Injury in humans: Difference between revisions
m added additional injury types from same NIH reference as mere "causes" of injury makes nature of injury vague without "types". |
m grammar and word improvements. addition of "wounds" in definition of injury per NIH reference. Respected terms in NIH reference, the NIH article referenced could have been better written Wiki now probably clearer than NIH. Useful word links were checked. |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Injury''' is hurt, harm, wound or damage to the body.<ref>http://etymonline.com/index.php?allowed_in_frame=0&search=injury</ref><ref name=NIH2014>{{cite web|url=http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/woundsandinjuries.html |title=Wounds and Injuries: MedlinePlus |publisher=Nlm.nih.gov |accessdate=2015-07-20}}</ref> This may be caused by accidents, falls, hits, weapons, or other |
'''Injury''' is hurt, harm, wound or damage to the body.<ref>http://etymonline.com/index.php?allowed_in_frame=0&search=injury</ref><ref name=NIH2014>{{cite web|url=http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/woundsandinjuries.html |title=Wounds and Injuries: MedlinePlus |publisher=Nlm.nih.gov |accessdate=2015-07-20}}</ref> This may be caused by [[accidents]] ([[collisions]]), falls, hits, [[weapons]], etc. [[Wounds]] are injuries that break the skin or other body tissues. Other common types of injuries include: [[animal bites]], [[bruises]], [[burn]]s, [[joint dislocations]], electrical injuries, [[bone fractures]], [[sprains]] and [[strain (injury)]].<ref name=NIH2014/> The words "injury" and "damage" are '''not''' synonymous. The word "[['''damage''']]" (singular form) means a "loss caused by injury"<ref>[[http://etymonline.com/index.php?term=damage]]</ref>) and should not confused with the word "[['''damages''']]" (plural form with an '''s''') which has special legal or economic meanings for [[loss]] due to bodily injury, [[property damage]], etc. "Damages" is measured in [[money]]. |
||
sprains and strains.<ref name=NIH2014/> The words "injury" and "damage", "damage" meaning a "loss caused by injury"<ref>[[http://etymonline.com/index.php?term=damage]]</ref> are not synonymous and should not confused with the word "[[damages]]". "Damages" has special legal or economic meanings for the value of a [[loss]] due to bodily injury, or property injury or destruction, as measured in money. |
|||
[[Major trauma]] is injury that has the potential to cause prolonged [[disability]] or [[death]]. |
"[[Major trauma]]" is injury that has the potential to cause prolonged [[disability]] or [[death]]. |
||
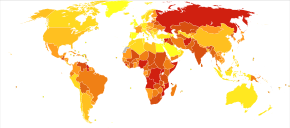
In 2013, 4.8 million people died from injuries, up from 4.3 million in 1990.<!-- <ref name=GDB2013/> --> More than 30% of these deaths were transport-related injuries.<!-- <ref name=GDB2013/> --> In 2013, 367,000 children under the age of five died from injuries, down from 766,000 in 1990.<ref name=GDB2013>{{cite journal|last1=GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death|first1=Collaborators|title=Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.|journal=Lancet|date=17 December 2014|pmid=25530442|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2|pmc=4340604|volume=385|pages=117–71}}</ref> Injuries are the cause of 9% of all deaths, and are the sixth-leading cause of death in the world.<ref>{{cite web|title=The top 10 causes of death|url=http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/index2.html|accessdate=24 May 2015}}</ref><ref name=Stein2015>{{cite journal|vauthors=Stein DM, Santucci RA |title=An update on urotrauma|journal=Current opinion in urology|volume=25|issue=4|pages=323–30|date=July 2015|pmid=26049876|doi=10.1097/MOU.0000000000000184}}</ref> |
In 2013, 4.8 million people died from injuries, up from 4.3 million in 1990.<!-- <ref name=GDB2013/> --> More than 30% of these deaths were transport-related injuries.<!-- <ref name=GDB2013/> --> In 2013, 367,000 children under the age of five died from injuries, down from 766,000 in 1990.<ref name=GDB2013>{{cite journal|last1=GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death|first1=Collaborators|title=Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.|journal=Lancet|date=17 December 2014|pmid=25530442|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2|pmc=4340604|volume=385|pages=117–71}}</ref> Injuries are the cause of 9% of all deaths, and are the sixth-leading cause of death in the world.<ref>{{cite web|title=The top 10 causes of death|url=http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/index2.html|accessdate=24 May 2015}}</ref><ref name=Stein2015>{{cite journal|vauthors=Stein DM, Santucci RA |title=An update on urotrauma|journal=Current opinion in urology|volume=25|issue=4|pages=323–30|date=July 2015|pmid=26049876|doi=10.1097/MOU.0000000000000184}}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 12:51, 19 June 2017
| Injury | |
|---|---|
 | |
| The knee of a person is examined with the help of radiography after an injury. | |
| Specialty | Emergency medicine, traumatology |
Injury is hurt, harm, wound or damage to the body.[1][2] This may be caused by accidents (collisions), falls, hits, weapons, etc. Wounds are injuries that break the skin or other body tissues. Other common types of injuries include: animal bites, bruises, burns, joint dislocations, electrical injuries, bone fractures, sprains and strain (injury).[2] The words "injury" and "damage" are not synonymous. The word "'''damage'''" (singular form) means a "loss caused by injury"[3]) and should not confused with the word "'''damages'''" (plural form with an s) which has special legal or economic meanings for loss due to bodily injury, property damage, etc. "Damages" is measured in money.
