Decarboxylative cross-coupling: Difference between revisions
→sp3C Carboxylic Acids: Fix header |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Orphan|date=February 2013}} |
{{Orphan|date=February 2013}} |
||
Decarboxylative cross coupling reactions are chemical reactions in which a stable, substituted [[carboxylic acid]] is reacted with a halide ( |
Decarboxylative cross coupling reactions are chemical reactions in which a stable, substituted [[carboxylic acid]] is reacted with a halide (R–X, R=[[aryl]], [[alkane|alkyl]], etc.) in the presence of a metal [[catalysis|catalyst]], [[base (chemistry)|base]] and [[oxidizing agent|oxidant]] to form a new carbon-carbon bond (with loss of carbon dioxide). |
||
[[File:Decarboxylative Cross Coupling General Reaction Scheme.png|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Decarboxylative |
[[File:Decarboxylative Cross Coupling General Reaction Scheme.png|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Decarboxylative cross-coupling general reaction scheme]] |
||
A significant advantage of this reaction is that it uses relatively inexpensive [[carboxylic acid]]s (or their salts) and is far less air and moisture sensitive in comparison to typical cross-coupling organometallic reagents. Furthermore, the carboxylic acid moiety is a common feature of [[natural product]]s and can also be prepared by relatively benign air [[redox|oxidations]]. Additional benefits include the broad tolerance of [[functional group]]s, as well as the capacity to avoid the use of strong bases. An important elementary step in this reaction is [[decarboxylation|protodecarboxylation]] or metallation to first convert the |
A significant advantage of this reaction is that it uses relatively inexpensive [[carboxylic acid]]s (or their salts) and is far less air and moisture sensitive in comparison to typical cross-coupling organometallic reagents. Furthermore, the carboxylic acid moiety is a common feature of [[natural product]]s and can also be prepared by relatively benign air [[redox|oxidations]]. Additional benefits include the broad tolerance of [[functional group]]s, as well as the capacity to avoid the use of strong bases. An important elementary step in this reaction is [[decarboxylation|protodecarboxylation]] or metallation to first convert the C–COOH bond to a C–H or C–M bond respectively. |
||
<ref name=Shang>Shang R, Liu, L. Transition metal-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling reactions. ''Science China-Chemistry'', '''2011''', ''11'', 54: |
<ref name=Shang>Shang R, Liu, L. Transition metal-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling reactions. ''Science China-Chemistry'', '''2011''', ''11'', 54: 1670–1687 DOI: 10.1007/s11426-011-4381-0</ref> |
||
== History and |
== History and catalyst development == |
||
===Copper |
===Copper monometallic systems=== |
||
The first reported decarboxylative cross coupling reaction was an [[Ullmann reaction]], in 1966 by Nilsson ''et al.'' Thermal decarboxylation of copper benzoates, in the presence of an [[aryl halide]], was found to produce (both symmetric and unsymmetric) biaryls through aryl-Cu intermediates.<ref>Nilsson M. A new biaryl synthesis illustrating a connection between the Ullmann biaryl synthesis and copper-catalyzed decarboxylation. ''Acta Chem Scand'', '''1966''', 20: 423–426. DOI: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.20-0423</ref> |
The first reported decarboxylative cross coupling reaction was an [[Ullmann reaction]], in 1966 by Nilsson ''et al.'' Thermal decarboxylation of copper benzoates, in the presence of an [[aryl halide]], was found to produce (both symmetric and unsymmetric) biaryls through aryl-Cu intermediates.<ref>Nilsson M. A new biaryl synthesis illustrating a connection between the Ullmann biaryl synthesis and copper-catalyzed decarboxylation. ''Acta Chem Scand'', '''1966''', 20: 423–426. DOI: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.20-0423</ref> |
||
[[File:Decarboxlyative Ullmann Coupling Reaction Scheme.png|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|First reported decarboxylative Ullmann coupling (Nilsson, 2005)]] |
[[File:Decarboxlyative Ullmann Coupling Reaction Scheme.png|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|First reported decarboxylative Ullmann coupling (Nilsson, 2005)]] |
||
This monometallic copper system required drastic conditions for complete cross-coupling, and had various intrinsic limitations, both of which prevented development of a [[catalysis|catalytic]], preparatory version of this reaction.<ref name=Rod>Rodriguez N, Goosen L. Decarboxylative coupling reactions: a modern strategy for C–C-bond formation. ''Chem Soc Rev'', '''2011''', 40: |
This monometallic copper system required drastic conditions for complete cross-coupling, and had various intrinsic limitations, both of which prevented development of a [[catalysis|catalytic]], preparatory version of this reaction.<ref name=Rod>Rodriguez N, Goosen L. Decarboxylative coupling reactions: a modern strategy for C–C-bond formation. ''Chem Soc Rev'', '''2011''', 40:5030–5048. DOI: 10.1039/C1CS15093F</ref> |
||
It was not until 2009 that Liu ''et al.'' found that decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl bromides and iodides with potassium polyfluorobenzoates could be achieved using monometallic copper iodide as a catalyst. The oxidative addition step was determined to be the [[Rate-determining step|rate-limiting step]] in the copper-only [[catalysis|catalyst]] cycle (a contrast |
It was not until 2009 that Liu ''et al.'' found that decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl bromides and iodides with potassium polyfluorobenzoates could be achieved using monometallic copper iodide as a catalyst. The oxidative addition step was determined to be the [[Rate-determining step|rate-limiting step]] in the copper-only [[catalysis|catalyst]] cycle (a contrast with [[#palladium monometallic systems|Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling]]).<ref name=refA>Shang R, Fu Y, Wang Y, Xu Q, Yu HZ, Liu L. Copper-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling of potassium polyfluorobenzoates with aryl iodides and bromides. ''Angew Chem Int Ed'', '''2009''', 48: 9350–9354. DOI:10.1002/anie.200904916</ref> |
||
[[File:Copper catalyzed decarboxylative biaryl synthesis reported by Goossen et al.png|thumbnail|none|700xpx|Copper catalyzed decarboxylative biaryl synthesis reported by Goossen et al.]] |
[[File:Copper catalyzed decarboxylative biaryl synthesis reported by Goossen et al.png|thumbnail|none|700xpx|Copper catalyzed decarboxylative biaryl synthesis reported by Goossen et al.]] |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
Catalysts for decarboxylative cross-coupling are of the general form ML2, with a wide variety of ligand types optimized for different substrates. Copper (and [[#Palladium/Silver Bimetallic Systems|silver]]) centers are often complexed with [[phenanthroline]]s, and activity is reported to increase with electron-rich substituents on the ligands.<ref name=Shang /> |
Catalysts for decarboxylative cross-coupling are of the general form ML2, with a wide variety of ligand types optimized for different substrates. Copper (and [[#Palladium/Silver Bimetallic Systems|silver]]) centers are often complexed with [[phenanthroline]]s, and activity is reported to increase with electron-rich substituents on the ligands.<ref name=Shang /> |
||
===Palladium |
===Palladium monometallic systems=== |
||
In 2000, Steglich ''et al.'' reported a Pd(II)-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling reaction in their synthesis of lamellarin L.<ref>Peschko C, Winklhofer C, Steglich W. Biomimetic total synthesis of lamellarin l by coupling of two different arylpyruvic acid units. ''Chem Eur J'', '''2000''', 6: |
In 2000, Steglich ''et al.'' reported a Pd(II)-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling reaction in their synthesis of lamellarin L.<ref>Peschko C, Winklhofer C, Steglich W. Biomimetic total synthesis of lamellarin l by coupling of two different arylpyruvic acid units. ''Chem Eur J'', '''2000''', 6: 1147–52 DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-3765(20000403)6:7<1147::AID-CHEM1147>3.0.CO;2-1</ref> |
