the Prussian Province of Saxony and the Free State of Anhalt
- Thuringia (Thüringen) was restored in the borders of 1944, when it had been augmented by neighbouring parts from the Prussian provinces of Saxony and Hesse-Nassau.
In 1949, the Soviet occupation zone was transformed into the German Democratic Republic. The five Länder (and East Berlin, though the latter only with consultative votes) participated in the legislative branch through the Länderkammer (Chamber of States), which was elected by the Landtage (state parliaments). However, the Länder were not constituting entities forming a federal state (as in West Germany) but rather decentralised administrative entities of a quasi-unitary state.
As a nod to the legal fiction that East Berlin was still occupied territory, it was neither counted as part of Brandenburg, nor as a state in its own right. East Germany claimed East Berlin as its capital, a status recognised by virtually all Eastern Bloc countries. However, most Western Bloc countries did not recognise this.
Division into Bezirke

On 23 July 1952, a law combined the GDR's municipal districts (Kreise) into regional districts (Bezirke), and subsequently, on 25 July 1952, the state governments transferred their administrative tasks to the new districts.[3]
With this law, the Länder were in effect dissolved. While they formally remained in existence, they no longer had any political or administrative function. The Länderkammer also remained in existence and its members were elected in 1954 by combined sessions of the Bezirkstage (district assemblies) in each Land and in 1958 directly by the Bezirkstage. However, on 8 December 1958, the Länderkammer was formally dissolved and the states abolished with no objections being raised.
The 14 new Bezirke were drawn without regard to the borders of the Länder and each named after their capitals, from north to south: Rostock, Neubrandenburg, Schwerin, Potsdam, Frankfurt (Oder), Magdeburg, Cottbus, Halle, Leipzig, Erfurt, Dresden, Karl-Marx-Stadt (named Chemnitz until 1953), Gera and Suhl.
Due to its special status, East Berlin was originally not counted as a Bezirk. In 1961, after the construction of the Berlin Wall, East Berlin came to be recognised in GDR administration as the Bezirk Berlin, though it retained a special status until the adoption of the revised 1968 Constitution.[4]
The Bezirke (with the exception of Berlin, which consisted of a single municipality) were subdivided into rural districts (Landkreise) and urban districts (Stadtkreise):
| Bezirk | subdivisions |
|---|---|
| Cottbus | Urban districts: Cottbus |
| Rural districts: Bad Liebenwerda · Calau · Cottbus-Land · Finsterwalde · Forst · Guben (Wokrejs Gubin) · Herzberg · Hoyerswerda · Jessen · Luckau · Lübben · Senftenberg · Spremberg · Weißwasser | |
| Dresden | Urban districts: Dresden · Görlitz |
| Rural districts: Bautzen · Bischofswerda · Dippoldiswalde · Dresden-Land · Freital · Görlitz-Land · Großenhain · Kamenz · Löbau · Meißen · Niesky · Pirna · Riesa · Sebnitz · Zittau | |
| Erfurt | Urban districts: Erfurt · Weimar |
| Rural districts: Apolda · Arnstadt · Eisenach · Erfurt-Land · Gotha · Heiligenstadt · Langensalza · Mühlhausen · Nordhausen · Sömmerda · Sondershausen · Weimar-Land | |
| Frankfurt (Oder) | Urban districts: Frankfurt (Oder) · Eisenhüttenstadt · Schwedt/Oder |
| Rural districts: Angermünde · Bad Freienwalde · Beeskow · Bernau · Eberswalde · Eisenhüttenstadt · Fürstenwalde · Seelow · Strausberg | |
| Gera | Urban districts: Gera · Jena |
| Rural districts: Eisenberg · Gera-Land · Greiz · Jena · Lobenstein · Pößneck · Rudolstadt · Saalfeld · Schleiz · Stadtroda · Zeulenroda | |
| Halle | Urban districts: Halle · Dessau · Halle-Neustadt (since 12 May 1967) |
| Rural districts: Artern · Aschersleben · Bernburg · Bitterfeld · Eisleben · Gräfenhainichen · Hettstedt · Hohenmölsen · Köthen · Merseburg · Naumburg · Nebra · Quedlinburg · Querfurt · Roßlau · Saalkreis · Sangerhausen · Weißenfels · Wittenberg · Zeitz | |
