Diisopromine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.025.230 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
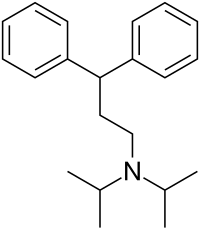
| Formula | C21H29N |
| Molar mass | 295.462 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Diisopromine or disoprominum, usually as the hydrochloride salt, is a synthetic spasmolytic which neutralizes spastic conditions of the biliary tract and of the sphincter of Oddi. It was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1955. It is sold in South Africa under the brand name Agofell syrup as a mixture with sorbitol,[1] and elsewhere as Megabyl.[2]
See also
References
- ^ "AGOFELL® Syrup". South African electronic package inserts. Retrieved 2 September 2015.
- ^ "Guide des medicaments". Doctissimo. Retrieved 2 September 2015.