||
This reaction was classified as a [[Heck reaction|Heck coupling]] and was further examined in 2002 by Myers ''et al.'' who reported decarboxylative olefination of [[Arene substitution patterns|''ortho''-substituted arene]] carboxylates in the presence of an [[oxidizing agent|oxidant]] (Ag2CO3).<ref>Myers AG, Tanaka D, Mannion MR. Development of a decarboxylative palladation reaction and its use in a Heck-type olefination of arene carboxylates. ''J Am Chem Soc'', '''2002''', 124: |
This reaction was classified as a [[Heck reaction|Heck coupling]] and was further examined in 2002 by Myers ''et al.'' who reported decarboxylative olefination of [[Arene substitution patterns|''ortho''-substituted arene]] carboxylates in the presence of an [[oxidizing agent|oxidant]] (Ag2CO3).<ref>Myers AG, Tanaka D, Mannion MR. Development of a decarboxylative palladation reaction and its use in a Heck-type olefination of arene carboxylates. ''J Am Chem Soc'', '''2002''', 124: 11250–51 DOI: 10.1021/ja027523m</ref> |
||
[[File:Pd-catalyzed Heck olefination, reported by Myers et al.png|550xpx|thumbnail|none|Pd-catalyzed Heck olefination, reported by Myers et al.]] |
[[File:Pd-catalyzed Heck olefination, reported by Myers et al.png|550xpx|thumbnail|none|Pd-catalyzed Heck olefination, reported by Myers et al.]] |
||
Subsequent studies showed that homogenous Pd catalysts were able to decarboxylate acids at lower temperatures than their Cu and Ag counterparts, but were limited to electron rich ''ortho''-substituted aromatic carboxylic acids.<ref>Dickstein JS, Mulrooney CA, O’Brien EM, Morgan BJ, Kozlowski MC. Development of a catalytic aromatic decarboxylation reaction. ''Org Lett'', '''2007''', 9: |
Subsequent studies showed that homogenous Pd catalysts were able to decarboxylate acids at lower temperatures than their Cu and Ag counterparts, but were limited to electron rich ''ortho''-substituted aromatic carboxylic acids.<ref>Dickstein JS, Mulrooney CA, O’Brien EM, Morgan BJ, Kozlowski MC. Development of a catalytic aromatic decarboxylation reaction. ''Org Lett'', '''2007''', 9: 2441–44 DOI: 10.1021/ol070749f</ref><ref name=meyers>Meyers et al. On the Mechanism of the Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Decarboxylative Olefination of Arene Carboxylic Acids. Crystallographic Characterization of Non-Phosphine Palladium(II) Intermediates and Observation of Their Stepwise Transformation in Heck-like Processes JACS, 2005, 127, 10323–33 DOI: 10.1021/ja052099l</ref> |
||
Despite this, palladium [[catalysis|catalysts]] are able to promote a wide variety of cross-coupling reactions including biaryl formation and aryl alkyne formation, along with a variety of cross-coupling reactions in which the carboxylic acid is not bonded to an aromatic.<ref name=refB /><ref>Zhang WW, Zhang XG, Li JH. Palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative coupling of alkynyl carboxylic acids with benzyl halides or [[aryl halide]]s. ''J Org Chem'', '''2010''', 75: 5259–5264 DOI: 10.1021/jo1010284</ref><ref>Yeung PY, Chung KH, Kwong FY. Palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative arylation of potassium cyanoacetate: Synthesis of α-diaryl nitriles from aryl halides. ''Org Lett'', '''2011''', 13: |
Despite this, palladium [[catalysis|catalysts]] are able to promote a wide variety of cross-coupling reactions including biaryl formation and aryl alkyne formation, along with a variety of cross-coupling reactions in which the carboxylic acid is not bonded to an aromatic.<ref name=refB /><ref>Zhang WW, Zhang XG, Li JH. Palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative coupling of alkynyl carboxylic acids with benzyl halides or [[aryl halide]]s. ''J Org Chem'', '''2010''', 75: 5259–5264 DOI: 10.1021/jo1010284</ref><ref>Yeung PY, Chung KH, Kwong FY. Palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative arylation of potassium cyanoacetate: Synthesis of α-diaryl nitriles from aryl halides. ''Org Lett'', '''2011''', 13: 2912–15 DOI: 10.1021/ol2009522</ref> |
||
Other Pd-catalyzed decarboxylation cross-coupling reactions include conjugated diene preparation (see [[#Dienes and Trienes|dienes and trienes]] below) and dehydrogenative reactions (with a variety of [[substrate (chemistry)|substrate]] and [[catalysis|catalyst]] combinations).<ref name=Shang /><ref>Yamashita M, Hirano K, Satoh T, Miura M. Synthesis of α,ω-diarylbutadienes and hexatrienes via decarboxylative coupling of cinnamic acids with vinyl bromides under palladium catalysis. ''Org Lett'', '''2010''', 12: |
Other Pd-catalyzed decarboxylation cross-coupling reactions include conjugated diene preparation (see [[#Dienes and Trienes|dienes and trienes]] below) and dehydrogenative reactions (with a variety of [[substrate (chemistry)|substrate]] and [[catalysis|catalyst]] combinations).<ref name=Shang /><ref>Yamashita M, Hirano K, Satoh T, Miura M. Synthesis of α,ω-diarylbutadienes and hexatrienes via decarboxylative coupling of cinnamic acids with vinyl bromides under palladium catalysis. ''Org Lett'', '''2010''', 12: 592–95 DOI: 10.1021/ol9027896</ref> |
||
[[File:Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl halides with potassium cyanoacetate, reported by Yeung et al.png|550xpx|thumbnail|none|Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl halides with potassium cyanoacetate, reported by Yeung et al.]] |
[[File:Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl halides with potassium cyanoacetate, reported by Yeung et al.png|550xpx|thumbnail|none|Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl halides with potassium cyanoacetate, reported by Yeung et al.]] |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
[[File:Decarboxylative cross-coupling of potassium polyfluorobenzoates, reported by Shang et al.png|thumbnail|700px|none|Decarboxylative cross-coupling of potassium polyfluorobenzoates, reported by Shang et al.]] |
[[File:Decarboxylative cross-coupling of potassium polyfluorobenzoates, reported by Shang et al.png|thumbnail|700px|none|Decarboxylative cross-coupling of potassium polyfluorobenzoates, reported by Shang et al.]] |
||
===Palladium |
===Palladium-–copper bimetallic systems=== |
||
A |
A Pd–Cu bimetallic system was not discovered until 2006 when Goossen ''et al.'' reported a decarboxylative cross-coupling of [[aryl halide]]s with ''ortho''-substituted aromatic carboxylic acids.<ref>Goossen LJ, Deng GJ, Levy LM. Synthesis of biaryls via catalytic decarboxylative coupling. ''Science'', '''2006''', 313: 662–64 DOI: 10.1126/science.1128684</ref> |
||
Through subsequent studies it was found that the use of aryl [[Trifluoromethanesulfonate|triflates]] allowed substrate scope for cross-coupling to be extended to some aromatic carboxylates lacking any [[Arene substitution patterns|''ortho''-substitution]] (less reactive). This was a result of the fact that any halide anion generated in the reaction inhibited the Cu-catalyzed decarboxylation process.<ref>Goossen LJ, Rodriǵ uez N, Linder C. Decarboxylative biaryl synthesis from aromatic carboxylates and aryl triflates. ''J Am Chem Soc'', '''2008''', 130: |
Through subsequent studies it was found that the use of aryl [[Trifluoromethanesulfonate|triflates]] allowed substrate scope for cross-coupling to be extended to some aromatic carboxylates lacking any [[Arene substitution patterns|''ortho''-substitution]] (less reactive). This was a result of the fact that any halide anion generated in the reaction inhibited the Cu-catalyzed decarboxylation process.<ref>Goossen LJ, Rodriǵ uez N, Linder C. Decarboxylative biaryl synthesis from aromatic carboxylates and aryl triflates. ''J Am Chem Soc'', '''2008''', 130: 15248–49 DOI: 10.1021/ja8050926</ref> |
||
Further optimization of the system and |
Further optimization of the system and catalyst conditions has made decarboxylative cross-coupling using bimetallic Pd–Cu systems applicable to organic synthesis, most predominantly in the formation of biaryls.<ref name=Rod /> |
||
As well, the variability of this combined |
