Human scale: Difference between revisions
Archon 2488 (talk | contribs) |
Reverted metrification of article as no consensus exists to do this |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
* [[Attention span]]: seconds to hours |
* [[Attention span]]: seconds to hours |
||
* [[Life expectancy|Life span]]: approximately 75 years |
* [[Life expectancy|Life span]]: approximately 75 years |
||
* [[Mass]]: [[1 E0 kg|kilograms]] |
* [[Mass]]: [[1 E0 kg|kilograms]] |
||
* [[Force]]: [[Newton (unit)|newton]]s |
* [[Force]]: [[Newton (unit)|newton]]s |
||
* [[Pressure]]: one [[standard atmosphere]] |
* [[Pressure]]: one [[standard atmosphere]] |
||
* [[Temperature]]: around 300 |
* [[Temperature]]: around 300 K (room temperature) |
||
== Human scale in architecture == |
== Human scale in architecture == |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
Human scale in architecture is deliberately violated: |
Human scale in architecture is deliberately violated: |
||
* for monumental effect. Buildings, statues, and memorials are constructed in a scale larger than life as a social/cultural signal that the subject matter is also larger than life. |
* for monumental effect. Buildings, statues, and memorials are constructed in a scale larger than life as a social/cultural signal that the subject matter is also larger than life. The extreme example is the [[The Motherland Calls|Rodina (Motherland) statue]] in [[Volgograd]] (Stalingrad). |
||
* for aesthetic effect. Many architects, particularly in the [[Modernist]] movement, design buildings that prioritize structural purity and clarity of form over concessions to human scale. This became the dominant American architectural style for decades. Some notable examples among many are [[Henry N. Cobb|Henry Cobb]]'s [[John Hancock Tower]] in [[Boston, Massachusetts|Boston]], much of [[I. M. Pei]]'s work including the [[Dallas City Hall]], and [[Mies van der Rohe]]'s [[Neue Nationalgalerie]] in [[Berlin]]. |
* for aesthetic effect. Many architects, particularly in the [[Modernist]] movement, design buildings that prioritize structural purity and clarity of form over concessions to human scale. This became the dominant American architectural style for decades. Some notable examples among many are [[Henry N. Cobb|Henry Cobb]]'s [[John Hancock Tower]] in [[Boston, Massachusetts|Boston]], much of [[I. M. Pei]]'s work including the [[Dallas City Hall]], and [[Mies van der Rohe]]'s [[Neue Nationalgalerie]] in [[Berlin]]. |
||
* to serve automotive scale. Commercial buildings that are designed to be legible from roadways assume a radically different shape. The human eye can distinguish about 3 objects or features per second. A pedestrian steadily walking along a |
* to serve automotive scale. Commercial buildings that are designed to be legible from roadways assume a radically different shape. The human eye can distinguish about 3 objects or features per second. A pedestrian steadily walking along a 100-foot (30-meter) length of department store can perceive about 68 features; a driver passing the same frontage at 30 mph (13 m/s or 44 ft/s) can perceive about six or seven features. Auto-scale buildings tend to be smooth and shallow, readable at a glance, simplified, presented outward, and with signage with bigger letters and fewer words. This urban form is traceable back to the innovations of developer A. W. Ross along [[Miracle Mile, Los Angeles, California|Wilshire Boulevard]] in Los Angeles in 1920. |
||
== Common sense and human scale == |
== Common sense and human scale == |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
"[[Common sense]]" ideas tend to relate to events within human experience, and thus commensurate with these scales. There is thus no commonsense intuition of, for example, interstellar distances or speeds approaching the speed of light. |
"[[Common sense]]" ideas tend to relate to events within human experience, and thus commensurate with these scales. There is thus no commonsense intuition of, for example, interstellar distances or speeds approaching the speed of light. |
||
[[Weights and measures]] tend to reflect human scale, and many older systems of measurement featured units based directly on the dimensions of the body |
[[Weights and measures]] tend to reflect human scale, and many older systems of measurement featured units based directly on the dimensions of the body. The [[metric system]], which is based on other more reproducible physical quantities, still attempts to keep its base units within the range of human experience. Other systems, such as [[Planck units]] are useful for theoretical purposes, but are not useful for everyday purposes. |
||
==Quotes== |
==Quotes== |
||
Revision as of 20:30, 25 June 2014
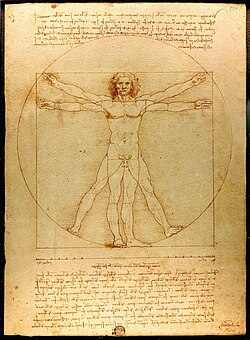
Human scale is the set of physical qualities, and quantities of information, characterizing the human body, its motor, sensory, or mental capabilities, and human social institutions.
