Osmosis: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by Ajaryanxyz73 (talk) to last version by ClueBot NG |
Ajaryanxyz73 (talk | contribs) No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
[[File:Osmosis computer simulation.jpg|thumb|One frame of a computer simulation of osmosis]] |
[[File:Osmosis computer simulation.jpg|thumb|One frame of a computer simulation of osmosis]] |
||
The [[osmotic pressure]] is defined to be the [[pressure]] required to maintain an equilibrium, with no net movement of solvent. Osmotic pressure is a [[colligative properties|colligative property]], meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the [[Concentration#Molarity|molar concentration]] of the solute but not on its identity. |
The [[osmotic pressure]] is defined to be the minimum [[pressure]] required to maintain an equilibrium, with no net movement of solvent. Osmotic pressure is a [[colligative properties|colligative property]], meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the [[Concentration#Molarity|molar concentration]] of the solute but not on its identity. |
||
Osmosis is a vital process in [[biology|biological systems]], as [[biological membrane]]s are semipermeable. In general, these membranes are impermeable to large and [[chemical polarity|polar]] molecules, such as [[ions]], [[proteins]], and [[polysaccharides]], while being permeable to non-polar and/or [[hydrophobic]] molecules like [[lipids]] as well as to small molecules like oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and nitric oxide. Permeability depends on solubility, charge, or chemistry, as well as solute size. Water molecules travel through the plasma membrane, tonoplast membrane (vacuole) or protoplast by diffusing across the phospholipid bilayer via [[aquaporin]]s (small transmembrane proteins similar to those responsible for facilitated [[diffusion]] and ion channels). Osmosis provides the primary means by which [[water]] is transported into and out of [[cell (biology)|cells]]. The [[turgor]] pressure of a cell is largely maintained by osmosis across the cell membrane between the cell interior and its relatively hypotonic environment. |
Osmosis is a vital process in [[biology|biological systems]], as [[biological membrane]]s are semipermeable. In general, these membranes are impermeable to large and [[chemical polarity|polar]] molecules, such as [[ions]], [[proteins]], and [[polysaccharides]], while being permeable to non-polar and/or [[hydrophobic]] molecules like [[lipids]] as well as to small molecules like oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and nitric oxide. Permeability depends on solubility, charge, or chemistry, as well as solute size. Water molecules travel through the plasma membrane, tonoplast membrane (vacuole) or protoplast by diffusing across the phospholipid bilayer via [[aquaporin]]s (small transmembrane proteins similar to those responsible for facilitated [[diffusion]] and ion channels). Osmosis provides the primary means by which [[water]] is transported into and out of [[cell (biology)|cells]]. The [[turgor]] pressure of a cell is largely maintained by osmosis across the cell membrane between the cell interior and its relatively hypotonic environment. |
||
Revision as of 07:53, 3 July 2014
This article's factual accuracy is disputed. (April 2013) |

Osmosis is the spontaneous net movement of solvent molecules through a partially permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides.[1][2][3] It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a semipermeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations.[4][5] Osmosis can be made to do work.[6]

The osmotic pressure is defined to be the minimum pressure required to maintain an equilibrium, with no net movement of solvent. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity.
Osmosis is a vital process in biological systems, as biological membranes are semipermeable. In general, these membranes are impermeable to large and polar molecules, such as ions, proteins, and polysaccharides, while being permeable to non-polar and/or hydrophobic molecules like lipids as well as to small molecules like oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and nitric oxide. Permeability depends on solubility, charge, or chemistry, as well as solute size. Water molecules travel through the plasma membrane, tonoplast membrane (vacuole) or protoplast by diffusing across the phospholipid bilayer via aquaporins (small transmembrane proteins similar to those responsible for facilitated diffusion and ion channels). Osmosis provides the primary means by which water is transported into and out of cells. The turgor pressure of a cell is largely maintained by osmosis across the cell membrane between the cell interior and its relatively hypotonic environment.
Jean-Antoine Nollet first documented observation of osmosis in 1748.[7] The word "osmosis" descends from the words "endosmose" and "exosmose", which were coined by French physician René Joachim Henri Dutrochet (1776–1847) from the Greek words ένδον (endon : within), έξο (exo : outside), and ωσμος (osmos : push, impulsion).[8]
Basic explanations
Osmosis is the movement of a solvent across a semipermeable membrane toward a higher concentration of solute. In biological systems, the solvent is typically water, but osmosis can occur in other liquids, supercritical liquids, and even gases.[9][10]
When a cell is submerged in water, the water molecules pass through the cell membrane from an area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration. For example, if the cell is submerged in saltwater, water molecules move out of the cell. If a cell is submerged in freshwater, water molecules move into the cell.

When the membrane has a volume of pure water on both sides, water molecules pass in and out in each direction at exactly the same rate. There is no net flow of water through the membrane.