As well, the variability of this combined catalytic system allows for promotion of a large spectrum of reactions, including aryl ketone formation, c-heteroatom cross-coupling, and many others.<ref name="Shang"/> |
||
[[File:Biaryl synthesis using a Cu-Pd catalyst system, reported by Shang et al.png|thumbnail|700px|none|Biaryl synthesis using a |
[[File:Biaryl synthesis using a Cu-Pd catalyst system, reported by Shang et al.png|thumbnail|700px|none|Biaryl synthesis using a Cu–Pd catalyst system, reported by Shang et al.]] |
||
===Palladium–silver bimetallic systems=== |
|||
===Palladium/Silver Bimetallic Systems=== |
|||
Silver being in the same group as copper, |
Silver being in the same group as copper, Pd–Ag(I) bimetallic systems are inherently similar to Pd–Cu [[catalysis|catalytic]] systems. However, silver salts are better suited for [[decarboxylation|protodecarboxylation]] of carboxylic acids than their copper equivalents, allowing milder reaction conditions in Pd–Ag cycles relative to Pd–Cu cylces.<ref>Goossen LJ, Rodríguez N, Linder C, Lange PP, Fromm A. Comparative study of copper- and silver-catalyzed protodecarboxylations of carboxylic acids. ''ChemCatChem'', '''2010''', 2: 430–42 DOI: 10.1002/cctc.200900277</ref> |
||
Ag(I) catalyzed monometallic systems have also been reported. Their proficiency (relative to [[#copper monometallic systems|copper]]) is likely attributed to lower [[electronegativity]] and greater expansion of [[atomic orbital|d-orbitals]], which promote decarboxylation of the substrate.<ref>Lu P, Sanchez C, Cornella J, Larrosa I. Silver-catalyzed protodecarboxylation of heteroaromatic carboxylic acids. ''Org Lett'', '''2009''', 11: 5710–5713 DOI:10.1021/ol902482p</ref> |
Ag(I) catalyzed monometallic systems have also been reported. Their proficiency (relative to [[#copper monometallic systems|copper]]) is likely attributed to lower [[electronegativity]] and greater expansion of [[atomic orbital|d-orbitals]], which promote decarboxylation of the substrate.<ref>Lu P, Sanchez C, Cornella J, Larrosa I. Silver-catalyzed protodecarboxylation of heteroaromatic carboxylic acids. ''Org Lett'', '''2009''', 11: 5710–5713 DOI:10.1021/ol902482p</ref> |
||
One limitation of this [[catalysis|catalyst]] combination is that the silver salts will form insoluble silver halides, forcing the reaction to require a stoichiometric amount of Ag if halides are present. This obstacle was overcome by Goossen ''et al.'' in 2010 by using aryl [[Trifluoromethanesulfonate|triflates]], and catalytic reaction with aryl [[sulfonate]]s has also been reported.<ref name=Rod /><ref>Goossen LJ, Lange PP, Rodríguez N, Linder C. Low-temperature Ag/Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl triflates with aromatic carboxylate salts. ''Chem Eur J'', '''2010''', 16: |
One limitation of this [[catalysis|catalyst]] combination is that the silver salts will form insoluble silver halides, forcing the reaction to require a stoichiometric amount of Ag if halides are present. This obstacle was overcome by Goossen ''et al.'' in 2010 by using aryl [[Trifluoromethanesulfonate|triflates]], and catalytic reaction with aryl [[sulfonate]]s has also been reported.<ref name=Rod /><ref>Goossen LJ, Lange PP, Rodríguez N, Linder C. Low-temperature Ag/Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl triflates with aromatic carboxylate salts. ''Chem Eur J'', '''2010''', 16: 3906–09 DOI: 10.1002/chem.200903319</ref> |
||
[[File:Decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl triflates with aryl carboxylates using a Pd-Ag catalyst system, reported by Goossen et al.png|thumbnail|700px|none|Decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl triflates with aryl carboxylates using a |
[[File:Decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl triflates with aryl carboxylates using a Pd-Ag catalyst system, reported by Goossen et al.png|thumbnail|700px|none|Decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl triflates with aryl carboxylates using a Pd–Ag catalyst system, reported by Goossen et al.]] |
||
== Product scope via variation of substrates == |
== Product scope via variation of substrates == |
||
The product scope of this reaction is extremely broad with the use of different substrates; however development of different functionalities has required accompanied studies to determine the proper catalyst system. The most typical class of reactions involves coupling between |
The product scope of this reaction is extremely broad with the use of different substrates; however development of different functionalities has required accompanied studies to determine the proper catalyst system. The most typical class of reactions involves coupling between C–COOH and C–X bonds, however C–COOH and C–M cross-coupling, homo-coupling of carboxylic acids, heck coupling, and dehydrogenative cross-coupling can also be including in this class as they release CO<sub>2</sub>. Heteroatom cross coupling reactions involving formation of C–N, C–S, C–P, and C–X bonds have also been demonstrated. |
||
<ref name="Shang"/> |
<ref name="Shang"/> |
||
===Biaryl formation=== |
===Biaryl formation=== |
||
Biaryls constitute an important class of structural motifs and can be found in a variety of applications including in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and liquid crystals for LCD screens. This reaction is an alternative to the traditional Suzuki and Stille cross-coupling reactions. A variety of catalysts has been employed for this transformation; Goossen et al. reported the formation of biaryls from |
Biaryls constitute an important class of structural motifs and can be found in a variety of applications including in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and liquid crystals for LCD screens. This reaction is an alternative to the traditional Suzuki and Stille cross-coupling reactions. A variety of catalysts has been employed for this transformation; Goossen et al. reported the formation of biaryls from Pd–Cu catalzyed cross-coupling reactions where an aryl or heteroaryl carboxylic acid and an aryl halide (I, Br, or Cl) are coupled in the presence of a base.<ref>Goossen LJ, Rodríguez N, Melzer B, Linder C, Deng GJ, Levy LM. Biaryl synthesis via Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative coupling of aromatic carboxylates with aryl halides. ''J Am Chem Soc'', '''2007''', 129: 4824–33 DOI: 10.1021/ja068993+</ref> |
||
[[File:Formation of Biaryls by Goossen et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of Biaryls (Goossen et al. (2007))]] |
[[File:Formation of Biaryls by Goossen et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of Biaryls (Goossen et al. (2007))]] |
||
===Aryl |
===Aryl alkynes=== |
||
Aryl alkynes are typically made utilizing the Sonogashira reaction. In 2010, Zhao et al. reported the coupling of an aryl halide and alkynyl carboxylic acid under mild reactions conditions and a copper-only catalyst to obtain aryl alkynes. |
Aryl alkynes are typically made utilizing the Sonogashira reaction. In 2010, Zhao et al. reported the coupling of an aryl halide and alkynyl carboxylic acid under mild reactions conditions and a copper-only catalyst to obtain aryl alkynes. |
||
<ref>Zhao DB, Gao C, Su XY, He YQ, You JS, Xue Y. Copper-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling of alkynyl carboxylic acids with arylhalides. ''Chem Commun'', '''2010''', 46: |
<ref>Zhao DB, Gao C, Su XY, He YQ, You JS, Xue Y. Copper-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling of alkynyl carboxylic acids with arylhalides. ''Chem Commun'', '''2010''', 46: 9049–51 DOI: 10.1039/c0cc03772a</ref> |
||
[[File:Formation of Aryl Alkynes by Zhao et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of Aryl Alkynes (Zhao et al. (2010))]] |
[[File:Formation of Aryl Alkynes by Zhao et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of Aryl Alkynes (Zhao et al. (2010))]] |
||
===Aryl |
===Aryl ketones=== |
||
Further work by Goossen et al. described the synthesis of ketones from α-oxocarboxylic acids with aryl or heteroaryl bromides through an acyl anion intermediate. |
