Omohyoid muscle: Difference between revisions
m robot Modifying: es:Músculo homohioideo |
Adamlankford (talk | contribs) →Innervation: Added differences in innervation between the superior and inferior bellies |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
==Innervation== |
==Innervation== |
||
The omohyoid is innervated by a branch of the [[cervical plexus]], the ansa cervicalis, and mostly acts to stabilise the hyoid bone. |
The omohyoid is innervated by a branch of the [[cervical plexus]], the ansa cervicalis, and mostly acts to stabilise the hyoid bone. Although the inferior belly of the omohyoid is innervated by branches of all three cervical rami (C1-C3) that make up the ansa cervicalis, the superior belly is innervated by the [[superior root of ansa cervicalis]] which contains only fibers from the first cervical spinal nerves (C1). |
||
==Additional images== |
==Additional images== |
||
Revision as of 20:38, 2 June 2010
| Omohyoid muscle | |
|---|---|
 Side of neck, showing chief surface markings. (Omohyoid visible at center.) | |
 Muscles of the neck. Anterior view. Omohyoid is labeled on both sides. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Upper border of the scapula |
| Insertion | Hyoid bone |
| Nerve | Ansa cervicalis (C1-C3) |
| Actions | Depresses the larynx and hyoid bone. Also carries hyoid bone backward and to the side. |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus omohyoideus |
| TA98 | A04.2.04.003 |
| TA2 | 2169 |
| FMA | 13342 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
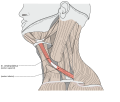
The omohyoid muscle is a muscle at the front of the neck that consists of two bellies separated by an intermediate tendon. It belongs to the group of infrahyoid muscles.
Structure
It arises from the upper border of the scapula, and occasionally from the superior transverse scapular ligament which crosses the scapular notch, its extent of attachment to the scapula varying from a few millimetres to 2.5 cm.
From this origin, the inferior belly forms a flat, narrow fasciculus, which inclines forward and slightly upward across the lower part of the neck, being bound down to the clavicle by a fibrous expansion; it then passes behind the sternocleidomastoid, becomes tendinous and changes its direction, forming an obtuse angle.
It ends in the superior belly, which passes almost vertically upward, close to the lateral border of the sternohyoid, to be inserted into the lower border of the body of the hyoid bone, lateral to the insertion of the sternohyoid.
The central tendon of this muscle varies much in length and form, and is held in position by a process of the deep cervical fascia, which sheaths it, and is prolonged down to be attached to the clavicle and first rib; it is by this means that the angular form of the muscle is maintained.
Triangles
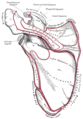
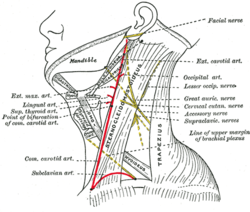
The inferior belly of the omohyoid divides the posterior triangle of the neck into an upper or occipital triangle and a lower or subclavian triangle.
Its superior belly divides the anterior triangle into an upper or carotid triangle and a lower or muscular triangle.
The Omohyoid muscle is proximally attached to the scapula and distally attached to the hyoid bone.
Variations
Doubling; absence; origin from clavicle; absence or doubling of either belly.
Innervation
The omohyoid is innervated by a branch of the cervical plexus, the ansa cervicalis, and mostly acts to stabilise the hyoid bone. Although the inferior belly of the omohyoid is innervated by branches of all three cervical rami (C1-C3) that make up the ansa cervicalis, the superior belly is innervated by the superior root of ansa cervicalis which contains only fibers from the first cervical spinal nerves (C1).
Additional images
-
Hyoid bone. Anterior surface. Enlarged.
-
Left scapula. Dorsal surface.
-
Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. Showing the arrangement of the fascia coli.
-
Muscles of the neck. Lateral view.
-
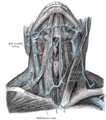
Superficial dissection of the right side of the neck, showing the carotid and subclavian arteries.
-
The veins of the neck, viewed from in front.
-
Hypoglossal nerve, cervical plexus, and their branches.
-
The right brachial plexus with its short branches, viewed from in front.
-
Musculi colli omohyoideus
The omohyoid muscle is innervated by the ansa cervicalis from the cervical plexus (C1-3)
External links
- . GPnotebook https://www.gpnotebook.co.uk/simplepage.cfm?ID=-1335164848.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - Anatomy photo:24:06-0100 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy figure: 24:01-09 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Template:MuscleLoyola
- lesson6 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 392 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 392 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)