Chrono Trigger: Crimson Echoes: Difference between revisions
GreenC bot (talk | contribs) |
Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.2.7.1) |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
[[File:Chrono Trigger Crimson Echoes art.jpg|thumb|alt=A gray scale sketch of a man standing in a cave. Additional characters are in the background.|Concept art illustrating the game's art style differing from ''Chrono Trigger''{{'}}s.]] |
[[File:Chrono Trigger Crimson Echoes art.jpg|thumb|alt=A gray scale sketch of a man standing in a cave. Additional characters are in the background.|Concept art illustrating the game's art style differing from ''Chrono Trigger''{{'}}s.]] |
||
The ''Crimson Echoes'' project was launched by ZeaLitY in 2004.<ref name="gamesradar"/> The development team, dubbed Kajar Laboratories, primarily consisted of members of the ''Chrono'' fansite Chrono Compendium.<ref name="1up">{{cite web|url=http://www.1up.com/features/posthumous-cult-favorites-games-endure?pager.offset=1|title=Posthumous Cult Gaming: Games That Endure|first= |
The ''Crimson Echoes'' project was launched by ZeaLitY in 2004.<ref name="gamesradar"/> The development team, dubbed Kajar Laboratories, primarily consisted of members of the ''Chrono'' fansite Chrono Compendium.<ref name="1up">{{cite web|url=http://www.1up.com/features/posthumous-cult-favorites-games-endure?pager.offset=1 |title=Posthumous Cult Gaming: Games That Endure |first=Bob |last=Mackey |date=March 17, 2010 |publisher=[[1UP.com]] |accessdate=May 8, 2011 |pages=2–3 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=http://www.webcitation.org/6Qg2KMdVb?url=http://www.1up.com/features/posthumous-cult-favorites-games-endure?pager.offset=1 |archivedate=June 28, 2014 |df= }}</ref> The team was led by a game director, Agent 12, and two co-directors, ZeaLitY and Chrono'99. To create a story that was compatible with ''Chrono Trigger'' and ''Chrono Cross'', the team took full advantage of the Chrono Compendium's encyclopedia and the fandom's knowledge and analysis of the series.<ref name="1up"/> |
||
The game took the form of a [[ROM hacking|ROM hack]] of the Super Nintendo Entertainment System version of ''Chrono Trigger''.<ref name="guardian">{{cite web|url=http://www.theguardian.com/technology/gamesblog/2009/may/21/game-theory-copyright|title=Game theory: Fans should be embraced, not treated as criminals|first=Keith|last=Stuart|date=May 21, 2009|publisher=''[[The Guardian]]''|accessdate=May 8, 2011|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150120192753/http://www.theguardian.com/technology/gamesblog/2009/may/21/game-theory-copyright|archivedate=January 20, 2015}}</ref> It was coded using ''Chrono Trigger'' ROM editing software,<ref>{{cite journal|last= Muñoz Sánchez|first=Pablo|editor1-last=Kockaert|editor1-first=Hendrik J.|editor2-last=Lommel| editor2-first=Arle|year=2009|title=Video Game Localisation for Fans by Fans: The Case of Romhacking |journal=The Journal of Internationalisation and Localisation|volume=1|page=181|location=[[Antwerp]], [[Belgium]]|publisher=[[Lessius Hogeschool|Lessius University College]]|issn=2032-6904 |oclc=661095707|accessdate=May 8, 2011|url=http://www.lessius.eu/jial/documents/JIAL_2009_1_2009_APA.pdf}}</ref> and was meant to be played on a Super Nintendo Entertainment System emulator. The finished game was intended to be released as a [[Patch (computing)|patch]] file in the IPS (International Patching System) format, so as to avoid illegal distribution of a full ''Chrono Trigger'' ROM.<ref name="guardian"/> |
