Fresnel equations: Difference between revisions
Sbyrnes321 (talk | contribs) →Conventions used here: change convention description to match the change to rp. This convention does seem more common IMHO |
Rv change in sign convention. The forumulas in this article are supported by references. If you want to use some other formulation, please present a case for your change on the talk page, and provide references that we can use to verify the forumulas. |
||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
In this treatment, the coefficient ''r'' is the ratio of the reflected wave's [[complex number|complex]] electric field amplitude to that of the incident wave. The coefficient ''t'' is the ratio of the transmitted wave's electric field amplitude to that of the incident wave. The light is split into ''s'' and ''p'' polarizations as defined above. (In the figures to the right, ''s'' polarization is denoted "<math>\bot</math>" and ''p'' is denoted "<math>\parallel</math>".) |
In this treatment, the coefficient ''r'' is the ratio of the reflected wave's [[complex number|complex]] electric field amplitude to that of the incident wave. The coefficient ''t'' is the ratio of the transmitted wave's electric field amplitude to that of the incident wave. The light is split into ''s'' and ''p'' polarizations as defined above. (In the figures to the right, ''s'' polarization is denoted "<math>\bot</math>" and ''p'' is denoted "<math>\parallel</math>".) |
||
For ''s''-polarization, a positive ''r'' or ''t'' means that the electric fields of the incoming and reflected or transmitted wave are parallel, while negative means anti-parallel. For ''p''-polarization, a |
For ''s''-polarization, a positive ''r'' or ''t'' means that the electric fields of the incoming and reflected or transmitted wave are parallel, while negative means anti-parallel. For ''p''-polarization, a positive ''r'' or ''t'' means that the ''magnetic fields'' of the waves are parallel, while negative means anti-parallel.<ref name=Sernelius>Lecture notes by Bo Sernelius, [http://www.ifm.liu.se/courses/TFYY67/ main site], see especially [http://www.ifm.liu.se/courses/TFYY67/Lect12.pdf Lecture 12].</ref> It is also assumed that the magnetic permeability µ of both media is equal to the permeability of free space µ<sub>0</sub>. |
||
===Formulas=== |
===Formulas=== |
||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
:<math>t_s = \frac{2 n_1 \cos \theta_\text{i}}{n_1 \cos \theta_\text{i} + n_2 \cos \theta_\text{t}}</math> |
:<math>t_s = \frac{2 n_1 \cos \theta_\text{i}}{n_1 \cos \theta_\text{i} + n_2 \cos \theta_\text{t}}</math> |
||
:<math>r_p = \frac{ |
:<math>r_p = \frac{n_2 \cos \theta_\text{i} - n_1 \cos \theta_\text{t}}{n_1 \cos \theta_\text{t} + n_2 \cos \theta_\text{i}}</math> |
||
:<math>t_p = \frac{2 n_1\cos \theta_\text{i}}{n_1 \cos \theta_\text{t} + n_2 \cos \theta_\text{i}}</math> |
:<math>t_p = \frac{2 n_1\cos \theta_\text{i}}{n_1 \cos \theta_\text{t} + n_2 \cos \theta_\text{i}}</math> |
||
Revision as of 03:37, 24 June 2013
The Fresnel equations (or Fresnel conditions), deduced by Augustin-Jean Fresnel /frɛˈnɛl/, describe the behaviour of light when moving between media of differing refractive indices. The reflection of light that the equations predict is known as Fresnel reflection.
Overview
When light moves from a medium of a given refractive index n1 into a second medium with refractive index n2, both reflection and refraction of the light may occur. The Fresnel equations describe what fraction of the light is reflected and what fraction is refracted (i.e., transmitted). They also describe the phase shift of the reflected light.
The equations assume the interface is flat, planar, and homogeneous, and that the light is a plane wave.
Definitions and power equations

In the diagram on the right, an incident light ray IO strikes the interface between two media of refractive indices n1 and n2 at point O. Part of the ray is reflected as ray OR and part refracted as ray OT. The angles that the incident, reflected and refracted rays make to the normal of the interface are given as θi, θr and θt, respectively.