Further work by Goossen et al. described the synthesis of ketones from α-oxocarboxylic acids with aryl or heteroaryl bromides through an acyl anion intermediate. |
||
<ref>Goossen LJ, Rudolphi F, Oppel C, Rodríguez N. Synthesis of ketones from α-oxocarboxylates and aryl bromides by Cu/Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling. ''Angew Chem Int Ed'', '''2008''', 47: 3043–3045 DOI: 10.1002/anie.200705127</ref> |
<ref>Goossen LJ, Rudolphi F, Oppel C, Rodríguez N. Synthesis of ketones from α-oxocarboxylates and aryl bromides by Cu/Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling. ''Angew Chem Int Ed'', '''2008''', 47: 3043–3045 DOI: 10.1002/anie.200705127</ref> |
||
[[File:Formation of Aryl Ketones by Goossen et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of Aryl Ketones (Goossen et al. (2008))]] |
[[File:Formation of Aryl Ketones by Goossen et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of Aryl Ketones (Goossen et al. (2008))]] |
||
===Aryl |
===Aryl esters=== |
||
Shang et al. discovered the decarboxylative coupling of potassium oxalate monoesters with aryl halides to obtain aryl or alkenyl esters. |
Shang et al. discovered the decarboxylative coupling of potassium oxalate monoesters with aryl halides to obtain aryl or alkenyl esters. |
||
<ref name="refB"/> |
<ref name="refB"/> |
||
[[File:Formation of Aryl Esters by Shang et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of Aryl Esters (Shang et al. (2009))]] |
[[File:Formation of Aryl Esters by Shang et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of Aryl Esters (Shang et al. (2009))]] |
||
===sp<sup>3</sup>C |
===sp<sup>3</sup>C carboxylic acids === |
||
Many decarboxylative cross coupling reactions involve the breaking of <sub>sp<sup>2</sup></sub> |
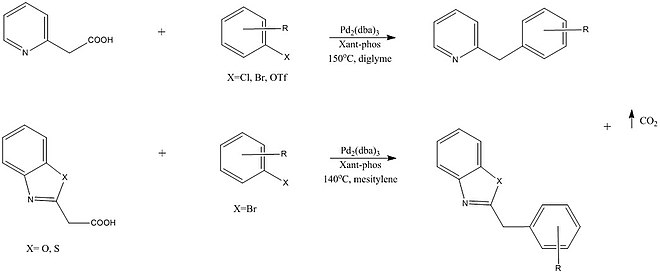
Many decarboxylative cross coupling reactions involve the breaking of <sub>sp<sup>2</sup></sub>C–COOH and <sub>sp</sub>C–COOH bonds, therefore subsequent studies have attempted to enable cross coupling with <sub>sp<sup>3</sup></sub>C carboxylic acids. One such reaction by Shang et al. described a palladium catalyzed cross coupling that enables the formation of functionalized pyridines, pyrazines, quinolines, benzothiazoles, and benzoxazoles. The position of the nitrogen atom in the '2' position relative to the linkage is found to be required, therefore implying its binding to Pd in a transition state. |
||
<ref>Shang R, Yang ZW, Wang Y, Zhang SL, Liu L. Palladium-catalyzed |
<ref>Shang R, Yang ZW, Wang Y, Zhang SL, Liu L. Palladium-catalyzed |
||
decarboxylative couplings of 2-(2-azaaryl)acetates with aryl halides |
decarboxylative couplings of 2-(2-azaaryl)acetates with aryl halides |
||
and triflates. ''J Am Chem Soc'', '''2010''', 132: |
and triflates. ''J Am Chem Soc'', '''2010''', 132: 14391–93 DOI:10.1021/ja107103b</ref> |
||
[[File:Formation of sp3C-heteroaromatics by Shang et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of sp3C-heteroaromatics by Shang et al. |
[[File:Formation of sp3C-heteroaromatics by Shang et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of sp3C-heteroaromatics by Shang et al. 2010)]] |
||
===Dienes and |
===Dienes and trienes=== |
||
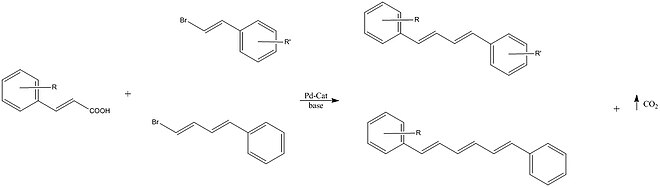
Miura et al. reported the cross coupling of vinyl bromides with an alkenyl carboxylic acid using a palladium catalyst. Some of the conjugated dienes prepared were reported to exhibit solid state fluorescence. |
Miura et al. reported the cross coupling of vinyl bromides with an alkenyl carboxylic acid using a palladium catalyst. Some of the conjugated dienes prepared were reported to exhibit solid state fluorescence. |
||
<ref>Yamashita M, Hirano K, Satoh T, Miura M. Synthesis of |
<ref>Yamashita M, Hirano K, Satoh T, Miura M. Synthesis of |
||
α,ω-diarylbutadienes and-hexatrienes via decarboxylative coupling of |
α,ω-diarylbutadienes and-hexatrienes via decarboxylative coupling of |
||
cinnamic acids with vinyl bromides under palladium catalysis. ''Org |
cinnamic acids with vinyl bromides under palladium catalysis. ''Org |
||
Lett'', '''2010''', 12: |
Lett'', '''2010''', 12: 592–95 DOI: 10.1021/ol9027896</ref> |
||
[[File:Conjugated dienes by Miura et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of |
[[File:Conjugated dienes by Miura et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of conjugated dienes (Miura et al. (2010))]] |
||
===Olefins via Heck-type=== |
===Olefins via Heck-type=== |
||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
<ref>Hu P, Kan J, Su W, Hong M. Pd(O2CCF3)2/benzoquinone: A versatile |
<ref>Hu P, Kan J, Su W, Hong M. Pd(O2CCF3)2/benzoquinone: A versatile |
||
catalyst system for the decarboxylative olefination of arene |
catalyst system for the decarboxylative olefination of arene |
||
carboxylic acids. ''Org Lett'', '''2009''', 11: |
carboxylic acids. ''Org Lett'', '''2009''', 11: 2341–44 DOI: 10.1021/ol9007553</ref> |
||
[[File:Formation of Olefins via Heck-type reaction by Hu et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of olefins by Hu et al. (Hu et al. (2009))]] |
[[File:Formation of Olefins via Heck-type reaction by Hu et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of olefins by Hu et al. (Hu et al. (2009))]] |
||
===Phenanthrene |
===Phenanthrene derivatives=== |
||
Wang et al. proposed a novel method for [4+2] annulation via a palladium catalyzed intermolecular pathway. Derivatives are formed in moderate to good yield; acridine is essential for high reaction efficiency. |
Wang et al. proposed a novel method for [4+2] annulation via a palladium catalyzed intermolecular pathway. Derivatives are formed in moderate to good yield; acridine is essential for high reaction efficiency. |
||
<ref>Wang CY, Rakshit S, Glorius F. Palladium-catalyzed intermolecular |
<ref>Wang CY, Rakshit S, Glorius F. Palladium-catalyzed intermolecular |
||
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
[[File:Formation of Phenanthrene derivatives by Wang et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of phenanthrene derivatives by Wang et al. (Wang et al. (2010))]] |
[[File:Formation of Phenanthrene derivatives by Wang et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|Formation of phenanthrene derivatives by Wang et al. (Wang et al. (2010))]] |
||
=== |
===C–N coupling=== |
||
Jiao et al. enabled the formation of a |
Jiao et al. enabled the formation of a C–N bond via cross-coupling using air as an oxidant and a copper catalyst. No conditions are known for a C–N cross-coupling that breaks a sp<sup>3</sup> or sp<sup>2</sup> C–COOH bond. |
||
<ref>Jia W, Jiao N. Cu-catalyzed oxidative amidation of propiolic acids |
<ref>Jia W, Jiao N. Cu-catalyzed oxidative amidation of propiolic acids |
||
under air via decarboxylative coupling. ''Org Lett'', '''2010''', 12: 2000– |
under air via decarboxylative coupling. ''Org Lett'', '''2010''', 12: 2000– |
||
03 DOI: 10.1021/ol1004615</ref> |
|||
[[File:C-N cross-coupling by Jiao et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|C-N cross-coupling by Jiao et al. (Jiao et al. (2010))]] |
[[File:C-N cross-coupling by Jiao et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|C-N cross-coupling by Jiao et al. (Jiao et al. (2010))]] |
||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
[[File:C-S Cross-Coupling by Liu et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|C-S cross-coupling by Liu et al. (Liu et al. (2009))]] |
[[File:C-S Cross-Coupling by Liu et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|C-S cross-coupling by Liu et al. (Liu et al. (2009))]] |
||
=== |
===C–P coupling=== |
||
Using either |
Using either Pd–Cu or Cu cataylsts Yang et al. reported the first example of decarboxylative C–P cross-coupling. |
||
<ref>Hu J, Zhao N, Yang B, Wang G, Guo LN, Liang YM, Yang SD. |
<ref>Hu J, Zhao N, Yang B, Wang G, Guo LN, Liang YM, Yang SD. |
||
Copper-catalyzed C–P coupling through decarboxylation. ''Chem Eur |
Copper-catalyzed C–P coupling through decarboxylation. ''Chem Eur |
||
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
[[File:C-P Cross-Coupling by Yang et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|C-P cross-coupling by Yang et al. (Yang et al. (2011))]] |
