Northrop YA-13
| YA-13 /XA-16 | |
|---|---|
| |
| YA-13 | |
| Role | Attack aircraft |
| National origin | United States Army Air Corps |
| Manufacturer | Northrop |
| Status | Prototype |
| Primary user | United States Army Air Corps |
| Number built | 1 |
| Developed from | Northrop Gamma |
The Northrop YA-13 was an attack version of the Northrop Gamma type aircraft. After receiving an engine change, the aircraft was redesignated XA-16.
Design and development
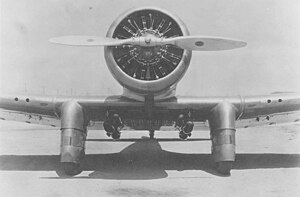
The Northrop Gamma 2C was a company funded demonstrator based on the Northrop Gamma 2A and 2B designs. These early designs were primarily designed as racers or for speed record attempts. The cockpits both of the 2A and 2B aircraft were far back on the fuselage near the tail, but for the Gamma 2C the cockpit was moved forward to a more conventional position. The Air Corps evaluated the Northrop Gamma 2C attack aircraft in mid-1933. Testing revealed the need for some modifications which were done in the first part of 1934. The aircraft was returned to the Army for testing at Wright Field in the summer of 1934. By this time, the Air Corps purchased the aircraft and designated it YA-13 and assigned it the serial number 34-27.
Further testing of the YA-13 revealed the aircraft to be underpowered and the Army recommended the aircraft be fitted with a more powerful engine. The original engine was a large diameter single-row radial engine, which partially obstructed the pilot's forward vision. The replacement engine, a twin-row radial, was more powerful and had a smaller diameter. The propeller was changed from a two-blade to three-blade type also.[1]
After the engine change was completed, the aircraft was returned to Wright Field for additional testing. The Air Corps followed standard practice and re-designated the aircraft XA-16 based on the engine change. Unfortunately, with the new more powerful engine, the aircraft went from being underpowered to overpowered.[2]
Northrop was developing another attack aircraft at this time in a more or less parallel development program. This aircraft was initially designated Gamma 2F and was based on an improved Gamma 2C design. This aircraft eventually became the A-17, the primary single engine attack aircraft used by the Army Air Corps during the late 1930s. With the success of the A-17, the YA-13/XA-16 program never progressed past the test phase.
Variants
- YA-13
- XA-16
Operators
Specifications (XA-16)

Data from [3]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 29 ft 8 in (9.04 m)
- Wingspan: 48 ft 0 in (14.63 m)
- Height: 9 ft 2 in (2.79 m)
- Max takeoff weight: 6,748 lb (3,061 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney R-1830-9 Twin Wasp, 950 hp (708 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 212 mph (341 km/h, 184 kn)
- Cruise speed: 195 mph (314 km/h, 170 kn)
- Range: 1,000 mi (1,609 km, 869 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 22,000 ft (6,706 m)
Armament
- Guns: 4 × forward firing .30 in (7.62 mm) M1919 Browning machine guns and 1 × flexible .30 in (7.62 mm) machine gun for the rear gunner
- Bombs: Provisions for up to 1,100 lb (500 kg) of bombs mounted on wing racks
See also
Related development
Related lists