The mechanism responsible for driving osmosis has commonly been represented in biology and chemistry texts as either the dilution of water by solute (resulting in lower concentration of water on the higher solute concentration side of the membrane and therefore a diffusion of water along a concentration gradient) or by a solute's attraction to water (resulting in less free water on the higher solute concentration side of the membrane and therefore net movement of water toward the solute). Both of these notions have been conclusively refuted.
The diffusion model of osmosis is rendered untenable by the fact that osmosis can drive water across a membrane toward a higher concentration of water.[11] The "bound water" model is refuted by the fact that osmosis is independent of the size of the solute molecules--a colligative property[12]--or how hydrophilic they are.

Osmosis, unlike diffusion, requires a force to work. This force is supplied by the solute's interaction with the membrane. Solute particles move randomly due to Brownian motion. If they move towards pores in the membrane, they are repelled, and in being repelled, acquire momentum directed away from the membrane. The momentum is rapidly transferred to surrounding water molecules, driving them away from the membrane as well.
Osmotic pressure is the main cause of support in many plants. The osmotic entry of water raises the turgor pressure exerted against the cell wall, until it equals the osmotic pressure, creating a steady state.
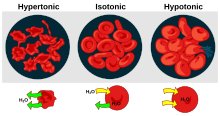
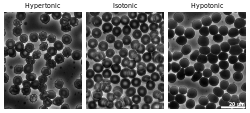
When a plant cell is placed in a solution that is hypertonic relative to the cytoplasm, water moves out of the cell and the cell shrinks. In doing so, the cell becomes flaccid. In extreme cases, the cell becomes plasmolyzed – the cell membrane disengages with the cell wall due to lack of water pressure on it.
When a plant cell is placed in a solution that is hypotonic relative to the cytoplasm, water move into the cell and the cell swells to become turgid.
Osmosis is responsible for the ability of plant roots to draw water from the soil. Plants concentrate solutes in their root cells by active transport, and water enters the roots by osmosis. Osmosis is also responsible for controlling the movement of guard cells.
Osmosis can be demonstrated when potato slices are added to a high salt solution. The water from inside the potato moves out to the solution, causing the potato to shrink and to lose its 'turgor pressure'. The more concentrated the salt solution, the bigger the difference in size and weight of the potato slice.
In unusual environments, osmosis can be very harmful to organisms. For example, freshwater and saltwater aquarium fish placed in water of a different salinity than that to which they are adapted to will die quickly, and in the case of saltwater fish, dramatically. Another example of a harmful osmotic effect is the use of table salt to kill leeches and slugs.
Suppose an animal or a plant cell is placed in a solution of sugar or salt in water.
- If the medium is hypotonic relative to the cell cytoplasm — the cell will gain water through osmosis.
- If the medium is isotonic — there will be no net movement of water across the cell membrane.
- If the medium is hypertonic relative to the cell cytoplasm — the cell will lose water by osmosis.
Essentially, this means that if a cell is put in a solution which has a solute concentration higher than its own, it will shrivel, and if it is put in a solution with a lower solute concentration than its own, the cell will swell and may even burst.
Chemical gardens demonstrate the effect of osmosis in inorganic chemistry.
Factors
Osmotic pressure
As mentioned before, osmosis may be opposed by increasing the pressure in the region of high solute concentration with respect to that in the low solute concentration region. The force per unit area, or pressure, required to prevent the passage of water through a selectively permeable membrane and into a solution of greater concentration is equivalent to the osmotic pressure of the solution, or turgor. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the property depends on the concentration of the solute, but not on its identity. It also is involved in facilitated diffusion.
Osmotic gradient
The osmotic gradient is the difference in concentration between two solutions on either side of a semipermeable membrane, and is used to tell the difference in percentages of the concentration of a specific particle dissolved in a solution.
Usually the osmotic gradient is used while comparing solutions that have a semipermeable membrane between them allowing water to diffuse between the two solutions, toward the hypertonic solution (the solution with the higher concentration). Eventually, the force of the column of water on the hypertonic side of the semipermeable membrane will equal the force of diffusion on the hypotonic (the side with a lesser concentration) side, creating equilibrium. When equilibrium is reached, water continues to flow, but it flows both ways in equal amounts as well as force, therefore stabilizing the solution.
Variation
Reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis is a separation process that uses pressure to force a solvent through a semi-permeable membrane that retains the solute on one side and allows the pure solvent to pass to the other side, forcing it from a region of high solute concentration through a membrane to a region of low solute concentration by applying a pressure in excess of the osmotic pressure.