The game took the form of a [[ROM hacking|ROM hack]] of the Super Nintendo Entertainment System version of ''Chrono Trigger''.<ref name="guardian">{{cite web|url=http://www.theguardian.com/technology/gamesblog/2009/may/21/game-theory-copyright|title=Game theory: Fans should be embraced, not treated as criminals|first=Keith|last=Stuart|date=May 21, 2009|publisher=''[[The Guardian]]''|accessdate=May 8, 2011|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150120192753/http://www.theguardian.com/technology/gamesblog/2009/may/21/game-theory-copyright|archivedate=January 20, 2015}}</ref> It was coded using ''Chrono Trigger'' ROM editing software,<ref>{{cite journal|last= Muñoz Sánchez|first=Pablo|editor1-last=Kockaert|editor1-first=Hendrik J.|editor2-last=Lommel| editor2-first=Arle|year=2009|title=Video Game Localisation for Fans by Fans: The Case of Romhacking |journal=The Journal of Internationalisation and Localisation|volume=1|page=181|location=[[Antwerp]], [[Belgium]]|publisher=[[Lessius Hogeschool|Lessius University College]]|issn=2032-6904 |oclc=661095707|accessdate=May 8, 2011|url=http://www.lessius.eu/jial/documents/JIAL_2009_1_2009_APA.pdf}}</ref> and was meant to be played on a Super Nintendo Entertainment System emulator. The finished game was intended to be released as a [[Patch (computing)|patch]] file in the IPS (International Patching System) format, so as to avoid illegal distribution of a full ''Chrono Trigger'' ROM.<ref name="guardian"/> |
||
Revision as of 07:39, 24 November 2016
| Chrono Trigger: Crimson Echoes | |
|---|---|
 The logo of the game | |
| Developer(s) | Kajar Laboratories |
| Director(s) | Agent 12 |
| Designer(s) | ZeaLitY Agent 12 Chrono'99 |
| Series | Chrono (unofficial) |
| Engine | Chrono Trigger engine |
| Platform(s) | Super Nintendo Entertainment System |
| Release | None (set to May 31, 2009 before cancellation) |
| Genre(s) | Role-playing game |
| Mode(s) | Single-player |
Chrono Trigger: Crimson Echoes is a fangame developed by the international team Kajar Laboratories as a ROM hack of Square's role-playing video game Chrono Trigger for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System. It was conceived as an unofficial installment in the Chrono series, set between the events of Chrono Trigger and its sequel Chrono Cross.
The game, as a ROM hack, runs on the Chrono Trigger game engine and has gameplay similar to the original. It is based five years after the events of Chrono Trigger and features all the playable characters from the original game, who come together across different time periods to fight an enemy attempting to change the past. The plot includes elements from both official games. Crimson Echoes concludes by setting up several plot points that were used in Chrono Cross.
The project was in development from 2004–09, with 98% of the game completed. The game reportedly totaled around 35 hours of play time, and had ten alternate endings. A few weeks prior to the expected released date, Square Enix sent the developers a cease-and-desist letter for knowingly violating Square Enix's intellectual property, which led to the cancellation of the project. This cancellation was widely reported in the gaming press, who were largely sympathetic to the project. Despite its cancellation, versions of the game ranging from an alpha to a release candidate have since been leaked onto the internet and can be played through to the end.
Gameplay
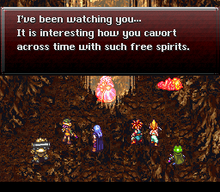
As Crimson Echoes runs on the Chrono Trigger game engine, the gameplay is similar to that of the original title.[1] Players and enemies may use physical or magical attacks to wound targets during battle, and players may use items to heal or protect themselves. Each character and enemy has a certain number of hit points that are reduced by successful attacks and can be restored through potions and spells. When a playable character loses all hit points, he or she faints. It also uses the Active Time Battle 2.0 system from the first game. The game features new maps, graphics and sprites.[2] New minigames were designed to reward players with items and equipment, including a "Coliseum" battle mode based on that of Final Fantasy VII and a casino featuring luck-based games.
