United States Department of Education: Difference between revisions
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
Unlike the systems of most other countries, [[education in the United States]] is highly decentralized, and the federal government and Department of Education are not heavily involved in determining curricula or educational standards (with the recent exception of the [[No Child Left Behind Act]]). This has been left to state and local school districts. The quality of educational institutions and their degrees is maintained through an informal private process known as [[educational accreditation|accreditation]], over which the Department of Education has no direct public jurisdictional control. |
Unlike the systems of most other countries, [[education in the United States]] is highly decentralized, and the federal government and Department of Education are not heavily involved in determining curricula or educational standards (with the recent exception of the [[No Child Left Behind Act]]). This has been left to state and local school districts. The quality of educational institutions and their degrees is maintained through an informal private process known as [[educational accreditation|accreditation]], over which the Department of Education has no direct public jurisdictional control. |
||
Rather, the primary function of the Department of Education is to formulate federal funding programs involving education and to enforce federal educational laws regarding privacy and civil rights. |
Rather, the primary function of the Department of Education is to [http://www.evolutionwriters.com/ writing services] formulate federal funding programs involving education and to enforce federal educational laws regarding privacy and civil rights. |
||
On March 23, 2007, President [[George W. Bush]] signed into law H.R. 584, which designates the ED Headquarters building as the [[Lyndon Baines Johnson]] Department of Education Building.<sup>[http://georgewbush-whitehouse.archives.gov/news/releases/2007/03/20070323-6.html]</sup> |
On March 23, 2007, President [[George W. Bush]] signed into law H.R. 584, which designates the ED Headquarters building as the [[Lyndon Baines Johnson]] Department of Education Building.<sup>[http://georgewbush-whitehouse.archives.gov/news/releases/2007/03/20070323-6.html]</sup> |
||
Revision as of 09:48, 1 October 2010
 Seal of the US Department of Education | |
| Department overview | |
|---|---|
| Formed | October 17, 1979 |
| Preceding agencies |
|
| Jurisdiction | Federal government of the United States |
| Employees | 5,000 (2007) |
| Annual budget | US$32 billion (2009)[1] US$56 billion (est. 2010) US$71 billion (est. 2011) ARRA Funding: US$102 billion (2009)[2] US$51 billion (est. 2010) US$23 billion (est. 2011) |
| Department executives |
|
| Child Department | |
| Website | www.ed.gov |

The United States Department of Education, also referred to as ED or the ED for (the) Education Department, is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government. Created by the Department of Education Organization Act (Public Law 96-88) and signed into law by President Jimmy Carter on October 17, 1979, it began operating on May 16, 1980.
The Department of Education Organization Act divided the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare into the Department of Education and the Department of Health and Human Services. The Department of Education is administered by the United States Secretary of Education.
It is by far the smallest Cabinet-level department, with about 5,000 employees. The agency's official acronym is ED (and not DOE, which refers to the United States Department of Energy). It is also often abbreviated informally as DoED.
Establishment
A previous Department of Education was created in 1867 but soon was demoted to an Office in 1868. As an agency not represented in the president's cabinet, it quickly became a relatively minor bureau in the Department of the Interior. In 1939, the bureau was transferred to the Federal Security Agency, where it was renamed the Office of Education. In 1953, the Federal Security Agency was upgraded to cabinet-level status as the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare.
Upgrading Education to cabinet level status a century later in 1979 was controversial and opposed by many in the Republican Party, who saw the department as an unconstitutional, unnecessary federal bureaucratic intrusion into local affairs.
Unlike the systems of most other countries, education in the United States is highly decentralized, and the federal government and Department of Education are not heavily involved in determining curricula or educational standards (with the recent exception of the No Child Left Behind Act). This has been left to state and local school districts. The quality of educational institutions and their degrees is maintained through an informal private process known as accreditation, over which the Department of Education has no direct public jurisdictional control.
Rather, the primary function of the Department of Education is to writing services formulate federal funding programs involving education and to enforce federal educational laws regarding privacy and civil rights.
