Cocaethylene: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
rv |
m minor formatting |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{drugbox |
{{drugbox |
||
| IUPAC_name = ethyl ( |
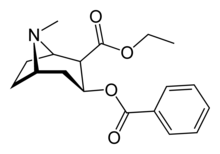
| IUPAC_name = ethyl (2''R'',3''S'')-3-benzoyloxy-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-2-carboxylate |
||
| image = Cocaethylene-2D-skeletal.png |
| image = Cocaethylene-2D-skeletal.png |
||
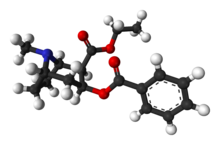
| image2 = Cocaethylene-3D-balls.png |
| image2 = Cocaethylene-3D-balls.png |
||
Revision as of 12:59, 5 November 2009
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | from prodrugs cocaine and ethanol |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.816 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H23NO4 |
| Molar mass | 317.38 g/mol g·mol−1 |
Cocaethylene is the ethyl ester of benzoylecgonine. It is chemically related to cocaine, which is the corresponding methyl ester. Cocaethylene is formed in the body when cocaine and alcohol have been taken simultaneously: the transesterification is catalysed by carboxylesterases in the liver. It does not occur naturally in coca leaves.
Cocaethylene produces a more euphoric stimulation than cocaine in most users, and is longer lasting in the body. Some studies suggest that it may have a higher cardiovascular toxicity than cocaine. Cocaethylene however is less potent at binding to serotonin and norepinephrine transporters than cocaine is.[1]
References
- ^ Therapeutic Drug Monitoring: August 1996 - Volume 18 - Issue 4 - pp 460-464 Proceedings Of The Fourth International Congress Of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring And Clinical Toxicology. Alcohol plus Cocaine: The Whole Is More Than the Sum of Its Parts. Jatlow, Peter; McCance, Elinore F.; Bradberry, Charles W.; Elsworth, John D.; Taylor, Jane R.; Roth, Robert H. © Lippincott-Raven Publishers
- M. J. Landry, J. Psychoactive Drugs 1992, 24, 273-6.
- M. Perez et al., Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 1994, 116, 428-32.,
- M. J. Landry, Behavioral Health Management 1994, September 1.
- S. C. Laizure et al., Drug Metabolism Disposition 2003, 31, 16-20.
