Mevalonate kinase deficiency (HIDS): Difference between revisions
Deepak1409 (talk | contribs) mevalonate kinase deficiency |
Deepak1409 (talk | contribs) No edit summary Tags: nowiki added Visual edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Autosomal recessive.png|thumb|MKD is an autosomal recessive diorder]] |
|||
=== Introduction === |
=== Introduction === |
||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
=== Diagnosis === |
=== Diagnosis === |
||
In many affected individuals the level of Immunoglobin D is elevated beyond the normal level and it is also known as HIDS (hyper-IgD with periodic fever syndrome) or mevalonate aciduria (MVA). The symptoms include painful swelling of lymph nodes (in the neck), skin rash, headache, and sore throat, ulcers in the mouth, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, joint pain and joint swelling, psychomotor delay, cataracts, recurrent febrile episodes [2] The small children have abnormally enlarged spleen known as splenomegaly [1, wiki, <nowiki>http://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/hyper-igd-syndrome/</nowiki>].. The severely affected individuals may develop fever attacks in the infant stage and may also have developmental delay, hypotonia, progressive ataxia, myopathy impaired vision and kidney damage [5]. In a patient hepatic fibrosis was also observed (uncommon in MKD) and also novel mutations V8F (t25a), and F38I (t112a) [11]. |
In many affected individuals the level of Immunoglobin D is elevated beyond the normal level and it is also known as HIDS (hyper-IgD with periodic fever syndrome) or mevalonate aciduria (MVA). The symptoms include painful swelling of lymph nodes (in the neck), skin rash, headache, and sore throat, ulcers in the mouth, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, joint pain and joint swelling, psychomotor delay, cataracts, recurrent febrile episodes [2] The small children have abnormally enlarged spleen known as splenomegaly [1, wiki, <nowiki>http://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/hyper-igd-syndrome/</nowiki>].. The severely affected individuals may develop fever attacks in the infant stage and may also have developmental delay, [[Hypotonia|hypotonia,]] progressive [[ataxia]], [[myopathy]] impaired vision and kidney damage [5]. In a patient hepatic fibrosis was also observed (uncommon in MKD) and also novel mutations V8F (t25a), and F38I (t112a) [11]. |
||
=== Genetics === |
=== Genetics === |
||
Mevalonate kinase deficiency is an example of loss-of-function mutation. There is a mutation in the gene which is coding for mevalonate kinase which is at 12q24 |
Mevalonate kinase deficiency is an example of loss-of-function mutation. There is a mutation in the gene which is coding for mevalonate kinase which is at 12q24 locus[http://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/hyper-igd-syndrome/]. There are almost 63 pathological sequence variations which is present throughout the 10 exons. The most common mutations are V377I, I268T, H20P/N and P167L. These mutations are present in 70% of the affected individuals [9]. A person with HIDS has two HIDS-mutations only id the parents of the patients are carriers. The risk of a child of parents who are both carriers to get the disease is 25%. In half of the cases, the child of such parents will be a carrier of the mutation. But a child does not always get the inherited predisposition. The inheritance of genes is purely coincidental. So, either all the children ae unaffected or three-fourth are affected. If the affected individual has both the mutations and he marries an unaffected individual, then the children of the affected individuals won’t be ill but will act as carrier . |
||
Immunoglobin D |
Immunoglobin D |
||
Immunoglobulin D (IgD) is a protein produced by a certain type of white blood cells. There are five classes of Immunoglobin like IgG, IgA and IgM, IgE and IgD. They play an important role in the immune system. The function of IgD is still unclear |
Immunoglobulin D (IgD) is a protein produced by a certain type of white blood cells. There are five classes of [[Immunoglobin]] like IgG, IgA and IgM, IgE and IgD. They play an important role in the immune system. The function of IgD is still unclear. |
||
[[File:Mevalonate Pathway Wiki Page.png|alt=The biosynthesis process of isoprenoids|thumb|The biosynthesis process of isoprenoids]] |
|||
=== Mechanism === |
|||
There is a relationship between MKD and the interleukin 1beta (IL-Iβ). There is an increased IL-1β secretion and mevalonate kinase deficiency in MKD is most likely mediated by defective protein prenylation (Prenylation refers to addition of hydrophobic residues to proteins) |
