Piriformis nerve
Appearance
| Piriformis nerve | |
|---|---|
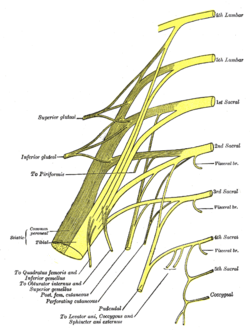 Diagram of sacral plexus and pudendal plexus. (Label "to piriformis" is at center left.) | |
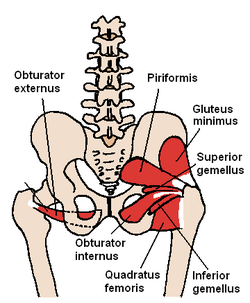 The piriformis and nearby muscles | |
| Details | |
| From | Sacral plexus (S1–S2) |
| Innervates | Piriformis muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus musculi piriformis |
| TA98 | A14.2.07.029 |
| TA2 | 6545 |
| FMA | 16509 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The piriformis nerve, also known as the nerve to piriformis, is the peripheral nerve that provides motor innervation to the piriformis muscle.
Structure
[edit]Origin
[edit]The nerve to piriformis is a branch of the sacral plexus.[1][2] It (typically[3]) arises from the posterior divisions[4]/branches[3] of anterior rami of S1 and S2.[1][2][3][5]
Course
[edit]It enters the anterior surface of the piriformis muscle.[3][6]
Variation
[edit]Origin
It may sometimes arise from the anterior ramus of S2 only.[3]
Number
It may be doubled. An additional branch may arise from the superior gluteal nerve.[3]
Distribution
[edit]The piriformis nerve innervates the piriformis muscle.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 957 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 957 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b c Pan, Jason; Vasudevan, John (2018-01-01), Freedman, Mitchell K.; Gehret, Jeffrey A.; Young, George W.; Kamen, Leonard B. (eds.), "Chapter 24 - Piriformis Syndrome: A Review of the Evidence and Proposed New Criteria for Diagnosis", Challenging Neuropathic Pain Syndromes, Elsevier, pp. 205–215, ISBN 978-0-323-48566-1, retrieved 2021-02-03
- ^ a b Khan, Dost; Nelson, Ariana (2018). "67 - Piriformis Syndrome". Essentials of Pain Medicine. Elsevier. pp. 613–618. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-40196-8.00067-X. ISBN 978-0-323-40196-8.
- ^ a b c d e f Apaydin, Nihal (2015). "Chapter 47 - Variations of the Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses and Their Branches". Nerves and Nerve Injuries. Vol. 1: History, Embryology, Anatomy, Imaging, and Diagnostics. Academic Press. p. 634. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-410390-0.00049-4. ISBN 978-0-12-410390-0.
- ^ Mirjalili, S. Ali (2015-01-01), Tubbs, R. Shane; Rizk, Elias; Shoja, Mohammadali M.; Loukas, Marios (eds.), "Chapter 46 - Anatomy of the Sacral Plexus L4-S4", Nerves and Nerve Injuries, San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 619–626, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-410390-0.00048-2, ISBN 978-0-12-410390-0, retrieved 2021-02-28
- ^ Mirjalili, S. Ali (2015-01-01), Tubbs, R. Shane; Rizk, Elias; Shoja, Mohammadali M.; Loukas, Marios (eds.), "Chapter 46 - Anatomy of the Sacral Plexus L4-S4", Nerves and Nerve Injuries, San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 619–626, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-410390-0.00048-2, ISBN 978-0-12-410390-0, retrieved 2021-02-28
- ^ Mirjalili, S. Ali (2015-01-01), Tubbs, R. Shane; Rizk, Elias; Shoja, Mohammadali M.; Loukas, Marios (eds.), "Chapter 46 - Anatomy of the Sacral Plexus L4-S4", Nerves and Nerve Injuries, San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 619–626, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-410390-0.00048-2, ISBN 978-0-12-410390-0, retrieved 2021-02-28
홍재기