On March 23, 2007, President George W. Bush signed into law H.R. 584, which designates the ED Headquarters building as the Lyndon Baines Johnson Department of Education Building.[2]
Organization
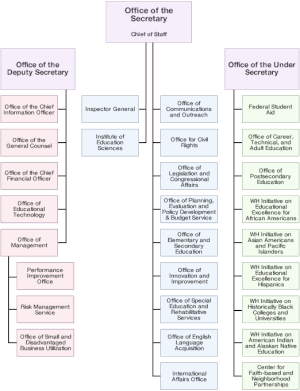
- Office of Communications and Outreach (OCO)
- Office of the General Counsel (OGC)
- Office of Inspector General
- Office of Legislation and Congressional Affairs (OLCA)
- Office for Civil Rights (OCR)
- Institute of Education Sciences (IES)
- Office of Innovation and Improvement (OII)
- Office of the Chief Financial Officer
- Office of Management
- Office of the Chief Information Officer
- Office of Planning, Evaluation and Policy Development
- Risk Management Service
- Office of Postsecondary Education (OPE)
- Office of Vocational and Adult Education (OVAE)
- Office of Federal Student Aid (FSA)
- President's Advisory Board on Tribal Colleges and Universities (WHITCU)
- President's Advisory Board on Historically Black Colleges and Universities (WHIHBCU)
- Office of Elementary and Secondary Education (OESE)
- Office of English Language Acquisition, Language Enhancement and Academic Achievement for Limited English Proficient Students (OELA)
- Office of Special Education and Rehabilitative Services (OSERS)
- Office of Safe and Drug Free Schools (OSDFS)
- Office of Innovation and Improvement
- Associated federal organizations
- Advisory Councils and Committees
- National Assessment Governing Board (NAGB)[3]
- National Institute for Literacy (NIFL)[4]
- Federal Interagency Committee on Education (FICE)
- Federally aided organizations
Opposition
President Ronald Reagan promised during the 1980 presidential election to eliminate the Department of Education as a cabinet post,[3] but he was not able to do so with a Democratic House of Representatives. In the 1982 State of the Union Address, he pledged:
The budget plan I submit to you on Feb. 8 will realize major savings by dismantling the Department of Education.[4]
Throughout the 1980s, the abolition of the Department of Education was a part of the Republican Party platform, but the administration of President George H. W. Bush declined to implement this idea. In 1996, the Republican Party made abolition of the Department a cornerstone of their campaign promises, calling it an inappropriate federal intrusion into local, state, and family affairs.[4] The GOP platform read:
The Federal government has no constitutional authority to be involved in school curricula or to control jobs in the market place. This is why we will abolish the Department of Education, end federal meddling in our schools, and promote family choice at all levels of learning.[4][5]
During his 1996 presidential run, Senator Bob Dole promised, "We're going to cut out the Department of Education."[5]
In 2000, the Republican Liberty Caucus passed a resolution to abolish the Department of Education.[6]
Abolition of the organization was not pursued under the George W. Bush administration, which made reform of federal education a key priority of the President's first term. In 2008, presidential candidate Ron Paul campaigned in part on an opposition to the Department.[7]
No Child Left Behind

Under President George W. Bush, the Department primarily focused on elementary and secondary education, expanding its reach through the "No Child Left Behind" law. The Department's budget increased 69.6% between 2002 and 2004.[4]
FICE Code
As with other federal agencies, the ED operates with the assistance of several advisory committees. The Federal Interagency Committee on Education (FICE) is known in higher education for originating the FICE code, the six-digit institutional identifier assigned to each higher education (two-year and above) institution.
The FICE code is a six-digit identification code that was used to identify all schools doing business with the Office of Education during the early sixties. This code is no longer used in IPEDS; it has been replaced by the Office of Postsecondary Education (OPE) ID code.[8]
Budget
For 2006, the ED discretionary budget was US$56 billion and the mandatory budget contained $23.4 billion. Currently, the budget is $68.6 billion, according to the Dept. of Education website.
Related legislation
- 1965: Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA)
- 1965: Higher Education Act of 1965 (HEA) (Pub. L. No. 89-329)
- 1974: Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA)
- 1974: Equal Educational Opportunities Act of 1974 (EEOA)
- 1975: Education for All Handicapped Children Act (EHA) (Pub. L. No. 94-142)
- 1978: Protection of Pupil Rights Amendment
- 1980: Department of Education Organization Act (Pub. L. No. 96-88)
- 1984: Equal Access Act
- 1990: The Jeanne Clery Disclosure of Campus Security Policy and Campus Crime Statistics Act (Clery Act)
- 1994: Improving America's Schools Act of 1994
- 2001: No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB)
- 2004: Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
- 2005: Higher Education Reconciliation Act of 2005 (HERA) (Pub. L. No. 109-171)
- 2006: Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Improvement Act
- 2007: America COMPETES Act
- 2008: Higher Education Opportunity Act (HEOA) (Pub. L. No. 110-315)
- 2009: Race to the Top
- 2009: Student Aid and Fiscal Responsibility Act
- 2010: Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010
See also
{{{inline}}}
- Educational attainment in the United States
- Education in the United States
- Secretary of Education
- Office of Federal Student Aid
- Free Application for Federal Student Aid
- Council for Higher Education Accreditation
- National Diffusion Network
- School Improvement Grant
References
- ^ FY2011 Federal Budget
- ^ FY2011 Federal Budget
- ^ "Online Backgrounders: The Department of Education". PBS. Fall 1996. Retrieved 2005-07-26.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ a b c d "Elimination Lost: What happened to abolishing the Department of Education?". Cato Institute. 2004-02-11. Retrieved 2005-07-26.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ a b "Department of Education must be abolished". World Net Daily. 2004-12-07. Retrieved 2005-07-26.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Education". 2007. Retrieved 2007-09-14.
- ^ Stossel, John (2007-12-10). "Ron Paul Unplugged". ABC News. Retrieved 2008-01-30.
- ^ "IPEDS Glossary". Retrieved 2007-04-07.
Further reading
- Cabinetmakers: Story of the Three-Year Battle to Establish the U.S. Department of Education. Author: Robert V. Heffernan. 2001. ISBN: 9780595158706
External links
- United States Department of Education Official Website
- How is the Department of Education Organized
- ERIC Digests - Informational digests on educational topics produced by the U.S. Department of Education before 1983.
- Proposed and finalized federal regulations from the United States Department of Education
- Speech writing
You may be looking for
- Template:United States federal executive departments, a template to which this was previously a redirect
- Template:Infobox cabinet members
- Template:Infobox Colombia Cabinet
{{Template disambiguation}} should never be transcluded in the main namespace.