[[File:C-P Cross-Coupling by Yang et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|C-P cross-coupling by Yang et al. (Yang et al. (2011))]] |
||
=== |
===C–X coupling=== |
||
Wu et al. reported a |
Wu et al. reported a C–X cross coupling using CuX<sub>2</sub> (X= Br, Cl) and a silver catalyst to obtain aryl halides. |
||
<ref>Luo Y, Pan XL, Wu J. Silver-catalyzed decarboxylative halogenation of carboxylic acids. ''Tetrahedron Lett'', '''2010''', 51: |
<ref>Luo Y, Pan XL, Wu J. Silver-catalyzed decarboxylative halogenation of carboxylic acids. ''Tetrahedron Lett'', '''2010''', 51: 6646–48 DOI: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2010.10.054</ref> |
||
[[File:C-X Cross-Coupling by Wu et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|C-X cross-coupling by Wu et al. |
[[File:C-X Cross-Coupling by Wu et al.jpg|frameless|none|Alt=A|upright=3.0|C-X cross-coupling by Wu et al. 2010)]] |
||
==Mechanistic |
==Mechanistic studies== |
||
===Decarboxylative Heck |
===Decarboxylative Heck type=== |
||
In 2005 |
In 2005, Meyers et al. Proposed the following mechanism for the decarboxylative cross-coupling reaction.<ref name=meyers /> The initial and rate determining step is the decarboxylation. The ipso carbon of the arene ring is thought to coordinate to the palladium centre initially and is followed by the expulsion of carbon dioxide, forming an aryl–palladium intermediate. The olefin then inserts between the arene and palladium center, which then undergoes beta elimination to form the desired vinyl halide, as well as a palladium hydride. This proton is abstracted by silver carbonate, which acts a both a base and an oxidant to regenerate the starting palladium complex completing the catalytic cycle. |
||
[[File:Decarboxylative Cross coupling Heck Type Mechanism.png|frameless|centre|Alt=A|upright=3.0| by Meyers et al. |
[[File:Decarboxylative Cross coupling Heck Type Mechanism.png|frameless|centre|Alt=A|upright=3.0| by Meyers et al. 2005]] |
||
===Biaryl |
===Biaryl synthesis via decarboxylative cross-coupling=== |
||
In 2006 Goossen et al. proposed a reaction to synthesize biaryl compounds via catalytic decarboxylative cross coupling.<ref>Lukas J. Gooßen et al. Synthesis of Biaryls via Catalytic Decarboxylative Coupling, Science 313, 662 (2006), DOI: 10.1126/science.1128684</ref> |
In 2006 Goossen et al. proposed a reaction to synthesize biaryl compounds via catalytic decarboxylative cross coupling.<ref>Lukas J. Gooßen et al. Synthesis of Biaryls via Catalytic Decarboxylative Coupling, Science 313, 662 (2006), DOI: 10.1126/science.1128684</ref> |
||
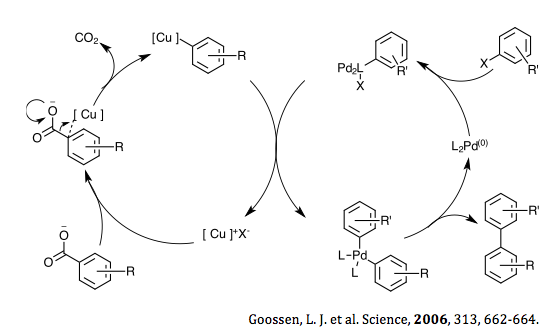
The mechanism involves two overlapping cycles, one using a copper halide and the other using palladium. The decarboxylation step occurs between the substituted benzoic acid and copper halide to form the intermediate aryl copper species. The palladium initially undergoes oxidative addition from the aryl halide to form a Pd(II) aryl complex. After both of these initial steps, the substituted aryl copper undergoes trans-metallation with the palladium complex. This step forms the copper halide, which then undergoes anion exchange with the substituted benzoic acid to reform the aryl copper intermediate, continuing the catalytic cycle. The other complex formed in the trans-metallation step is a bis-aryl palladium(II), which then undergoes reductive elimination to form the desired bis-aryl species as well as the starting Pd(0) complex, thus completing the catalytic cycle. |
The mechanism involves two overlapping cycles, one using a copper halide and the other using palladium. The decarboxylation step occurs between the substituted benzoic acid and copper halide to form the intermediate aryl copper species. The palladium initially undergoes oxidative addition from the aryl halide to form a Pd(II) aryl complex. After both of these initial steps, the substituted aryl copper undergoes trans-metallation with the palladium complex. This step forms the copper halide, which then undergoes anion exchange with the substituted benzoic acid to reform the aryl copper intermediate, continuing the catalytic cycle. The other complex formed in the trans-metallation step is a bis-aryl palladium(II), which then undergoes reductive elimination to form the desired bis-aryl species as well as the starting Pd(0) complex, thus completing the catalytic cycle. |
||
[[File:Decarboxylative Biaryl Synthesis Mechanism.png|frameless|centre|Alt=A|upright=4.0| Decarboxylative |
[[File:Decarboxylative Biaryl Synthesis Mechanism.png|frameless|centre|Alt=A|upright=4.0| Decarboxylative biaryl synthesis mechanism, Goossen et al. 2006]] |
||
===Heteroaromatic |
===Heteroaromatic acid coupling=== |
||
Forgione, P. |
Forgione, P., Bilodeau, F et al. reported that heteroatoms containing a carboxylic acid also are tolerated by palladium monometallic systems and undergo decarboxylative cross coupling with aryl halides.<ref>Forgione, P., Bilodeau. F. et al. Unexpected Intermolecular Pd-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reaction Employing Heteroaromatic Carboxylic Acids as Coupling Partners J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128 (35), pp 11350–51 DOI: 10.1021/ja063511f</ref> In the proposed mechanism the initial step is oxidative addition of the aryl halide forming an aryl–palladium intermediate. Electrophilic palladation then occurs at carbon-3 of the heteroatom. From this intermediate there are two possible pathways for the cycle to continue on. The first is palladium migration from carbon-3 to carbon-2 along with the expulsion of carbon dioxide. This forms the aryl–palladium–heteroatom intermediate, which undergoes reductive elimination to form the final heteroaromatic compound. The second pathway only occurs when R is a proton. If this is the case, deprotonation occurs to regain aromaticity of the heteroatom. This intermediate then undergoes reductive elimination, coupling the aryl to the carbon-3 position of the heteroatom. As this compound still contains the carboxylic acid it is then free to re enter the catalytic cycle where it undergoes coupling at the carbon 2 position, along with the expulsion of carbon dioxide to form a biaryl heteroatom. As this pathway competes with the decarboxylation step, two products are formed making this reaction less selective. As a result, heteroatoms, which are substituted at the carbon 3 position and are more favored due to the higher level of control they provide. |
||
[[File:Proposed Mechanism of Heteroaromatic Acid Coupling.png|frameless|centre|Alt=A|upright=4.0|Proposed |
[[File:Proposed Mechanism of Heteroaromatic Acid Coupling.png|frameless|centre|Alt=A|upright=4.0|Proposed mechanism of heteroaromatic acid coupling, Forgione et al. 2006]] |
||
== References == |
== References == |
||
Revision as of 10:36, 23 May 2013
Decarboxylative cross coupling reactions are chemical reactions in which a stable, substituted carboxylic acid is reacted with a halide (R–X, R=aryl, alkyl, etc.) in the presence of a metal catalyst, base and oxidant to form a new carbon-carbon bond (with loss of carbon dioxide).
A significant advantage of this reaction is that it uses relatively inexpensive carboxylic acids (or their salts) and is far less air and moisture sensitive in comparison to typical cross-coupling organometallic reagents. Furthermore, the carboxylic acid moiety is a common feature of natural products and can also be prepared by relatively benign air oxidations. Additional benefits include the broad tolerance of functional groups, as well as the capacity to avoid the use of strong bases. An important elementary step in this reaction is protodecarboxylation or metallation to first convert the C–COOH bond to a C–H or C–M bond respectively. [1]
History and catalyst development
Copper monometallic systems
The first reported decarboxylative cross coupling reaction was an Ullmann reaction, in 1966 by Nilsson et al. Thermal decarboxylation of copper benzoates, in the presence of an aryl halide, was found to produce (both symmetric and unsymmetric) biaryls through aryl-Cu intermediates.[2]

