User:Etabs1089/sandbox
Introduction[edit]

Methyltransferases are a large group of enzymes that all methylate their substrates but can be split into several subclasses based on their structural features. The most common class of methyltransferases is class I, all of which contain a Rossman fold for binding S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM). Class II methyltransferases contain a SET domain, which are exemplified by SET domain Histone methyltransferases, and class II methyltransferases, which are membrane associated. [1] Methyltransferases can also be grouped as different types utilizing different substrates in methyl transfer reactions. These types include Protein methyltransferases, DNA methyltransferases, Natural product methyltransferases, and Non-SAM dependent methyltransferases. SAM is the classical methyl donor for methyltrasferases, however, examples of other methyl donors are seen in nature. The general mechanism for methyl transfer is a SN2-like nucleophilic attack where the methionine sulfur serves as the nucleophile that transfers the methyl group to the enzyme substrate. SAM is converted to S-Adenosyl homocysteine (SAH) during this process. The breaking of the SAM-methyl bond and the formation of the substrate-methyl bond happen nearly simultaneously. These enzymatic reactions are found in many pathways and are implicated in genetic diseases, cancer, and metabolic diseases.
Function[edit]
Genetics[edit]
Regulation[edit]
Methylation of proteins has a regulatory role in protein-protein interactions, protein-DNA interactions, and protein activation.
Examples: RCC1, an important mitotic protein, is methylated so that it can interact with centromeres of chromosomes. This is an example of regulation of protein-protein interaction, as methylation regulates the attachment of RCC1 to histone proteins H2A and H2B. The RCC1-chromatin interaction is also an example of a protein-DNA interaction, as another domain of RCC1 interacts directly with DNA when this protein is methylated. When RCC1 is not methylated, dividing cells have multiple spindle poles and usually cannot survive.
p53 methylated on lysine to regulate its activation and interaction with other proteins in the DNA damage response. This is an example of regulation of protein-protein interactions and protein activation. p53 is a known tumor suppressor that activates DNA repair pathways, initiates apoptosis, and pauses the cell cycle. Overall, it responds to mutations in DNA, signaling to the cell to fix them or to initiate cell death so that these mutations cannot contribute to cancer.
NF-κB (a protein involved in inflammation) is a known methylation target of the methyltransferase SETD6, which turns off NF-κB signaling by inhibiting of one of its subunits, RelA. This reduces the transcriptional activation and inflammatory response, making methylation of NF-κB a regulatory process by which cell signaling through this pathway is reduced.[2]
Natural product methyltransferases provide a variety of inputs into metabolic pathways, including the availability of cofactors, signalling molecules, and metabolites. This regulates various cellular pathways by controlling protein activity.
Types[edit]
Histone Methyltransferases[edit]
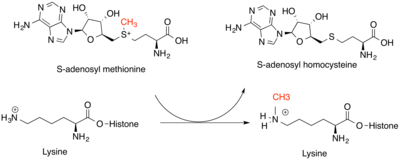
Histone methyltransferases are critical for genetic regulation at the epigenetic level. They modify mainly Lysine on the ε-nitrogen and the Arginine guanidinium group on histone tails. Lysine methyltransferases and Arginine methyltransferases are unique classes of enzymes, but both bind SAM as a methyl donor for their histone substrates. Lysine amino acids can be modified with one, two, or three methyl groups, while Arginine amino acids can be modified with one or two methyl groups. This increases the strength of the positive charge and residue hydrophobicity, allowing other proteins to recognize methyl marks. The effect of this modification depends on the location of the modification on the histone tail and the other histone modifications around it. The location of the modifications can be partially determined by DNA sequence, as well as small non-coding RNAs and the methylation of the DNA itself. Most commonly, it is histone H3 or H4 that is methylated in vertebrates. Either increased or decreased transcription of genes around the modification can occur. Increased transcription is a result of decreased chromatin condensation, while decreased transcription results from increased chromatin condensation.[3] Methyl marks on the histones contribute to these changes by serving as sites for recruitment of other proteins that can further modify chromatin.[4]
N-terminal Methyltransferases[edit]

N-alpha methyltransferases transfer a methyl group from SAM to the N-terminal nitrogen on protein targets. The N-terminal methionine is first cleaved by another enzyme and the X-Proline-Lysine consensus sequence is recognized by the methyltransferase. For all known substrates, the X amino acid is Alanine, Serine, or Proline. This reaction yields a methylated protein and SAH. Known targets of these methyltransferases in humans include RCC-1 (a regulator of nuclear transport proteins) and Retinoblastoma protein (a tumor suppressor protein that inhibits excessive cell division). RCC-1 methylation is especially important in mitosis as it coordinates the localization of some nuclear proteins in the absence of the nuclear envelope. When RCC-1 is not methylated, cell division is abnormal following the formation of extra spindle poles. [5]The function of Retinoblastoma protein N-terminal methylation is not known.
DNA Methyltransferases[edit]
Natural Product Methyltransferases[edit]