Forward osmosis
Osmosis may be used directly to achieve separation of water from a solution containing unwanted solutes. A "draw" solution of higher osmotic pressure than the feed solution is used to induce a net flow of water through a semi-permeable membrane, such that the feed solution becomes concentrated as the draw solution becomes dilute. The diluted draw solution may then be used directly (as with an ingestible solute like glucose), or sent to a secondary separation process for the removal of the draw solute. This secondary separation can be more efficient than a reverse osmosis process would be alone, depending on the draw solute used and the feedwater treated. Forward osmosis is an area of ongoing research, focusing on applications in desalination, water purification, water treatment, food processing, etc.
See also
References
- ^ "Osmosis". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ Osmosis, Encyclopædia Britannica on-line
- ^ Haynie, Donald T. (2001). Biological Thermodynamics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 130–136. ISBN 0-521-79549-4.
- ^ Waugh, A. (2007). Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Illness. Edinburgh: Elsevier. pp. 25–26. ISBN 0-443-10101-9.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Osmosis. University of Hamburg. last change: 31 July 2003
- ^ "Statkraft to build the world's first prototype osmotic power plant". Statkraft. 3 October 2007. Archived from the original on 27 February 2009.
- ^ L’Abbé Nollet (June 1748) “Recherches sur les causes du bouillonnement des liquides” (Researches on the causes of the boiling of liquids) Mémoires de Mathématique et de Physique, tirés des registres de l’Académie Royale des Sciences de l’année 1748, pp. 57–104; especially pp. 101–103. The Mémoires (1748) were printed in: Histoire de l’Académie Royale des Sciences Année 1748, which was published in 1752 and which contains a condensed version of Nollet's article on pages 10–19.
Original text : Avant que de finir ce Mémoire, je crois devoir rendre compte d'un fait que je dois au hasard, & qui me parut d'abord … singulier … j'en avois rempli une fiole cylindrique, longue de cinq pouces, & d'un pouce de diamètre ou environ ; & l'ayant couverte d'un morceau de vessie mouillée & ficelée au col du vaisseau, je l'avois plongée dans un grand vase plein d'eau, afin d'être sûr qu'il ne rentrât aucun air dans l'esprit de vin. Au bout de cinq ou six heures, je fus tout surpris de voir que la fiole étoit plus pleine qu'au moment de son immersion, quoiqu'elle le fût alors autant que ses bords pouvoient le permettre ; la vessie qui lui servoit de bouchon, étoit devenue convexe & si tendue, qu’en la piquant avec une épingle, il en sortit un jet de liqueur qui s'éleva à plus d'un pied de hauteur.
Translation : Before finishing this memoir, I think I should report an event that I owe to chance and which at first seemed to me … strange … I filled [with alcohol] a cylindrical vial, five inches long and about one inch in diameter; and [after] having covered it with piece of damp bladder [which was] tied to the neck of the vial, I immersed it in a large bowl full of water, in order to be sure that no air re-entered the alcohol. At the end of 5 or 6 hours, I was very surprised to see that the vial was fuller than at the moment of its immersion, although it [had been filled] as far as its sides would allow ; the bladder that served as its cap, bulged and had become so stretched that on pricking it with a needle, there came from it a jet of alcohol that rose more than a foot high.
- ^ Etymology of "osmosis" :
- Henri Dutrochet, L'Agent Immédiat du Movement Vital Dévoilé dans sa Nature et dans son Mode d'Action chez les Végétaux et chez les Animaux [The immediate agent of living movement, its nature and mode of action revealed in plants and animals] (Paris, France: Dentu, 1826), pp. 115 and 126.
- The intermediate word "osmose" and the word "osmotic" were coined by Scottish chemist Thomas Graham. See: Thomas Graham (1854) "VII. The Bakerian Lecture – On Osmotic Force," Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society (London), vol. 144, pp. 177–288; see especially pp. 177, 178, and 227. See also: Thomas Graham and Henry Watts, Elements of Chemistry: Including the Applications of the Sciences in the Arts, 2nd ed. (London, England: Hippolyte Bailliere, 1858), vol. 2, p. 616.
- The word "osmosis" first appeared in: Jabez Hogg, The Microscope: Its History, Construction, and Application..., 6th ed. (London, England: George Routledge and Sons, 1867), p. 226.
- The etymology of the word "osmosis" is discussed in: Homer W. Smith (1960). "I. Theory of Solutions: A knowledge of the laws of solutions" (PDF). Circulation. 21: 808–817 (810). doi:10.1161/01.CIR.21.5.808.
- ^ Kramer, Eric. "Osmosis is not driven by water dilution". Trends in Plant Science. 18 (4): 195–197.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Kramer, Eric. "Five popular misconceptions of osmosis". American Journal of Physics. 80 (694). Bibcode:2012AmJPh..80..694K. doi:10.1119/1.4722325.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Kosinski, R. J. (2008). "Challenging misconceptions about osmosis". Association for Biology Laboratory Education. 30: 63–87.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Borg, Frank (2003). "What is osmosis? Explanation and understanding of a physical phenomenon". arXiv:physics/0305011.
External links