This monometallic copper system required drastic conditions for complete cross-coupling, and had various intrinsic limitations, both of which prevented development of a catalytic, preparatory version of this reaction.[3] It was not until 2009 that Liu et al. found that decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl bromides and iodides with potassium polyfluorobenzoates could be achieved using monometallic copper iodide as a catalyst. The oxidative addition step was determined to be the rate-limiting step in the copper-only catalyst cycle (a contrast with Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling).[4]

Cu(I)-only systems have also been found to promote coupling of alkynyl carboxylic acids with aryl halides (see aryl alkynes below), as well as decarboxylative dehydrogenative cross-coupling of amino acids with alkynes (or similar nucleophiles).[5][6]

Catalysts for decarboxylative cross-coupling are of the general form ML2, with a wide variety of ligand types optimized for different substrates. Copper (and silver) centers are often complexed with phenanthrolines, and activity is reported to increase with electron-rich substituents on the ligands.[1]
Palladium monometallic systems
In 2000, Steglich et al. reported a Pd(II)-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling reaction in their synthesis of lamellarin L.[7] This reaction was classified as a Heck coupling and was further examined in 2002 by Myers et al. who reported decarboxylative olefination of ortho-substituted arene carboxylates in the presence of an oxidant (Ag2CO3).[8]