The relationship between these angles is given by the law of reflection:
and Snell's law:
The fraction of the incident power that is reflected from the interface is given by the reflectance R and the fraction that is refracted is given by the transmittance T.[1] The media are assumed to be non-magnetic.
The calculations of R and T depend on polarisation of the incident ray. Two cases are analyzed:
- The incident light is polarized with its electric field parallel to the plane containing the incident, reflected, and refracted rays, i.e. in the plane of the diagram above. Such light is described as p-polarized.
- The incident light is polarized with its electric field perpendicular to the plane described above. The light is said to be s-polarized, from the German senkrecht (perpendicular).
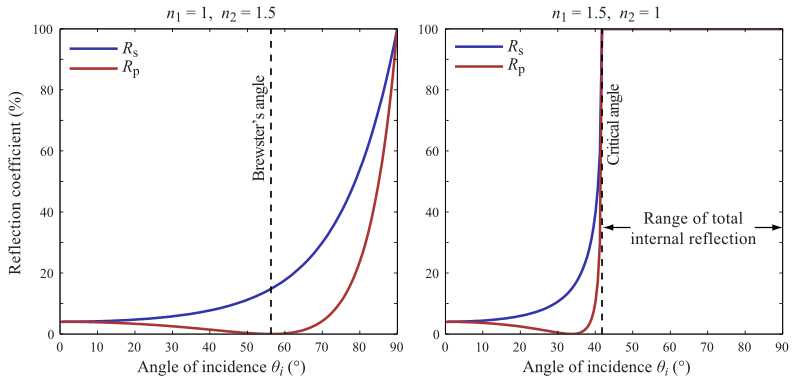
For the s-polarized light, the reflection coefficient is given by
- ,
where the second form is derived from the first by eliminating θt using Snell's law and trigonometric identities.
For the p-polarized light, the R is given by
- .
As a consequence of the conservation of energy, the transmission coefficients are given by [2]
and
These relationships hold only for power coefficients, not for amplitude coefficients as defined below.
If the incident light is unpolarised (containing an equal mix of s- and p-polarisations), the reflection coefficient is
For common glass, the reflection coefficient is about 4%. Note that reflection by a window is from the front side as well as the back side, and that some of the light bounces back and forth a number of times between the two sides. The combined reflection coefficient for this case is 2R/(1 + R), when interference can be neglected (see below).
The discussion given here assumes that the permeability μ is equal to the vacuum permeability μ0 in both media. This is approximately true for most dielectric materials, but not for some other types of material. The completely general Fresnel equations are more complicated.
Special angles
At one particular angle for a given n1 and n2, the value of Rp goes to zero and a p-polarised incident ray is purely refracted. This angle is known as Brewster's angle, and is around 56° for a glass medium in air or vacuum. Note that this statement is only true when the refractive indices of both materials are real numbers, as is the case for materials like air and glass. For materials that absorb light, like metals and semiconductors, n is complex, and Rp does not generally go to zero.
When moving from a denser medium into a less dense one (i.e., n1 > n2), above an incidence angle known as the critical angle, all light is reflected and Rs = Rp = 1. This phenomenon is known as total internal reflection. The critical angle is approximately 41° for glass in air.
Amplitude equations
Equations for coefficients corresponding to ratios of the electric field complex-valued amplitudes of the waves (not necessarily real-valued magnitudes) are also called "Fresnel equations". These take several different forms, depending on the choice of formalism and sign convention used. The amplitude coefficients are usually represented by lower case r and t.

Conventions used here
In this treatment, the coefficient r is the ratio of the reflected wave's complex electric field amplitude to that of the incident wave. The coefficient t is the ratio of the transmitted wave's electric field amplitude to that of the incident wave. The light is split into s and p polarizations as defined above. (In the figures to the right, s polarization is denoted "" and p is denoted "".)
For s-polarization, a positive r or t means that the electric fields of the incoming and reflected or transmitted wave are parallel, while negative means anti-parallel. For p-polarization, a positive r or t means that the magnetic fields of the waves are parallel, while negative means anti-parallel.[3] It is also assumed that the magnetic permeability µ of both media is equal to the permeability of free space µ0.
