Solar inverter: Difference between revisions
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
* Beacon Power |
* Beacon Power |
||
* [http://enphaseenergy.com Enphase Energy] |
* [http://enphaseenergy.com Enphase Energy] |
||
* Fronius IG |
* Fronius IG [http://www.dulas.org.uk/?id=253] |
||
* [http://www.deltaenergysystems.com Delta Energy Systems] |
* [http://www.deltaenergysystems.com Delta Energy Systems] |
||
* KACO Geraetetechnik GmbH |
* KACO Geraetetechnik GmbH |
||
Revision as of 16:44, 25 March 2009
A solar inverter is a type of electrical inverter that is made to change the direct current (DC) electricity from a photovoltaic array into alternating current (AC) for use with home appliances and possibly a utility grid.
Solar inverters may be classified into three broad types:
- Stand-alone inverters, used in isolated systems where the inverter draws its DC energy from batteries charged by photovoltaic arrays and/or other sources, such as wind turbines, hydro turbines, or engine generators. Many stand-alone inverters also incorporate integral battery chargers to replenish the battery from an AC source, when available. Normally these do not interface in any way with the utility grid, and as such, are not required to have anti-islanding protection.
- Grid-tie inverters, which match phase with a utility-supplied sine wave. Grid-tie inverters are designed to shut down automatically upon loss of utility supply, for safety reasons. They do not provide backup power during utility outages.
- Battery backup inverters. These are special inverters which are designed to draw energy from a battery, manage the battery charge via an onboard charger, and export excess energy to the utility grid. These inverters are capable of supplying AC energy to selected loads during a utility outage, and are required to have anti-islanding protection
Solar inverters use special procedures to deal with the PV array, including maximum power point tracking and anti-islanding protection.
Maximum power point tracking (MPPT)
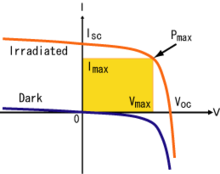
Maximum power point tracking is a technique that solar inverters use to get the most possible power from the PV array. Any given PV module or string of modules will have a maximum power point: essentially, this defines current that the inverter should draw from the PV in order to get the most possible power (power is equal to voltage times current).
Anti-islanding protection
Normally, grid-tied inverters will shut off if they do not detect the presence of the utility grid. If, however, there are load circuits in the electrical system that happen to resonate at the frequency of the utility grid, the inverter may be fooled into thinking that the grid is still active even after it had been shut down. This is called islanding.
An inverter designed for grid-tie operation will have anti-islanding protection built in; it will inject small pulses that are slightly out of phase with the AC electrical system in order to cancel any stray resonances that may be present when the grid shuts down.
Since 1999, the standard for anti-islanding protection in the United States has been UL 1741, harmonized with IEEE 1547. Any inverter which is listed to the UL 1741 standard may be connected to a utility grid without the need for additional anti-islanding equipment, anywhere in the United States or other countries where UL standards are accepted. [1]
Grid-tie inverters
Many solar inverters are designed to be connected to a utility grid, and will not operate when they do not detect the presence of the grid. They contain special circuitry to precisely match the voltage and frequency of the grid.
Charge controllers
Stand-alone inverters -- that is, inverters that are designed to be used without the presence of the electrical utility grid -- can be run from PV panels and batteries using a charge controller. The charge controller regulates the input from the PV and the batteries, regulates the battery output, and handles charging the batteries.
Manufacturers
- Advanced Energy
- Beacon Power
- Enphase Energy
- Fronius IG [1]
- Delta Energy Systems
- KACO Geraetetechnik GmbH
- OutBack Power Systems
- PV Powered
- SatCon Technologies
- SMA
- Selectronic Australia
- Solar Energy Australia
- Solectria Renewables
- Sputnik Engineering AG (www.Solarmax.com)
- Sunways AG
- Sustainable Energy Technologies
- Mastervolt
- Xantrex