Subsequent studies showed that homogenous Pd catalysts were able to decarboxylate acids at lower temperatures than their Cu and Ag counterparts, but were limited to electron rich ortho-substituted aromatic carboxylic acids.[9][10] Despite this, palladium catalysts are able to promote a wide variety of cross-coupling reactions including biaryl formation and aryl alkyne formation, along with a variety of cross-coupling reactions in which the carboxylic acid is not bonded to an aromatic.[5][11][12] Other Pd-catalyzed decarboxylation cross-coupling reactions include conjugated diene preparation (see dienes and trienes below) and dehydrogenative reactions (with a variety of substrate and catalyst combinations).[1][13]

Contrarily to Cu-only systems, decarboxylative palladation is the rate-limiting step in the palladium catalytic cycle.[4]

Palladium-–copper bimetallic systems
A Pd–Cu bimetallic system was not discovered until 2006 when Goossen et al. reported a decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl halides with ortho-substituted aromatic carboxylic acids.[14] Through subsequent studies it was found that the use of aryl triflates allowed substrate scope for cross-coupling to be extended to some aromatic carboxylates lacking any ortho-substitution (less reactive). This was a result of the fact that any halide anion generated in the reaction inhibited the Cu-catalyzed decarboxylation process.[15] Further optimization of the system and catalyst conditions has made decarboxylative cross-coupling using bimetallic Pd–Cu systems applicable to organic synthesis, most predominantly in the formation of biaryls.[3] As well, the variability of this combined catalytic system allows for promotion of a large spectrum of reactions, including aryl ketone formation, c-heteroatom cross-coupling, and many others.[1]
Palladium–silver bimetallic systems
Silver being in the same group as copper, Pd–Ag(I) bimetallic systems are inherently similar to Pd–Cu catalytic systems. However, silver salts are better suited for protodecarboxylation of carboxylic acids than their copper equivalents, allowing milder reaction conditions in Pd–Ag cycles relative to Pd–Cu cylces.[16] Ag(I) catalyzed monometallic systems have also been reported. Their proficiency (relative to copper) is likely attributed to lower electronegativity and greater expansion of d-orbitals, which promote decarboxylation of the substrate.[17] One limitation of this catalyst combination is that the silver salts will form insoluble silver halides, forcing the reaction to require a stoichiometric amount of Ag if halides are present. This obstacle was overcome by Goossen et al. in 2010 by using aryl triflates, and catalytic reaction with aryl sulfonates has also been reported.[3][18]

Product scope via variation of substrates
The product scope of this reaction is extremely broad with the use of different substrates; however development of different functionalities has required accompanied studies to determine the proper catalyst system. The most typical class of reactions involves coupling between C–COOH and C–X bonds, however C–COOH and C–M cross-coupling, homo-coupling of carboxylic acids, heck coupling, and dehydrogenative cross-coupling can also be including in this class as they release CO2. Heteroatom cross coupling reactions involving formation of C–N, C–S, C–P, and C–X bonds have also been demonstrated. [1]
Biaryl formation
Biaryls constitute an important class of structural motifs and can be found in a variety of applications including in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and liquid crystals for LCD screens. This reaction is an alternative to the traditional Suzuki and Stille cross-coupling reactions. A variety of catalysts has been employed for this transformation; Goossen et al. reported the formation of biaryls from Pd–Cu catalzyed cross-coupling reactions where an aryl or heteroaryl carboxylic acid and an aryl halide (I, Br, or Cl) are coupled in the presence of a base.[19]

Aryl alkynes
Aryl alkynes are typically made utilizing the Sonogashira reaction. In 2010, Zhao et al. reported the coupling of an aryl halide and alkynyl carboxylic acid under mild reactions conditions and a copper-only catalyst to obtain aryl alkynes. [20]

Aryl ketones
Further work by Goossen et al. described the synthesis of ketones from α-oxocarboxylic acids with aryl or heteroaryl bromides through an acyl anion intermediate. [21]

Aryl esters
Shang et al. discovered the decarboxylative coupling of potassium oxalate monoesters with aryl halides to obtain aryl or alkenyl esters. [5]

sp3C carboxylic acids
Many decarboxylative cross coupling reactions involve the breaking of sp2C–COOH and spC–COOH bonds, therefore subsequent studies have attempted to enable cross coupling with sp3C carboxylic acids. One such reaction by Shang et al. described a palladium catalyzed cross coupling that enables the formation of functionalized pyridines, pyrazines, quinolines, benzothiazoles, and benzoxazoles. The position of the nitrogen atom in the '2' position relative to the linkage is found to be required, therefore implying its binding to Pd in a transition state. [22]
Dienes and trienes
Miura et al. reported the cross coupling of vinyl bromides with an alkenyl carboxylic acid using a palladium catalyst. Some of the conjugated dienes prepared were reported to exhibit solid state fluorescence. [23]
Olefins via Heck-type
A decarboxylative Heck coupling by Su et al. can be used to obtain an aryl olefin using benzoquinone as the oxidant. [24]

Phenanthrene derivatives
Wang et al. proposed a novel method for [4+2] annulation via a palladium catalyzed intermolecular pathway. Derivatives are formed in moderate to good yield; acridine is essential for high reaction efficiency. [25]

C–N coupling
Jiao et al. enabled the formation of a C–N bond via cross-coupling using air as an oxidant and a copper catalyst. No conditions are known for a C–N cross-coupling that breaks a sp3 or sp2 C–COOH bond. [26]

C-S Coupling
Liu et al. reported the C-S coupling of aryl carboxylic acids with disulphides or thiols using a Pd/Cu catalyst system. [27]

C–P coupling
Using either Pd–Cu or Cu cataylsts Yang et al. reported the first example of decarboxylative C–P cross-coupling. [28]

C–X coupling
Wu et al. reported a C–X cross coupling using CuX2 (X= Br, Cl) and a silver catalyst to obtain aryl halides. [29]

Mechanistic studies
Decarboxylative Heck type
In 2005, Meyers et al. Proposed the following mechanism for the decarboxylative cross-coupling reaction.[10] The initial and rate determining step is the decarboxylation. The ipso carbon of the arene ring is thought to coordinate to the palladium centre initially and is followed by the expulsion of carbon dioxide, forming an aryl–palladium intermediate. The olefin then inserts between the arene and palladium center, which then undergoes beta elimination to form the desired vinyl halide, as well as a palladium hydride. This proton is abstracted by silver carbonate, which acts a both a base and an oxidant to regenerate the starting palladium complex completing the catalytic cycle.

Biaryl synthesis via decarboxylative cross-coupling
In 2006 Goossen et al. proposed a reaction to synthesize biaryl compounds via catalytic decarboxylative cross coupling.[30] The mechanism involves two overlapping cycles, one using a copper halide and the other using palladium. The decarboxylation step occurs between the substituted benzoic acid and copper halide to form the intermediate aryl copper species. The palladium initially undergoes oxidative addition from the aryl halide to form a Pd(II) aryl complex. After both of these initial steps, the substituted aryl copper undergoes trans-metallation with the palladium complex. This step forms the copper halide, which then undergoes anion exchange with the substituted benzoic acid to reform the aryl copper intermediate, continuing the catalytic cycle. The other complex formed in the trans-metallation step is a bis-aryl palladium(II), which then undergoes reductive elimination to form the desired bis-aryl species as well as the starting Pd(0) complex, thus completing the catalytic cycle.
Heteroaromatic acid coupling
Forgione, P., Bilodeau, F et al. reported that heteroatoms containing a carboxylic acid also are tolerated by palladium monometallic systems and undergo decarboxylative cross coupling with aryl halides.[31] In the proposed mechanism the initial step is oxidative addition of the aryl halide forming an aryl–palladium intermediate. Electrophilic palladation then occurs at carbon-3 of the heteroatom. From this intermediate there are two possible pathways for the cycle to continue on. The first is palladium migration from carbon-3 to carbon-2 along with the expulsion of carbon dioxide. This forms the aryl–palladium–heteroatom intermediate, which undergoes reductive elimination to form the final heteroaromatic compound. The second pathway only occurs when R is a proton. If this is the case, deprotonation occurs to regain aromaticity of the heteroatom. This intermediate then undergoes reductive elimination, coupling the aryl to the carbon-3 position of the heteroatom. As this compound still contains the carboxylic acid it is then free to re enter the catalytic cycle where it undergoes coupling at the carbon 2 position, along with the expulsion of carbon dioxide to form a biaryl heteroatom. As this pathway competes with the decarboxylation step, two products are formed making this reaction less selective. As a result, heteroatoms, which are substituted at the carbon 3 position and are more favored due to the higher level of control they provide.