| Karl-Marx-Stadt | Urban districts: Karl-Marx-Stadt · Plauen · Zwickau · Johanngeorgenstadt (until 1957) · Schneeberg (until 1958) |
| Rural districts: Annaberg · Aue · Auerbach · Brand-Erbisdorf · Flöha · Freiberg · Glauchau · Hainichen · Hohenstein-Ernstthal · Karl-Marx-Stadt-Land · Klingenthal · Marienberg · Oelsnitz · Plauen-Land · Reichenbach · Rochlitz · Schwarzenberg · Stollberg · Werdau · Zschopau · Zwickau-Land | |
| Leipzig | Urban districts: Leipzig |
| Rural districts: Altenburg · Borna · Delitzsch · Döbeln · Eilenburg · Geithain · Grimma · Leipzig-Land · Oschatz · Schmölln · Torgau · Wurzen | |
| Magdeburg | Urban districts: Magdeburg |
| Rural districts: Burg · Gardelegen · Genthin · Halberstadt · Haldensleben · Havelberg · Kalbe (Milde) (until December 1987) · Klötze · Loburg (until June 1957) · Oschersleben · Osterburg · Salzwedel · Schönebeck · Seehausen (until July 1965) · Staßfurt · Stendal · Tangerhütte (until December 1987) · Wanzleben · Wernigerode · Wolmirstedt · Zerbst | |
| Neubrandenburg | Urban districts: Neubrandenburg (from January 1969) |
| Rural districts: Altentreptow · Anklam · Demmin · Malchin · Neubrandenburg-Land · Neustrelitz · Pasewalk · Prenzlau · Röbel/Müritz · Strasburg · Templin · Teterow · Ueckermünde · Waren | |
| Potsdam | Urban districts: Potsdam · Brandenburg an der Havel |
| Rural districts: Belzig · Brandenburg · Gransee · Jüterbog · Königs-Wusterhausen · Kyritz · Luckenwalde · Nauen · Neuruppin · Oranienburg · Potsdam · Pritzwalk · Rathenow · Wittstock · Zossen | |
| Rostock | Urban districts: Rostock · Greifswald (from January 1974) · Stralsund · Wismar |
| Rural districts: Bad Doberan · Greifswald Land · Grevesmühlen · Grimmen · Ribnitz-Damgarten · Rostock-Land · Rügen · Stralsund · Wismar · Wolgast | |
| Schwerin | Urban districts: Schwerin |
| Rural districts: Bützow · Gadebusch · Güstrow · Hagenow · Ludwigslust · Lübz · Parchim · Perleberg · Schwerin-Land · Sternberg | |
| Suhl | Urban districts: Suhl |
| Rural districts: Bad Salzungen · Hildburghausen · Ilmenau · Meiningen · Neuhaus · Schmalkalden · Sonneberg · Suhl-Land |
Reconstitution of the Länder

On 23 August 1990 — just over a month before German reunification on 3 October — East Germany reconstituted the five original Länder. In theory, it was these Länder that then ascended to the Federal Republic of Germany.[3]
The restored Länder did not fully reconstitute themselves until after reunification. On 14 October 1990, elections to the Landtage (state parliaments) were held in the five new states, initiating the formation of state governments.
Since changes to the boundaries of municipal districts were not reversed, and also due to considerations of expediency, the territorial make-up of the restored Länder differed somewhat from the borders prior to 1952.
Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt initially retained the rural and urban districts as administrative entities (Regierungsbezirke). Saxony-Anhalt later abolished them in 2003, while Saxony transformed them into directorates in 2008.
References
- ^ Orlow, Dietrich (1986-12-15). Weimar Prussia, 1918–1925: The Unlikely Rock of Democracy. University of Pittsburgh Pre. p. 3. ISBN 9780822976400.
- ^ Grieder, Peter (2012-11-02). The German Democratic Republic. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. xviii. ISBN 9780230356863.
- ^ a b Illing, Falk (2014-10-07). Die sächsische FDP seit 1990: Auf dem Weg zur etablierten Partei? (in German). Springer-Verlag. p. 71. ISBN 9783658046576.
- ^ Horváth, Gyula (2014-08-21). Spaces and Places in Central and Eastern Europe: Historical Trends and Perspectives. Routledge. p. 109. ISBN 9781317917540.
External links
![]() Media related to Districts of the German Democratic Republic at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Districts of the German Democratic Republic at Wikimedia Commons