Characters
Crimson Echoes features all the playable characters of the original game, and is set five years after the events of Chrono Trigger.[2] Crono and Marle are junior regents of the Kingdom of Guardia; Lucca continues her scientific endeavors. The three struggle to ease tensions with Porre, which has modernized its military and seeks to end Guardia's economic hegemony. Frog lives in 605 A.D., restored to his human form, though this was not implemented before the cease and desist letter. Magus searches for Schala in the still-frozen 11,995 B.C., and feuds with Dalton, obsessed with finding artifacts from the lost Kingdom of Zeal. Ayla dwells in 64,999,995 B.C., and has given birth to her tribe's successor. Robo assists the Guru of Time Belthasar, who has established a clandestine temporal research facility named Chronopolis in 2305 A.D. Belthasar claims it will be a guardian of time to ensure a threat such as Lavos will never arise. He nonetheless harbors darker wishes to leave a grand legacy in history, and is almost recklessly pragmatic. He fixes the Epoch during the story's course, which returns as the Neo-Epoch (akin to its design in Chrono Cross).[2]
The main villain of Crimson Echoes is King Zeal, revived by Lavos through the Frozen Flame. Confused and saddened by the loss of his kingdom, he is easily manipulated by Lavos, who uses him to attempt revenge on Crono and his friends. He later learns of his deception, and seeks to dominate Lavos and recreate his kingdom through unmatched temporal power. While under Lavos's influence, he recruits Dalton and Kasmir to his cause. Kasmir is an illusionist who served under Magus in the Mystic War. King Zeal gives him the Masamune, and he assumes leadership of the Mystics after 600 A.D. Other foes come from the Reptite timeline, an alternate universe temporarily brought into existence by King Zeal's meddling. They number the Dragon God—a Reptite artificial intelligence created in an alternate timeline—and the Xamoltan time travelers, who were used by King Zeal and survive into the restored human world. The party also visit 1 A.D., the era of the founding of Guardia. There, they meet Cedric the Executor, the ruthless first King of Guardia, as well as Antaeus, the ancestor of Porre.[2]
Plot
The game begins as Crono, Marle, and Lucca attend a political meeting between the Kingdom of Guardia and Porre. An assassin attacks; the party pursues him to the Denadoro Mts., where Lucca's prototype Time Egg backfires and sends them to the future. They find Belthasar there, who has established a research facility called Chronopolis. He warns of a new threat to the timeline, and sends the party to the Ocean Palace ruins of 11,995 B.C. to investigate. They find Magus, still searching for Schala and feuding with Dalton. They confront a mysterious villain who resurrects Schala and robs the early Masamune, still embedded in the husk of the Mammon Machine. Its theft changes history, causing the Mystics' war in the Middle Ages to drag on another 50 years, led by the illusionist Kasmir. The party retrieve Frog (named Glenn in Crimson Echoes) from 605 A.D. and meet with Belthasar.[2]
He explains the mysterious villain was King Zeal, somehow alive and in possession of the Frozen Flame, a shard of Lavos with incredible powers. Melchior takes up residence in Chronopolis to aid the fight against him. The party goes to 64,999,995 B.C. to find the Dragon's Tooth, an enchanted totem that will assist Chronopolis. King Zeal confronts them at the old Lavos impact crater, scattering them through time and unleashing the "Atash Kedah", a destructive spell that changes history. Marle awakens in 1 A.D. to discover Reptites have survived the long ice age, and war with humanity for control of the planet.[3] Lucca and Robo arrive in 2305 A.D., awaking in the midst of a futuristic Reptite civilization. They ally with rebellious, sentient robots and venture to Dinopolis, the equivalent of Chronopolis in this timeline. They destroy the Vision Serpent, an artificial intelligence created to administrate the world. Crono, Magus, and Glenn awaken in 1005 A.D., and assault the earlier Dinopolis, where Reptite time travelers from 2305 A.D. have come to conduct research on the past. The party use the temporal technology in place to return to 64,999,995 B.C. and stop the Atash Kedah spell, restoring the human timeline.[2]