"Major trauma" is injury that has the potential to cause prolonged disability or death.
In 2013, 4.8 million people died from injuries, up from 4.3 million in 1990. More than 30% of these deaths were transport-related injuries. In 2013, 367,000 children under the age of five died from injuries, down from 766,000 in 1990.[4] Injuries are the cause of 9% of all deaths, and are the sixth-leading cause of death in the world.[5][6]
Classification

The World Health Organization (WHO) developed the International Classification of External Causes of Injury (ICECI). Under this system, injuries are classified by
- mechanism of injury,
- objects/substances producing injury,
- place of occurrence,
- activity when injured,
- the role of human intent,
and additional modules. These codes allow the identification of distributions of injuries in specific populations and case identification for more detailed research on causes and preventive efforts.[7][8]
The United States Bureau of Labor Statistics developed the Occupational Injury and Illness Classification System (OIICS). Under this system injuries are classified by
- nature,
- part of body affected,
- source and secondary source, and
- event or exposure.
The OIICS was first published in 1992 and has been updated several times since.[9]
The Orchard Sports Injury Classification System (OSICS) is used to classify injuries to enable research into specific sports injuries.[10]
By cause
- Intentional injury
- Accidents
By modality
- Traumatic injury, a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical collision or movement[11]
- Repetitive strain injury or other strain injury
- Other injuries from external physical causes, such as radiation poisoning, burn, or frostbite
- Injury from toxin or as adverse effect of a pharmaceutical drug
- Injury from internal causes such as reperfusion injury
By location
- Wound, an injury in which skin is torn, cut or punctured (an open wound), or where blunt force trauma causes a contusion (a closed wound). In pathology, it specifically refers to a sharp injury which damages the dermis of the skin.
- Brain injury
- Nerve injury
- Soft tissue injury
- Cell damage, including direct DNA damage
- Lisfranc injury
- Tracheobronchial injury
- Eye injury
- Acute kidney injury
- Knee injury
- Back injury
- Hand injury
- Liver injury
- Head injury
- Musculoskeletal injury
- Acute lung injury
- Pancreatic injury
- Thoracic aorta injury
- Biliary injury
- Chest injury
By activity
- Occupational injury
- Ventilator-associated lung injury
- Sea urchin injury
- Transfusion-related acute lung injury
- Illness and injuries during spaceflight
Injury severity score
The injury severity score (ISS) is a medical score to assess trauma severity.[12][13] It correlates with mortality, morbidity, and hospitalization time after trauma. It is used to define the term major trauma (polytrauma), recognized when the ISS is greater than 15.[13] The AIS Committee of the Association for the Advancement of Automotive Medicine designed and updates the scale.
See also
References
- ^ http://etymonline.com/index.php?allowed_in_frame=0&search=injury
- ^ a b "Wounds and Injuries: MedlinePlus". Nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2015-07-20.
- ^ [[1]]
- ^ GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators (17 December 2014). "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013". Lancet. 385: 117–71. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. PMC 4340604. PMID 25530442.
{{cite journal}}:|first1=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "The top 10 causes of death". Retrieved 24 May 2015.
- ^ Stein DM, Santucci RA (July 2015). "An update on urotrauma". Current opinion in urology. 25 (4): 323–30. doi:10.1097/MOU.0000000000000184. PMID 26049876.
- ^ "International Classification of External Causes of Injury (ICECI)". World Health Organization. Retrieved 2014-03-24.
- ^ Robertson, LS (2015) Injury Epidemiology: Fourth Edition. Free online at www.nanlee.net
- ^ "Occupational Injury and Illness Classification System". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 2014-03-24.
- ^ Rae, K; Orchard, J (May 2007). "The Orchard Sports Injury Classification System (OSICS) version 10". Clin J Sport Med. 17 (3): 201–4. doi:10.1097/jsm.0b013e318059b536. PMID 17513912.
- ^ "Trauma". Dictionary.com. Dictionary.com, LLC. 2010. Retrieved 2010-10-31.
- ^ Baker SP, O'Neill B, Haddon W, Long WB (1974). "The Injury Severity Score: a method for describing patients with multiple injuries and evaluating emergency care". The Journal of Trauma. 14 (3). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: 187–196. doi:10.1097/00005373-197403000-00001. PMID 4814394.
- ^ a b Copes, W.S.; H.R. Champion; W.J. Sacco; M.M. Lawnick; S.L. Keast; L.W. Bain (1988). "The Injury Severity Score revisited". The Journal of Trauma. 28 (1). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: 69–77. doi:10.1097/00005373-198801000-00010. PMID 3123707.