Natural product methyltransferases (NPMTs) are a bdiverse group of enzymes that add methyl groups to naturally-produced small molecules. Like many methyltransferases, SAM is utilized as a methyl donor and SAH is produced. Methyl groups are added to S, N, O, or C atoms, and are classified by which of these atoms are modified, with O-methyltransferases representing the largest class. The methylated products of these reactions serve a variety of functions, including co-factors, pigments, signalling compounds, and metabolites. NPMTs can serve a regulatory role by modifying the reactivity and availability of these compounds. These enzymes are not highly conserved across different species, as they serve a more specific function in providing small molecules for specialized pathways in species or smaller groups of species. Reflective of this diversity is the variety of catalytic strategies, including general acid-base catalysis, metal-based catalysis, and proximity and desolvation effects not requiring catalytic amino acids. NPMTs are the most functionally diverse class of methyltransferases. [6]
Important examples of this enzyme class in humans include Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT), which converts norepinephrine to epinephrine[7] , and Histamine N-methyltransferase (HNMT), which methylates histamine in the process of histamine metabolism.[8] Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) degrades a class of molecules known as catcholamines that includes dopamine, epinephrine, and norepenepherine.[9]
Non-SAM Dependent Methyltransferases[edit]
Clinical Significance[edit]
Further Reading[edit]
"The Role of Methylation in Gene Expression" on Nature Scitable
"Nutrition and Depression: Nutrition, Methylation, and Depression" on Psychology Today
"DNA Methylation - What is DNA Methylation?" from News-Medical.net
References[edit]
- ^ Katz, Jonathan E.; Dlakić, Mensur; Clarke, Steven (18 July 2003). "Automated identification of putative methyltransferases from genomic open reading frames". Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 2 (8): 525–540. doi:10.1074/mcp.M300037-MCP200. PMID 12872006. S2CID 16966511.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Levy, Dan; Kuo, Alex J.; Chang, Yanqi; Schaefer, Uwe; Kitson, Christopher; Cheung, Peggie; Espejo, Alexsandra; Zee, Barry M.; Liu, Chih Long; Tangsombatvisit, Stephanie; Tennen, Ruth I.; Kuo, Andrew Y.; Tanjing, Song; Cheung, Regina; Chua, Katrin F.; Utz, Paul J.; Shi, Xiaobing; Prinjha, Rab K.; Lee, Kevin; Garcia, Benjamin A.; Bedford, Mark T.; Tarakhovsky, Alexander; Cheng, Xiaodong; Gozani, Or (5 December 2010). "Lysine methylation of the NF-κB subunit RelA by SETD6 couples activity of the histone methyltransferase GLP at chromatin to tonic repression of NF-κB signaling". Nature Immunology. 12 (1): 29–36. doi:10.1038/ni.1968. PMC 3074206. PMID 21131967.
- ^ Turner, Bryan M. (2001). Chromatin and gene regulation : mechanisms in epigenetics. Malden, MA: Blackwell Science. ISBN 0865427437.
- ^ Greer, Eric L.; Shi, Yang (3 April 2012). "Histone methylation: a dynamic mark in health, disease and inheritance". Nature Reviews Genetics. 13 (5): 343–357. doi:10.1038/nrg3173. PMC 4073795. PMID 22473383.
- ^ Clarke, Paul (May 2007). "Anchoring RCC1 by the tail". Nature Cell Biology. 9 (5): 485–487. doi:10.1038/ncb0507-485. PMID 17473856. S2CID 711645.
- ^ Liscombe, David K.; Louie, Gordon V.; Noel, Joseph P. (2012). "Architectures, mechanisms and molecular evolution of natural product methyltransferases". Natural Product Reports. 29 (10): 1238. doi:10.1039/c2np20029e. PMID 22850796.
- ^ "PNMT phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase". NCBI Genetic Testing Registry. Retrieved 18 February 2014.
- ^ "HNMT histamine N-methyltransferase". NCBI Genetic Testing Registry. Retrieved 18 February 2014.
- ^ "COMT catechol-O-methyltransferase". NCBI Genetic Testing Registry. Retrieved 18 February 2014.