Marle awakens in 1 A.D. once more, this time witnessing her ancestor, Cedric Guardia, brutally unify the world with the Frozen Flame. A ubiquitous agent from Chronopolis—code-named 12—brings her back to the future. The party learn that the Reptite time travelers—named Cakulha, Coyopa, and Yaluk—survived the human world's restoration, and had been manipulated by King Zeal. The party fix the Mystic War by retrieving the Masamune from Kasmir and putting it back in antiquity. In 1005 A.D., new diplomatic talks are about to begin. Porre instead launches an assault, backed by King Zeal and Dalton, placed in Porre's high command by the king. King Guardia dies in the attack. The party venture to 11,995 B.C. once more with Schala, intent on striking the Frozen Flame in antiquity to lure out King Zeal. This unleashes wild energies, and the party must overcome individual mental assaults by the Flame. King Zeal retreats, and the energies cause Schala to fall into the Darkness Beyond Time, a temporal netherworld. Unsuccessful, the party seek out Gaspar tens of millions of years in the past (known as the Dreamtime), where he's gone to witness the birth of the planet's consciousness. King Zeal attacks them there; Crono falls near the rifts of the forming planet and is partly infused with its natal awareness. The party learn that King Zeal's ultimate goal is to resurrect the Kingdom of Zeal in 11,995 B.C.[2]
The party return to antiquity and defeat Dalton. King Zeal nears the fruition of his plan, but Melchior and Belthasar enter the time period to dissuade him. King Zeal leaves the Sun Stone, the trigger for the revival of Zeal, with a follower and walks to the North Cape. He reveals that Lavos survived defeat in Chrono Trigger and clung to life in the Darkness Beyond Time. He used the Frozen Flame to revive King Zeal, manipulating him to take revenge on the heroes. He is now merging with Schala, as he has done with all the other "Arbiters" who have used the Frozen Flame throughout history. Lavos calls King Zeal, intending to merge with him as well and evolve to become the Dream Devourer (as seen in Chrono Trigger DS). The party convince Zeal's followers not to activate the Sun Stone, and pursue Zeal to the Darkness Beyond Time. King Zeal confronts them once more, revealing his will is stronger than that of Lavos; he'll merge, but become the dominant personality within the Dream Devourer and create a new Zeal using its vast power. The party defeat him and return to Chronopolis. They notice the planet's Gates are closing again, and depart to their homes, promising to stay in touch. Belthasar meanwhile reveals he has the Frozen Flame, which activates and informs him that Lavos is still alive and will become the Time Devourer, the enemy of Chrono Cross. It challenges Belthasar to a grand game, and he begins drawing up plans for Project Kid. The game closes with King Zeal, shown to be alive and imprisoned by Magus in 11,995 B.C., who forces him to teach advanced temporal magic.[2]
Development

The Crimson Echoes project was launched by ZeaLitY in 2004.[3] The development team, dubbed Kajar Laboratories, primarily consisted of members of the Chrono fansite Chrono Compendium.[4] The team was led by a game director, Agent 12, and two co-directors, ZeaLitY and Chrono'99. To create a story that was compatible with Chrono Trigger and Chrono Cross, the team took full advantage of the Chrono Compendium's encyclopedia and the fandom's knowledge and analysis of the series.[4]
The game took the form of a ROM hack of the Super Nintendo Entertainment System version of Chrono Trigger.[5] It was coded using Chrono Trigger ROM editing software,[6] and was meant to be played on a Super Nintendo Entertainment System emulator. The finished game was intended to be released as a patch file in the IPS (International Patching System) format, so as to avoid illegal distribution of a full Chrono Trigger ROM.[5]
The project lasted four and a half years, with a planned release date of May 31, 2009.[7][8] However, Square Enix sent ZeaLitY and Agent 12 a cease-and-desist letter on May 8, 2009 for trademark and copyright infringement, ordering that the team stop development and cancel all ROM hacking activities,[5] including translation and distribution of all their other projects that were in progress or already released.[7] The letter noted that ZeaLitY and Agent 12 risked being sued for "up to $150,000 per work" in damages.[1] At the time of the cancellation, the game was "around 98% complete"; it allegedly featured 23 story chapters adding up to roughly 35 hours of gameplay and ten alternate endings.[3][8]
Internet circulation