There is a relationship between MKD and the interleukin 1beta (IL-Iβ). There is an increased IL-1β secretion and mevalonate kinase deficiency in MKD is most likely mediated by defective protein [[prenylation]] (Prenylation refers to addition of hydrophobic residues to proteins) ] and non-sterol isoprenoids, such as [[farnesyl pyrophosphate]] (FPP) or [[geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate]] (GGPP) are coupled to a target protein, which affects the activity and the cellular location. In a human monocytic MKD model it was found that the deficiency of GGPP leads to overproduction of IL-1β and defective prenylation of RhoA. This causes an increased level of Rac1 and PKB which was affecting the GTPases and B7-Glycoproteins. It was earlier found that [[RAC1|Rac1]]/PI3K/PKB pathway had been linked to the pathogenesis of MKD. The inactivation of [[RHOA|RhoA]] acts an inducer of IL-1β mRNA transcription independent of NLRP3- or caspase-1 activity. Due to defective RhoA there is a formation of defective [[Mitochondrial DNA|mitochondria]] (elongated and instable) in the cell. If a defective mitochondria it is cleared in the cell by the mechanism of [[Autophagy|autophagia]]. But, in MKD the clearance of defective mitochondria from the cytosol is disrupted. As a result, the [[mitochondrial DNA]] starts accumulating inthe cytosol which binds and activates NLRP3 which is responsible for the production of IL-1β. The activation can be direct or indirect. It can also be activated by [[reactive oxygen species]] (ROS) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4491100/ <nowiki>[10]</nowiki>]. |
||
It is known that monocytes and macrophages also produce higher levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 6(IL-6) other than IL-Iβ [10]. During the febrile (fever) attacks and during the attacks the C - reactive protein (CRP) also increases. [9]. The CRP is released by liver which causes inflammation |
It is known that [[Monocyte|monocytes]] and [[Macrophage|macrophages]] also produce higher levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha ([[Tumor necrosis factor alpha|TNF-α]]), interleukin 6([[Interleukin-6 receptor|IL-6]]) other than [[IL-1β|IL-Iβ]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4491100/ <nowiki>[10]</nowiki>]. During the febrile (fever) attacks and during the attacks the C - reactive protein ([[C-reactive protein|CRP]]) also increases. [9]. The CRP is released by liver which causes inflammation[13]. |
||
=== Statistics === |
=== Statistics === |
||
| Line 30: | Line 31: | ||
* Canakinumab is a long acting monoclonal antibody which is directed against IL-1β has shown to be effective in reducing both frequency and severity in patients suffering from mild and severe MKD in case reports and observational case series. It reduces the physiological effects but the biochemical parameter still remain elevated (Galeotti et al. demonstrated that it is more effective than anakinra –considered 6 patients suffering from MKD). |
* Canakinumab is a long acting monoclonal antibody which is directed against IL-1β has shown to be effective in reducing both frequency and severity in patients suffering from mild and severe MKD in case reports and observational case series. It reduces the physiological effects but the biochemical parameter still remain elevated (Galeotti et al. demonstrated that it is more effective than anakinra –considered 6 patients suffering from MKD). |
||
* Anti-TNF therapy might be effective in MKD, but the effect is mostly partial and therapy failure and clinical deterioration have been described frequently in patients on infliximab or |
* Anti-TNF therapy might be effective in MKD, but the effect is mostly partial and therapy failure and clinical deterioration have been described frequently in patients on [[infliximab]] or [[Etanercept|etanercep]]<nowiki/>t [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4491100/ <nowiki>[10]</nowiki>]. A beneficial effect of human monoclonal anti-TNFα antibody adalimumab was seen in a small number of MKD patients. |
||
* Most MKD patients are benefited by anti-IL-1 therapy. However, anti-IL-1-resistant disease may also occur. Example. tocilizumab (a humanized monoclonal antibody against the interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor). This drug is used when the patients are unresponsive towards Anakinra. (Shendi et al. treated a young woman in whom anakinra was ineffective with tocilizumab). It was found that it was effective in reducing the biochemical and clinical inflammation [30].Stoffels et al. observed reduction of frequency and severity of the inflammatory attacks, although after several months of treatment one of these two patients persistently showed mild inflammatory symptoms in the absence of biochemical inflammatory markers. |
