Organ of Corti: Difference between revisions
Section deleted, content moved to lead. |
added citation.... |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
DorlandsSuf = 12596269 | |
DorlandsSuf = 12596269 | |
||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''organ of Corti''' (or '''spiral organ''') is the organ in the [[inner ear]] |
The '''organ of Corti''' (or '''spiral organ''') is the organ in the [[inner ear]] that is unique to [[mammal]]s that contains auditory sensory cells, or "[[hair cell]]s."<ref>[http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/organ+of+Corti Dictionary.com] - organ of Corti - LLC. Copyright © 2010. All rights reserved.</ref> |
||
The organ was named after the Italian anatomist Marquis [[Alfonso Giacomo Gaspare Corti]] (1822-1876), who conducted microscopic research of the mammalian auditory system. |
The organ was named after the Italian anatomist Marquis [[Alfonso Giacomo Gaspare Corti]] (1822-1876), who conducted microscopic research of the mammalian auditory system. |
||
Revision as of 08:54, 17 July 2010
| Organ of Corti | |
|---|---|
 A cross section of the cochlea illustrating the organ of Corti. | |
 Section through the spiral organ of Corti. Magnified. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | organum spirale |
| MeSH | D009925 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_2526 |
| TA98 | A15.3.03.121 |
| TA2 | 7035 |
| FMA | 75715 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The organ of Corti (or spiral organ) is the organ in the inner ear that is unique to mammals that contains auditory sensory cells, or "hair cells."[1]
The organ was named after the Italian anatomist Marquis Alfonso Giacomo Gaspare Corti (1822-1876), who conducted microscopic research of the mammalian auditory system.
Structure and function
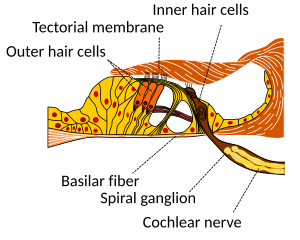
The organ of Corti has highly specialized structures that respond to fluid-borne vibrations in the cochlea with a shearing vector in the hairs of some cochlear hair cells. It contains between 15,000-20,000 auditory nerve receptors. Each receptor has its own hair cell. The shear on the hairs opens ion channels, leading to neural, electrical signaling to the auditory cortex. The pinna and middle ear act as mechanical transformers, so that by the time sound waves reach the Organ of Corti, their pressure amplitude is 22 times that of the air impinging on the pinna. The Organ of Corti can be damaged by excessive sound levels, leading to noise induced health effects. The Organ of Corti is the structure that transduces pressure waves to action potentials.
Hearing loss
The most common kind of hearing impairment, sensorineural hearing loss, includes as one major cause the reduction of function in the organ of Corti. Specifically, the active amplification function of the outer hair cells is very sensitive to damage from exposure to trauma from overly-loud sounds or to certain "ototoxic" drugs. Once outer hair cells are damaged, they do not regenerate, and the result is a loss of sensitivity and an abnormally large growth of loudness (known as recruitment) in the part of the spectrum that the damaged cells serve.[2]
Additional images
-
Transverse section of the cochlear duct of a fetal cat.
-
Diagrammatic longitudinal section of the cochlea.
-
Floor of ductus cochlearis.
-
Limbus laminæ spiralis and membrana basilaris.
-
Section through the spiral organ of Corti. Magnified.
Notes
- ^ Dictionary.com - organ of Corti - LLC. Copyright © 2010. All rights reserved.
- ^ Robert A. Dobie (2001). Medical-Legal Evaluation of Hearing Loss. Thomson Delmar Learning. ISBN 0769300529.
References
- Corti A (1851) "Recherches sur l'organe de Corti de l'ouïe des mammifères". Z wiss Zool 3: 1-106.
- Pritchard U. "On the organ of Corti in mammals". 2 March 1876, Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, volume 24, pp.346-52 OCLC 1778190
External links
- http://lobe.ibme.utoronto.ca/presentations/OHC_Electromotility/sld005.htm Diagram at University of Toronto
- http://mayoresearch.mayo.edu/mayo/research/ent_research/images/image02.gif Diagram at Mayo
- http://www.iurc.montp.inserm.fr/cric51/audition/english/corti/fcorti.htm at University of Montpellier 1