References
- ^ a b c d e Shang R, Liu, L. Transition metal-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling reactions. Science China-Chemistry, 2011, 11, 54: 1670–1687 DOI: 10.1007/s11426-011-4381-0
- ^ Nilsson M. A new biaryl synthesis illustrating a connection between the Ullmann biaryl synthesis and copper-catalyzed decarboxylation. Acta Chem Scand, 1966, 20: 423–426. DOI: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.20-0423
- ^ a b c Rodriguez N, Goosen L. Decarboxylative coupling reactions: a modern strategy for C–C-bond formation. Chem Soc Rev, 2011, 40:5030–5048. DOI: 10.1039/C1CS15093F
- ^ a b Shang R, Fu Y, Wang Y, Xu Q, Yu HZ, Liu L. Copper-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling of potassium polyfluorobenzoates with aryl iodides and bromides. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2009, 48: 9350–9354. DOI:10.1002/anie.200904916
- ^ a b c Shang R, Fu Y, Li JB, Zhang SL, Guo QX, Liu L. Synthesis of aromatic esters via Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative coupling of potassium oxalate monoesters with aryl bromides and chlorides. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131: 5738–5739 DOI: 10.1021/ja900984x
- ^ Bi HP, Zhao L, Liang YM, Li CJ. The copper-catalyzed decarboxylative coupling of the sp3–hybridized carbon atoms of α-amino acids. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2009, 48: 792–795 DOI: 10.1002/anie.200805122
- ^ Peschko C, Winklhofer C, Steglich W. Biomimetic total synthesis of lamellarin l by coupling of two different arylpyruvic acid units. Chem Eur J, 2000, 6: 1147–52 DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-3765(20000403)6:7<1147::AID-CHEM1147>3.0.CO;2-1
- ^ Myers AG, Tanaka D, Mannion MR. Development of a decarboxylative palladation reaction and its use in a Heck-type olefination of arene carboxylates. J Am Chem Soc, 2002, 124: 11250–51 DOI: 10.1021/ja027523m
- ^ Dickstein JS, Mulrooney CA, O’Brien EM, Morgan BJ, Kozlowski MC. Development of a catalytic aromatic decarboxylation reaction. Org Lett, 2007, 9: 2441–44 DOI: 10.1021/ol070749f
- ^ a b Meyers et al. On the Mechanism of the Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Decarboxylative Olefination of Arene Carboxylic Acids. Crystallographic Characterization of Non-Phosphine Palladium(II) Intermediates and Observation of Their Stepwise Transformation in Heck-like Processes JACS, 2005, 127, 10323–33 DOI: 10.1021/ja052099l
- ^ Zhang WW, Zhang XG, Li JH. Palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative coupling of alkynyl carboxylic acids with benzyl halides or aryl halides. J Org Chem, 2010, 75: 5259–5264 DOI: 10.1021/jo1010284
- ^ Yeung PY, Chung KH, Kwong FY. Palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative arylation of potassium cyanoacetate: Synthesis of α-diaryl nitriles from aryl halides. Org Lett, 2011, 13: 2912–15 DOI: 10.1021/ol2009522
- ^ Yamashita M, Hirano K, Satoh T, Miura M. Synthesis of α,ω-diarylbutadienes and hexatrienes via decarboxylative coupling of cinnamic acids with vinyl bromides under palladium catalysis. Org Lett, 2010, 12: 592–95 DOI: 10.1021/ol9027896
- ^ Goossen LJ, Deng GJ, Levy LM. Synthesis of biaryls via catalytic decarboxylative coupling. Science, 2006, 313: 662–64 DOI: 10.1126/science.1128684
- ^ Goossen LJ, Rodriǵ uez N, Linder C. Decarboxylative biaryl synthesis from aromatic carboxylates and aryl triflates. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130: 15248–49 DOI: 10.1021/ja8050926
- ^ Goossen LJ, Rodríguez N, Linder C, Lange PP, Fromm A. Comparative study of copper- and silver-catalyzed protodecarboxylations of carboxylic acids. ChemCatChem, 2010, 2: 430–42 DOI: 10.1002/cctc.200900277
- ^ Lu P, Sanchez C, Cornella J, Larrosa I. Silver-catalyzed protodecarboxylation of heteroaromatic carboxylic acids. Org Lett, 2009, 11: 5710–5713 DOI:10.1021/ol902482p
- ^ Goossen LJ, Lange PP, Rodríguez N, Linder C. Low-temperature Ag/Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling of aryl triflates with aromatic carboxylate salts. Chem Eur J, 2010, 16: 3906–09 DOI: 10.1002/chem.200903319
- ^ Goossen LJ, Rodríguez N, Melzer B, Linder C, Deng GJ, Levy LM. Biaryl synthesis via Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative coupling of aromatic carboxylates with aryl halides. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129: 4824–33 DOI: 10.1021/ja068993+
- ^ Zhao DB, Gao C, Su XY, He YQ, You JS, Xue Y. Copper-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling of alkynyl carboxylic acids with arylhalides. Chem Commun, 2010, 46: 9049–51 DOI: 10.1039/c0cc03772a
- ^ Goossen LJ, Rudolphi F, Oppel C, Rodríguez N. Synthesis of ketones from α-oxocarboxylates and aryl bromides by Cu/Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2008, 47: 3043–3045 DOI: 10.1002/anie.200705127
- ^ Shang R, Yang ZW, Wang Y, Zhang SL, Liu L. Palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative couplings of 2-(2-azaaryl)acetates with aryl halides and triflates. J Am Chem Soc, 2010, 132: 14391–93 DOI:10.1021/ja107103b
- ^ Yamashita M, Hirano K, Satoh T, Miura M. Synthesis of α,ω-diarylbutadienes and-hexatrienes via decarboxylative coupling of cinnamic acids with vinyl bromides under palladium catalysis. Org Lett, 2010, 12: 592–95 DOI: 10.1021/ol9027896
- ^ Hu P, Kan J, Su W, Hong M. Pd(O2CCF3)2/benzoquinone: A versatile catalyst system for the decarboxylative olefination of arene carboxylic acids. Org Lett, 2009, 11: 2341–44 DOI: 10.1021/ol9007553
- ^ Wang CY, Rakshit S, Glorius F. Palladium-catalyzed intermolecular decarboxylative coupling of 2-phenylbenzoic acids with alkynes via C-H and C-C bond activation. J Am Chem Soc, 2010, 132: 14006– 14008DOI: 10.1021/ja106130r
- ^ Jia W, Jiao N. Cu-catalyzed oxidative amidation of propiolic acids under air via decarboxylative coupling. Org Lett, 2010, 12: 2000– 03 DOI: 10.1021/ol1004615
- ^ Duan ZY, Ranjit S, Zhang PF, Liu XG. Synthesis of aryl sulfides by decarboxylative C-S cross-couplings. Chem Eur J, 2009, 15: 3666– 3669 DOI:10.1002/chem.200900133
- ^ Hu J, Zhao N, Yang B, Wang G, Guo LN, Liang YM, Yang SD. Copper-catalyzed C–P coupling through decarboxylation. Chem Eur J, 2011, 17: 5516–5521 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201003561
- ^ Luo Y, Pan XL, Wu J. Silver-catalyzed decarboxylative halogenation of carboxylic acids. Tetrahedron Lett, 2010, 51: 6646–48 DOI: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2010.10.054
- ^ Lukas J. Gooßen et al. Synthesis of Biaryls via Catalytic Decarboxylative Coupling, Science 313, 662 (2006), DOI: 10.1126/science.1128684
- ^ Forgione, P., Bilodeau. F. et al. Unexpected Intermolecular Pd-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reaction Employing Heteroaromatic Carboxylic Acids as Coupling Partners J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128 (35), pp 11350–51 DOI: 10.1021/ja063511f