* Most MKD patients are benefited by anti-IL-1 therapy. However, anti-IL-1-resistant disease may also occur. Example. tocilizumab (a humanized monoclonal antibody against the interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor). This drug is used when the patients are unresponsive towards Anakinra. (Shendi et al. treated a young woman in whom [[anakinra]] was ineffective with [[tocilizumab]]). It was found that it was effective in reducing the biochemical and clinical inflammation [30].Stoffels et al. observed reduction of frequency and severity of the inflammatory attacks, although after several months of treatment one of these two patients persistently showed mild inflammatory symptoms in the absence of biochemical inflammatory markers. |
||
* A beneficial effect of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation can be used in severe mevalonate kinase deficiency conditions |
* A beneficial effect of [[hematopoietic stem cell transplantation]] can be used in severe mevalonate kinase deficiency conditions (Improvement of cerebral [[myelinisation]] on MRI after allogenic stem cell transplantation was observed in one girl). But, liver transplantation did not influence febrile attacks in this patient [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4491100/ <nowiki>[10]</nowiki>]. |
||
* Recently, Neven, et al. described a successful allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in an MVA patient. However, as this is a fairly new treatment, no evidence is present regarding its effect on neurological development [Neven B, Valayannopoulos V, Quartier P, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in mevalonic aciduria. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 2700-3]. |
* Recently, Neven, et al. described a successful allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in an MVA patient. However, as this is a fairly new treatment, no evidence is present regarding its effect on neurological development [Neven B, Valayannopoulos V, Quartier P, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in mevalonic aciduria. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 2700-3]. |
||
'''References''' |
'''References''' |
||
# Mevalonate kinase defficiency (MKD) (or Hyper IgD Syndrome) |
|||
# Clinical, Genetic, and Therapeutic Diversity in 2 Patients With Severe Mevalonate Kinase Defi ciency |
|||
# CURRENT ADVANCES IN THE UNDERSTANDING AND TREATMENT OF MEVALONATE KINASE DEFICIENCY |
|||
# http://www.omim.org/entry/610377 |
|||
# http://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?Lng=EN&Expert=29 |
|||
# https://hidsnet.wordpress.com/patientindex/background-information/ |
|||
# http://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2013/715465/ |
|||
# http://www.diseaseinfosearch.org/Mevalonic+aciduria/4722 |
|||
# '''Mevalonate kinase deficiency (hyper IgD syndrome with''' '''periodic fever) - different faces with separate treatments:''' '''two cases and review of the literature''' Pınar Gençpınar1, Balahan B. Makay2, Marco Gattorno3, Francesco Caroli4, Erbil Ünsal2 ''1 Department of Pediatrics, and 2Division of Pediatric Rheumatology, Department of Pediatrics, Dokuz Eylül University'' ''Faculty ofMedicine, İzmir, Turkey, and 3UO Pediatria II, Reumatologia, and 4Laboratorio di Genetica Molecolare, IstitutoG'' ''Gaslini, Genova, Italy. E-mail: erbil.unsal@deu. edu.tr'' |
|||
# http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4491100/ |
|||
# Mevalonic Aciduria in a Child Featuring Hepatic Fibrosis and Novel Mevalonate Kinase Mutations M. Harel-Meir, Y. Bujanover*, Y. Berkun, N. Goldstein and Y. Anikster Department of Pediatrics B, Safra Children's Hospital, Sheba Medical Center, Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel |
|||
# [Neven B, Valayannopoulos V, Quartier P, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in mevalonic aciduria. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 2700-3]. |
|||
# www.healthline.com/health/c-reactive-protein |
|||
Revision as of 17:36, 28 March 2016
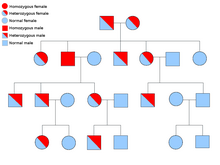
Introduction
Mevalonate kinase deficiency is a genetic disorder. MVA is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that disrupts the biosynthesis of cholesterol and isoprenoids. Discovery It was first described as HIDS in 1984. Within a short period of time, Prof. van der Meer and his colleagues saw a number of patients having strange, unexplained fever attacks, who all had high concentrations of IgD in their blood. They published a paper in a medical journal Lancet [1].It was found that, such a disease was never seen before [6]. Role The enzyme is involved in biosynthesis of cholesterols and isoprenoids. The enzyme is necessary for the conversion of mevalonate to mevalonate-5-phosphate in the presence of Mg2+ [Harper’s biochemistry manual]. Mevalonate kinase deficiency causes the accumulation of mevalonate in urine and hence the activity of the enzyme is again reduced [[[Mevalonate kinase deficiency|[2]].