Formulas
Using the conventions above,[3]
Notice that but .[4]
Because the reflected and incident waves propagate in the same medium and make the same angle with the normal to the surface, the amplitude reflection coefficient is related to the reflectance R by [5]
- .
The transmittance T is generally not equal to |t|2, since the light travels with different direction and speed in the two media. The transmittance is related to t by.[6]
- .
The factor of n2/n1 occurs from the ratio of intensities (closely related to irradiance). The factor of cos θt/cos θi represents the change in area m of the pencil of rays, needed since T, the ratio of powers, is equal to the ratio of (intensity × area). In terms of the ratio of refractive indices,
- ,
and of the magnification m of the beam cross section occurring at the interface,
- .
Multiple surfaces
When light makes multiple reflections between two or more parallel surfaces, the multiple beams of light generally interfere with one another, resulting in net transmission and reflection amplitudes that depend on the light's wavelength. The interference, however, is seen only when the surfaces are at distances comparable to or smaller than the light's coherence length, which for ordinary white light is few micrometers; it can be much larger for light from a laser.
An example of interference between reflections is the iridescent colours seen in a soap bubble or in thin oil films on water. Applications include Fabry–Pérot interferometers, antireflection coatings, and optical filters. A quantitative analysis of these effects is based on the Fresnel equations, but with additional calculations to account for interference.
The transfer-matrix method, or the recursive Rouard method[7] can be used to solve multiple-surface problems.
See also
- Index-matching material
- Fresnel rhomb, Fresnel's apparatus to produce circularly polarised light [1]
- Specular reflection
- Schlick's approximation
- Snell's window
- X-ray reflectivity
References
- ^ Hecht (1987), p. 100.
- ^ Hecht (1987), p. 102.
- ^ a b Lecture notes by Bo Sernelius, main site, see especially Lecture 12.
- ^ Hecht (2003), p. 116, eq.(4.49)-(4.50).
- ^ Hecht (2003), p. 120, eq.(4.56).
- ^ Hecht (2003), p. 120, eq.(4.57).
- ^ see, e.g. O.S. Heavens, Optical Properties of Thin Films, Academic Press, 1955, chapt. 4.
- Hecht, Eugene (1987). Optics (2nd ed.). Addison Wesley. ISBN 0-201-11609-X.
- Hecht, Eugene (2002). Optics (4th ed.). Addison Wesley. ISBN 0-321-18878-0.
Further reading
- The Cambridge Handbook of Physics Formulas, G. Woan, Cambridge University Press, 2010, ISBN 978-0-521-57507-2.
- Introduction to Electrodynamics (3rd Edition), D.J. Griffiths, Pearson Education, Dorling Kindersley, 2007, ISBN 81-7758-293-3
- Light and Matter: Electromagnetism, Optics, Spectroscopy and Lasers, Y.B. Band, John Wiley & Sons, 2010, ISBN 978-0-471-89931-0
- The Light Fantastic – Introduction to Classic and Quantum Optics, I.R. Kenyon, Oxford University Press, 2008, ISBN 978-0-19-856646-5
- Encyclopaedia of Physics (2nd Edition), R.G. Lerner, G.L. Trigg, VHC publishers, 1991, ISBN (Verlagsgesellschaft) 3-527-26954-1, ISBN (VHC Inc.) 0-89573-752-3
- McGraw Hill Encyclopaedia of Physics (2nd Edition), C.B. Parker, 1994, ISBN 0-07-051400-3
External links
- Fresnel Equations – Wolfram
- FreeSnell – Free software computes the optical properties of multilayer materials
- Thinfilm – Web interface for calculating optical properties of thin films and multilayer materials. (Reflection & transmission coefficients, ellipsometric parameters Psi & Delta)
- Simple web interface for calculating single-interface reflection and refraction angles and strengths.
- Reflection and transmittance for two dielectrics – Mathematica interactive webpage that shows the relations between index of refraction and reflection.
- A self-contained first-principles derivation of the transmission and reflection probabilities from a multilayer with complex indices of refraction.