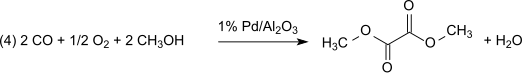Dimethyl oxalate

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dimethyl oxalate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.231 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O4 | |
| Molar mass | 118.088 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Melting point | 53 to 55 °C (127 to 131 °F; 326 to 328 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 166 to 167 °C (331 to 333 °F; 439 to 440 K)[1] |
| -55.7·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Diphenyl oxalate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Dimethyl oxalate is an organic compound with the formula (CO2CH3)2 or (CH3)2C2O4. It is the dimethyl ester of oxalic acid. Dimethyl oxalate is a colorless or white solid that is soluble in water.
Production
[edit]Dimethyl oxalate can be obtained by esterification of oxalic acid with methanol using sulfuric acid as a catalyst:[2]
Oxidative carbonylation route
[edit]The preparation by oxidative carbonylation has attracted interest because it requires only C1 precursors:[3]
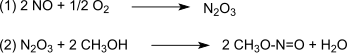
The reaction is catalyzed by Pd2+.[4][5] The synthesis gas is mostly obtained from coal or biomass. The oxidation proceeds via dinitrogen trioxide, which is formed according to (1) of nitrogen monoxide and oxygen and then reacts according to (2) with methanol forming methyl nitrite:[6]
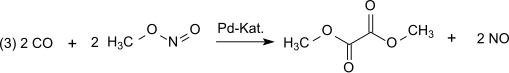
In the next step of dicarbonylation (3) carbon monoxide reacts with methyl nitrite to dimethyl oxalate in the vapor phase at atmospheric pressure and temperatures at 80-120 °C over a palladium catalyst:
The sum equation:
This method is lossless with respect to methyl nitrite, which acts practically as a carrier of oxidation equivalents. However, the water formed must be removed to prevent hydrolysis of the dimethyl oxalate product. With 1% Pd/α-Al2O3 dimethyl oxalate is produced selectively in a dicarbonylation reaction, under the same conditions with 2% Pd/C dimethyl carbonate is produced by monocarbonylation:
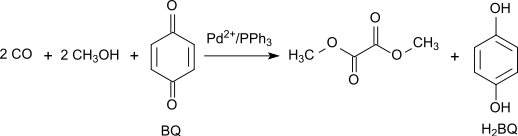
Alternatively, the oxidative carbonylation of methanol can be carried out with high yield and selectivity with 1,4-benzoquinone as an oxidant in the system Pd(OAc)2/PPh3/benzoquinone with mass ratio 1/3/100 at 65 °C and 70 atm CO:[5]
Reactions
[edit]Dimethyl oxalate (and the related diethyl ester) is used in diverse condensation reactions.[7] For example, diethyl oxalate condenses with cyclohexanone to give the diketo-ester, a precursor to pimelic acid.[8] With diamines, the diesters of oxalic acid condense to give cyclic diamides. Quinoxalinedione is produced by condensation of dimethyloxalate and o-phenylenediamine:
- C2O2(OMe)2 + C6H4(NH2)2 → C6H4(NHCO)2 + 2 MeOH
Hydrogenation gives ethylene glycol.[9] Dimethyl oxalate can be converted into ethylene glycol in high yields (94.7%)[10][11]
The methanol formed is recycled in the process of oxidative carbonylation.[12] Other plants with a total annual capacity of more than 1 million tons of ethylene glycol per year are planned.
Decarbonylation gives dimethyl carbonate.[13]
Diphenyl oxalate is obtained by transesterification with phenol in the presence of titanium catalysts,[14] which is again decarbonylated to diphenyl carbonate in the liquid or gas phase.
Dimethyl oxalate can also be used as a methylating agent. It is notably less toxic than other methylating agents such as methyl iodide or dimethyl sulfate.[15]
References
[edit]- ^ a b P. P. T. Sah and S-L. Chien, Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1931, 53, 3901-3903.
- ^ Everett Bowden (1930). "Methyl Oxalate". Organic Syntheses. 10: 78. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.010.0078.
- ^ Hans-Jürgen Arpe: Industrielle Organische Chemie: Bedeutende Vor- und Zwischenprodukte, S. 168; ISBN 978-3-527-31540-6.
- ^ US 4467109, Susumu Tahara et al., "Process for Continuous preparation of diester of oxalic acid", issued 1983-05-19, assigned to Ube Industries and EP 108359, K. Masunaga et al., "Process for the preparation of a diester of oxalic acid", assigned to Ube IndustriesEP 425197, K. Nishihira & K. Mizutare, "Process for preparing diester of carbonic acid", published 1991-05-2, assigned to Ube IndustriesUS 4451666, J.A. Sofranko, A.M. Gaffney, "Synthesis of oxalate esters by the oxidative carbonylation of alcohols", published 1984-05-29, assigned to Atlantic Richfield Co.
- ^ a b E. Amadio: Oxidative Carbonylation of Alkanols Catalyzed by Pd(II)-Phosphine Complexes, PhD Thesis, Ca'Foscari University Venice, 2009
- ^ X.-Z. Jiang, Palladium Supported Catalysts in CO + RONO Reactions, Platinum Metals Rev., 1990, 34, (4), 178–180
- ^ Bergman, Jan; Norrby, Per-Ola; Sand, Peter (1990). "Alkylation with Oxalic Esters. Scope and mechanism". Tetrahedron. 46 (17): 6113–6124. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)87933-3. S2CID 94945519.
- ^ H. R. Snyder; L. A. Brooks; S. H. Shapiro; A. Müller (1931). "Pimelic Acid". Organic Syntheses. 11: 42. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.011.0042.
- ^ Nexant/Chemsystems, "Coal to MEG, Changing the Rules of the Game" (PDF). Archived from the original on July 14, 2011. Retrieved 2016-08-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) (PDF; 5,4 MB), 2011 Prospectus - ^ 983 EP 046 983, S. Tahara et al., "Process for continuously preparing ethylene glycol", assigned to Ube Industries and H. T. Teunissen and C. J. Elsevier, Ruthenium catalyzed hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to ethylene glycol, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1997, 667-668), DOI:10.1039/A700862G.
- ^ S. Zhang et al., Highly-Dispersed Copper-Based Catalysts from Cu–Zn–Al Layered Double Hydroxide Precursor for Gas-Phase Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Oxalate to Ethylene Glycol, Catalysis Letters, Sept. 2012, 142 (9), 1121–1127, DOI:10.1007/s10562-012-0871-8
- ^ "Individual news".
- ^ US 4544507, P. Foley, "Production of carbonate diesters from oxalate diesters", assigned to Celanese Corp
- ^ US 5834614, K. Nishihira et al., "Process for producing diaryl carbonate", assigned to Ube Industries, Ltd. and X.B. Ma et al., Preparation of Diphenyl Oxalate from Transesterification of Dimethyl Oxalate with Phenol over TS-1 Catalyst, Chinese Chem. Lett., 14 (5), 461–464 (2003), DOI:10.1016/s0378-3820(03)00075-4.
- ^ Bergman, Jan; Norrby, Per-Ola; Sand, Peter (1990-01-01). "Alkylation with Oxalic Esters. Scope and mechanism". Tetrahedron. 46 (17): 6113–6124. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)87933-3. ISSN 0040-4020. S2CID 94945519.