Diagnosis
In many affected individuals the level of Immunoglobin D is elevated beyond the normal level and it is also known as HIDS (hyper-IgD with periodic fever syndrome) or mevalonate aciduria (MVA). The symptoms include painful swelling of lymph nodes (in the neck), skin rash, headache, and sore throat, ulcers in the mouth, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, joint pain and joint swelling, psychomotor delay, cataracts, recurrent febrile episodes [2] The small children have abnormally enlarged spleen known as splenomegaly [1, wiki, http://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/hyper-igd-syndrome/].. The severely affected individuals may develop fever attacks in the infant stage and may also have developmental delay, hypotonia, progressive ataxia, myopathy impaired vision and kidney damage [5]. In a patient hepatic fibrosis was also observed (uncommon in MKD) and also novel mutations V8F (t25a), and F38I (t112a) [11].
Genetics
Mevalonate kinase deficiency is an example of loss-of-function mutation. There is a mutation in the gene which is coding for mevalonate kinase which is at 12q24 locus[3]. There are almost 63 pathological sequence variations which is present throughout the 10 exons. The most common mutations are V377I, I268T, H20P/N and P167L. These mutations are present in 70% of the affected individuals [9]. A person with HIDS has two HIDS-mutations only id the parents of the patients are carriers. The risk of a child of parents who are both carriers to get the disease is 25%. In half of the cases, the child of such parents will be a carrier of the mutation. But a child does not always get the inherited predisposition. The inheritance of genes is purely coincidental. So, either all the children ae unaffected or three-fourth are affected. If the affected individual has both the mutations and he marries an unaffected individual, then the children of the affected individuals won’t be ill but will act as carrier .
Immunoglobin D
Immunoglobulin D (IgD) is a protein produced by a certain type of white blood cells. There are five classes of Immunoglobin like IgG, IgA and IgM, IgE and IgD. They play an important role in the immune system. The function of IgD is still unclear.

There is a relationship between MKD and the interleukin 1beta (IL-Iβ). There is an increased IL-1β secretion and mevalonate kinase deficiency in MKD is most likely mediated by defective protein prenylation (Prenylation refers to addition of hydrophobic residues to proteins) ] and non-sterol isoprenoids, such as farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) or geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) are coupled to a target protein, which affects the activity and the cellular location. In a human monocytic MKD model it was found that the deficiency of GGPP leads to overproduction of IL-1β and defective prenylation of RhoA. This causes an increased level of Rac1 and PKB which was affecting the GTPases and B7-Glycoproteins. It was earlier found that Rac1/PI3K/PKB pathway had been linked to the pathogenesis of MKD. The inactivation of RhoA acts an inducer of IL-1β mRNA transcription independent of NLRP3- or caspase-1 activity. Due to defective RhoA there is a formation of defective mitochondria (elongated and instable) in the cell. If a defective mitochondria it is cleared in the cell by the mechanism of autophagia. But, in MKD the clearance of defective mitochondria from the cytosol is disrupted. As a result, the mitochondrial DNA starts accumulating inthe cytosol which binds and activates NLRP3 which is responsible for the production of IL-1β. The activation can be direct or indirect. It can also be activated by reactive oxygen species (ROS) [10]. It is known that monocytes and macrophages also produce higher levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 6(IL-6) other than IL-Iβ [10]. During the febrile (fever) attacks and during the attacks the C - reactive protein (CRP) also increases. [9]. The CRP is released by liver which causes inflammation[13].
Statistics
In the world less than 1 in 1.00.000 have HIDS [5]. 200 individuals throughout the world do suffer from MVK [4]. At this moment, no family with HIDS is known in which this has happened, because the disease is so rare. A rough estimate is that at most about 1 in 500 persons in the Netherlands are carrier of a HIDS-mutation. So for a Dutch patient marrying a Dutch partner, the chances of a child with HIDS are at most 1 in 1000[6]. A paper on case study of two patients suffering from HIDS was published as ‘The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics’ in 2012 [9].