Shortly after the project received the cease and desist letter, an alpha version of the patch was leaked on the internet. ZeaLitY expressed his disapproval and embarrassment on the Crimson Echoes website, noting that the alpha version was extremely buggy and lacked many of the improvements made in the beta version.[8] In January 2011, a more complete beta version was leaked which could be played from beginning to end, believed to be the final build of the project prior to cancellation.[9]
Reaction
Kajar Laboratories complied with the cease-and-desist letter and all traces of Crimson Echoes were removed from the Chrono Compendium.[4] CNET senior associate editor Eric Franklin noted that it was "sad to see four and a half years of work go spinning down the drain," stating: "I feel for the fans who were anticipating this."[7] 1UP.com called the project "ambitious," noting that "This wasn't just some fly-by-night hack."[4] Earnest Cavalli, from Wired, stated: "I fully understand Square Enix’s desire to protect its properties, but that doesn’t make this any less depressing. The game looked quite good (if obviously derivative)."[1] The project's cancellation was also reported by gaming journalists in the Netherlands,[10] France,[11] and Japan.[12] In February 2010, GamesRadar included the game in an article about the "10 fan games that shouldn't be ceased or desisted".[3]
Keith Stuart, from The Guardian, pointed out the contrast between Square Enix's policy and that of companies like Valve, which officially adopted the Half-Life fan mods Counter-Strike and Day of Defeat, and Vivendi Universal Games, which granted a licence to the King's Quest fan game The Silver Lining. He noted that since Crimson Echoes was a ROM hack, it was in a "trickier area of copy protection law" than those other projects, but felt that its release would have had next to no commercial impact since the game was to be distributed as an IPS patch rather than a ROM image. Finally, he noted that an official port of the fangame to the Nintendo DS or WiiWare would have had more "marketing benefits" for Square Enix.[5]
References
- ^ a b c Cavalli, Earnest (May 11, 2009). "Square Enix Kills Near Complete Chrono Trigger Fan Project". Wired.com. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on May 14, 2009. Retrieved May 8, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h "Crimson Echoes: Plot". Kajar Laboratories. March 4, 2010. Archived from the original on March 23, 2012. Retrieved May 8, 2011.
- ^ a b c d Chiang, Oliver J. (February 18, 2010). "10 fan games that shouldn't be ceased or desisted". GamesRadar. Future US. p. 1. Archived from the original on November 13, 2014. Retrieved May 8, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d Mackey, Bob (March 17, 2010). "Posthumous Cult Gaming: Games That Endure". 1UP.com. pp. 2–3. Archived from the original on June 28, 2014. Retrieved May 8, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d Stuart, Keith (May 21, 2009). "Game theory: Fans should be embraced, not treated as criminals". The Guardian. Archived from the original on January 20, 2015. Retrieved May 8, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Muñoz Sánchez, Pablo (2009). Kockaert, Hendrik J.; Lommel, Arle (eds.). "Video Game Localisation for Fans by Fans: The Case of Romhacking" (PDF). The Journal of Internationalisation and Localisation. 1. Antwerp, Belgium: Lessius University College: 181. ISSN 2032-6904. OCLC 661095707. Retrieved May 8, 2011.
- ^ a b c Franklin, Eric (May 14, 2009). "Square Enix pulls rug from under Chrono sequel". CNET. Archived from the original on October 25, 2012. Retrieved May 8, 2011.
- ^ a b c ZeaLitY (August 12, 2009). "Crimson Echoes". Kajar Laboratories. Archived from the original on May 13, 2012. Retrieved May 8, 2011.
- ^ Schramm, Mike (January 18, 2011). "Fan-made Chrono Trigger sequel finds release". Joystiq. Archived from the original on January 31, 2015. Retrieved April 7, 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Dechesne, Youri (May 11, 2009). "Square Enix roept officieuze Chrono Trigger 2 halt toe" (in Dutch). Gamer.nl. Archived from the original on March 25, 2013. Retrieved May 8, 2011.
- ^ H., Fabien (May 13, 2009). "Chrono Trigger: Crimson Echoes annulé par Square Enix" (in French). Génération-NT. Archived from the original on September 11, 2012. Retrieved May 8, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ riot_兄 (May 23, 2009). スクエニが4年掛かりの海外ファンプロジェクトを差し止め → 一部から批判の声 (in Japanese). Game Spark. Archived from the original on January 28, 2010. Retrieved May 8, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)