Science vs. human scale
Many of the objects of scientific interest in the universe are much larger than human scale (stars, galaxies) or much smaller than human scale (molecules, atoms, subatomic particles).
Similarly, many time periods studied in science involve time scales much greater than human timescales (geological and cosmological time scales) or much shorter than human timescales (atomic and subatomic events).
Mathematicians and scientists use very large and small numbers to describe physical quantities, and have created even larger and smaller numbers for theoretical purposes.
Human scale measurements, however, are more in the order of:
- Distance: one to two metres (human arm's reach, stride, height)
- Attention span: seconds to hours
- Life span: approximately 75 years
- Mass: kilograms
- Force: newtons
- Pressure: one standard atmosphere
- Temperature: around 300 K (room temperature)
Human scale in architecture
Humans interact with their environments based on their physical dimensions, capabilities and limits. The field of anthropometrics (human measurement) has unanswered questions, but it's still true that human physical characteristics are fairly predictable and objectively measurable. Buildings scaled to human physical capabilities have steps, doorways, railings, work surfaces, seating, shelves, fixtures, walking distances, and other features that fit well to the average person.
Humans also interact with their environments based on their sensory capabilities. The fields of human perception systems, like perceptual psychology and cognitive psychology, are not exact sciences, because human information processing is not a purely physical act, and because perception is affected by cultural factors, personal preferences, experiences, and expectations. So human scale in architecture can also describe buildings with sightlines, acoustic properties, task lighting, ambient lighting, and spatial grammar that fit well with human senses. However, one important caveat is that human perceptions are always going to be less predictable and less measurable than physical dimensions.
Human scale in architecture is deliberately violated:
- for monumental effect. Buildings, statues, and memorials are constructed in a scale larger than life as a social/cultural signal that the subject matter is also larger than life. The extreme example is the Rodina (Motherland) statue in Volgograd (Stalingrad).
- for aesthetic effect. Many architects, particularly in the Modernist movement, design buildings that prioritize structural purity and clarity of form over concessions to human scale. This became the dominant American architectural style for decades. Some notable examples among many are Henry Cobb's John Hancock Tower in Boston, much of I. M. Pei's work including the Dallas City Hall, and Mies van der Rohe's Neue Nationalgalerie in Berlin.
- to serve automotive scale. Commercial buildings that are designed to be legible from roadways assume a radically different shape. The human eye can distinguish about 3 objects or features per second. A pedestrian steadily walking along a 100-foot (30-meter) length of department store can perceive about 68 features; a driver passing the same frontage at 30 mph (13 m/s or 44 ft/s) can perceive about six or seven features. Auto-scale buildings tend to be smooth and shallow, readable at a glance, simplified, presented outward, and with signage with bigger letters and fewer words. This urban form is traceable back to the innovations of developer A. W. Ross along Wilshire Boulevard in Los Angeles in 1920.
Common sense and human scale
"Common sense" ideas tend to relate to events within human experience, and thus commensurate with these scales. There is thus no commonsense intuition of, for example, interstellar distances or speeds approaching the speed of light.
Weights and measures tend to reflect human scale, and many older systems of measurement featured units based directly on the dimensions of the body. The metric system, which is based on other more reproducible physical quantities, still attempts to keep its base units within the range of human experience. Other systems, such as Planck units are useful for theoretical purposes, but are not useful for everyday purposes.
Quotes
- "Man is the measure of all things, of things that are, that they are; and of things that are not, that they are not". -- Protagoras
See also
- Anthropic principle
- Anthropic units
- Anthropometrics
- Ergonomics
- List of human-based units of measure
- Scales of measurement
- Small Is Beautiful
- Standard temperature and pressure