Treatment
There is no treatment for MKD. But, the inflammation and the other effects can be reduced to a certain extent.
- IL-1 targeting drugs can be used to reduce the effects of the disorder. Anakinra is antagonist to IL-1 receptors. Anakinra binds the IL-1 receptor, preventing the actions of both IL-1α and IL-1β, and it has been proved to reduce the clinical and biochemical inflammation in MKD. It can effectively decreases the frequency as well as the severity of inflammatory attacks when used on a daily basis. Disadvantages with the usage of this drug are occurrence of painful injection site reaction and as the drug is discontinued in the near future the febrile attacks start. (Examined in a 12 year old patient).
- Canakinumab is a long acting monoclonal antibody which is directed against IL-1β has shown to be effective in reducing both frequency and severity in patients suffering from mild and severe MKD in case reports and observational case series. It reduces the physiological effects but the biochemical parameter still remain elevated (Galeotti et al. demonstrated that it is more effective than anakinra –considered 6 patients suffering from MKD).
- Anti-TNF therapy might be effective in MKD, but the effect is mostly partial and therapy failure and clinical deterioration have been described frequently in patients on infliximab or etanercept [10]. A beneficial effect of human monoclonal anti-TNFα antibody adalimumab was seen in a small number of MKD patients.
- Most MKD patients are benefited by anti-IL-1 therapy. However, anti-IL-1-resistant disease may also occur. Example. tocilizumab (a humanized monoclonal antibody against the interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor). This drug is used when the patients are unresponsive towards Anakinra. (Shendi et al. treated a young woman in whom anakinra was ineffective with tocilizumab). It was found that it was effective in reducing the biochemical and clinical inflammation [30].Stoffels et al. observed reduction of frequency and severity of the inflammatory attacks, although after several months of treatment one of these two patients persistently showed mild inflammatory symptoms in the absence of biochemical inflammatory markers.
- A beneficial effect of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation can be used in severe mevalonate kinase deficiency conditions (Improvement of cerebral myelinisation on MRI after allogenic stem cell transplantation was observed in one girl). But, liver transplantation did not influence febrile attacks in this patient [10].
- Recently, Neven, et al. described a successful allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in an MVA patient. However, as this is a fairly new treatment, no evidence is present regarding its effect on neurological development [Neven B, Valayannopoulos V, Quartier P, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in mevalonic aciduria. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 2700-3].
References
- Mevalonate kinase defficiency (MKD) (or Hyper IgD Syndrome)
- Clinical, Genetic, and Therapeutic Diversity in 2 Patients With Severe Mevalonate Kinase Defi ciency
- CURRENT ADVANCES IN THE UNDERSTANDING AND TREATMENT OF MEVALONATE KINASE DEFICIENCY
- http://www.omim.org/entry/610377
- http://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?Lng=EN&Expert=29
- https://hidsnet.wordpress.com/patientindex/background-information/
- http://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2013/715465/
- http://www.diseaseinfosearch.org/Mevalonic+aciduria/4722
- Mevalonate kinase deficiency (hyper IgD syndrome with periodic fever) - different faces with separate treatments: two cases and review of the literature Pınar Gençpınar1, Balahan B. Makay2, Marco Gattorno3, Francesco Caroli4, Erbil Ünsal2 1 Department of Pediatrics, and 2Division of Pediatric Rheumatology, Department of Pediatrics, Dokuz Eylül University Faculty ofMedicine, İzmir, Turkey, and 3UO Pediatria II, Reumatologia, and 4Laboratorio di Genetica Molecolare, IstitutoG Gaslini, Genova, Italy. E-mail: erbil.unsal@deu. edu.tr
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4491100/
- Mevalonic Aciduria in a Child Featuring Hepatic Fibrosis and Novel Mevalonate Kinase Mutations M. Harel-Meir, Y. Bujanover*, Y. Berkun, N. Goldstein and Y. Anikster Department of Pediatrics B, Safra Children's Hospital, Sheba Medical Center, Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel
- [Neven B, Valayannopoulos V, Quartier P, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in mevalonic aciduria. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 2700-3].
- www.healthline.com/health/c-reactive-protein
