Persian Empire
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
This article is missing information about Error: you must specify what information is missing.. (March 2017) |
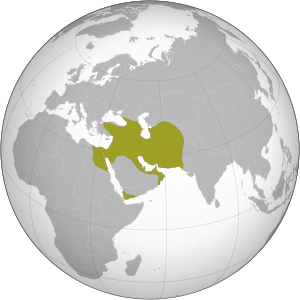
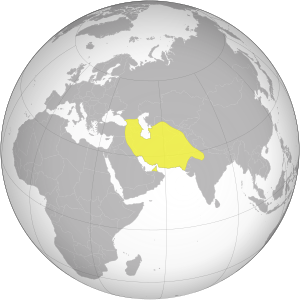
The Persian Empire (Persian: شاهنشاهی ایران, translit. shāhanshāhi-ye irān, lit. 'Imperial Iran') is one of a series of imperial dynasties centered in Iran (formerly known as Persia in the Western world until 1935). The first of these was the Achaemenid Empire established by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC with the conquest of Median, Lydian and Babylonian empires[1]. It covered much of the Ancient world when it was conquered by Alexander the Great. Persia was then ruled by the Parthian Empire which supplanted the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire, and then by the Sassanian Empire which ruled up until the mid-7th century.[2]
Iranian dynastic history was interrupted by the Arab conquest of Persia in 651 AD, establishing the even larger Islamic caliphate, and later by the Mongol invasion. The main religion of ancient Persia was the native Zoroastrianism, but after the seventh century, it was replaced by Islam.
The Safavid Empire was the first great Persian Empire established after Arab conquest of Persia by Shah Ismail I. From their base in Ardabil, the Safavid Persians established control over parts of Greater Iran and reasserted the Iranian identity of the region, thus becoming the first native Persian dynasty since the Sasanian Empire to establish a unified Iranian state.
List of Iranian dynasties described as a Persian Empire
- Achaemenid Empire (550–330 BC)
- Sasanian Empire (224–651)
- Safavid dynasty (1501–1736)
- Afsharid dynasty (1736–1796)
- Zand dynasty (1751-1794)
- Qajar dynasty (1785–1925)
- Pahlavi dynasty (1925–1979)
-
Extent of the first Persian Empire, the Achaemenid Empire -
Extent of the Sasanian Empire in 621 -
The maximum extent of the Safavid Empire under Shah Abbas I -
Extent of the Afsharid Empire under Nader Shah
See also
- List of monarchs of Persia
- Iranian monarchy
- List of Iranian dynasties and countries
- Persia
- Iranian peoples
- Persian people
- List of tombs of Iranian people
References
- ^ Herodotus. The Histories. Halicarnassus. ISBN 978-0143107545.
- ^ History of the World in 1,000 Objects (DK Publishing, 2014), p. 71.
External links
 Media related to Persian Empire at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Persian Empire at Wikimedia Commons Persian Empire travel guide from Wikivoyage
Persian Empire travel guide from Wikivoyage- . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.