Triangle wave: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
{{Listen|filename=220 Hz anti-aliased triangle wave.ogg|title=Triangle wave sound sample|description=5 seconds of [[anti-aliasing|anti-aliased]] triangle wave at 220 Hz|format=[[Ogg]]}} |
{{Listen|filename=220 Hz anti-aliased triangle wave.ogg|title=Triangle wave sound sample|description=5 seconds of [[anti-aliasing|anti-aliased]] triangle wave at 220 Hz|format=[[Ogg]]}} |
||
Another definition of the triangle wave, with period 2''a'' is: |
Another definition of the triangle wave, with range from -1 to 1 and period 2''a'' is: |
||
<math> x(t)=(t-a \left \lfloor\frac{t}{a}-\frac{1}{2} \right \rfloor)(-1)^\left \lfloor\frac{t}{a}-\frac{1}{2} \right \rfloor</math> |
<math> x(t)=\frac{2}{a} \left (t-a \left \lfloor\frac{t}{a}-\frac{1}{2} \right \rfloor \right )(-1)^\left \lfloor\frac{t}{a}-\frac{1}{2} \right \rfloor</math> |
||
Also, the triangle wave can be the absolute value of the [[sawtooth wave]]:<br> |
|||
<math> x(t)= \left | 2 \left ( {t \over a} - \left \lfloor {t \over a} + {1 \over 2} \right \rfloor \right) \right | </math> |
|||
The triangle wave can also be expressed as the integral of the [[square wave]]:<br> |
The triangle wave can also be expressed as the integral of the [[square wave]]:<br> |
||
Revision as of 22:39, 8 January 2010
A triangle wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform named for its triangular shape.
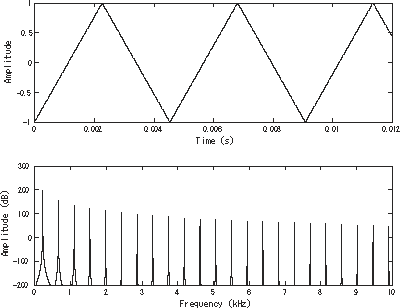
Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics. However, the higher harmonics roll off much faster than in a square wave (proportional to the inverse square of the harmonic number as opposed to just the inverse).
It is possible to approximate a triangle wave with additive synthesis by adding odd harmonics of the fundamental, multiplying every (4n−1)th harmonic by −1 (or changing its phase by π), and rolling off the harmonics by the inverse square of their relative frequency to the fundamental.
This infinite Fourier series converges to the triangle wave:

Another definition of the triangle wave, with range from -1 to 1 and period 2a is:
Also, the triangle wave can be the absolute value of the sawtooth wave:
The triangle wave can also be expressed as the integral of the square wave:
See also






